Abstract
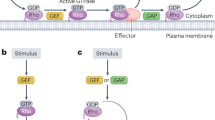
Rho GTPases are molecular switches that control a wide variety of signal transduction pathways in all eukaryotic cells. They are known principally for their pivotal role in regulating the actin cytoskeleton, but their ability to influence cell polarity, microtubule dynamics, membrane transport pathways and transcription factor activity is probably just as significant. Underlying this biological complexity is a simple biochemical idea, namely that by switching on a single GTPase, several distinct signalling pathways can be coordinately activated. With spatial and temporal activation of multiple switches factored in, it is not surprising to find Rho GTPases having such a prominent role in eukaryotic cell biology.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
We are sorry, but there is no personal subscription option available for your country.
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ridley, A. J. & Hall, A. The small GTP-binding protein Rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell 70, 389–399 (1992)
Ridley, A. J., Paterson, C. L., Johnston, C. L., Diekmann, D. & Hall, A. The small GTP-binding protein Rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell 70, 401–410 (1992)
Nobes, C. D. & Hall, A. Rho, Rac and Cdc42 regulate the assembly of multimolecular focal complexes associated with actin stress fibers, lamellipodia and filopodia. Cell 81, 53–62 (1995)
Kozma, R., Ahmed, S., Best, A. & Lim, L. The Ras-related protein Cdc42Hs and bradykinin promote formation of peripheral actin microspikes and filopodia in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 1942–1952 (1995)
Pruyne, D. & Bretscher, A. Polarization of cell growth in yeast. I. Establishment and maintenance of polarity states. J. Cell Sci. 113, 365–375 (2000)
Schmidt, A. & Hall, M. N. Signaling to the actin cytoskeleton. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 14, 305–338 (1998)
Butty, A.-C. et al. A positive feedback loop stabilizes the guanine-exchange factor Cdc24 at sites of polarization. EMBO J. 21, 1565–1576 (2002)
Kemphues, K. PARsing embryonic polarity. Cell 101, 345–348 (2000)
Ohno, S. Intercellular juntions and cellular polarity: the PAR-aPKC complex, a conserved core cassette playing fundamental roles in cell polarity. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 13, 641–648 (2001)
Gotta, M., Abraham, M. C. & Ahringer, J. CDC-42 controls early cell polarity and spindle orientation in C. elegans. Curr. Biol. 11, 482–488 (2001)
Kay, A. J. & Hunter, C. P. CDC-42 regulates PAR protein localization and function to control cellular and embryonic polarity in C. elegans. Curr. Biol. 11, 474–481 (2001)
Joberty, G., Petersen, C., Gao, L. & Macara, I. G. The cell-polarity protein Par6 links Par3 and atypical protein kinase C to Cdc42. Nature Cell Biol. 2, 531–539 (2000)
Qiu, R.-G., Abo, A. & Martin, G. S. A human homolog of the C. elegans polarity determinant Par-6 links Rac and Cdc42 to PKCζ signaling and cell transformation. Curr. Biol. 10, 697–707 (2000)
Lin, D. et al. A mammalian PAR-3-PAR-6 complex implicated in Cdc42/Rac1 and aPKC signalling and cell polarity. Nature Cell Biol. 2, 540–547 (2000)
Van Aelst, L. & Symons, M. Role of Rho family GTPases in epithelial morphogenesis. Genes Dev. 16, 1032–1054 (2002)
Vasioukhin, V., Bauer, C., Yin, M. & Fuchs, E. Directed actin polymerization is the driving force for epithelial cell-cell adhesion. Cell 100, 209–219 (2000)
Raich, W. B., Agbunag, C. & Hardin, J. Rapid epithelial-sheet sealing in the Caenorhabditis elegans embryo requires cadherin-dependent filopodial priming. Curr. Biol. 9, 1139–1146 (1999)
Jacinto, A., Martinez-Arias, A. & Martin, P. Mechanisms of epithelial fusion and repair. Nature Cell Biol. 3, E117–E123 (2001)
Yamanaka, T. et al. PAR-6 regulates aPKC activity in a novel way and mediates cell-cell contact-induced formation of the epithelial junctional complex. Genes Cells 6, 721–731 (2001)
Rojas, R., Ruiz, W. G., Leung, S. M., Jou, T. S. & Apodaca, G. Cdc42-dependent modulation of tight junctions and membrane protein traffic in polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 12, 2257–2274 (2001)
Gao, L., Joberty, G. & Macara, I. G. Assembly of epithelial tight junctions is negatively regulated by Par-6. Curr. Biol. 12, 221–225 (2002)
Ebnet, K. et al. The cell polarity protein ASIP/PAR-3 directly associates with junctional adhesion molecule (JAM). EMBO J. 20, 3738–3748 (2001)
O'Brien, L. E. et al. Rac1 orientates epithelial apical polarity through effects on basolateral laminin assembly. Nature Cell Biol. 3, 831–838 (2001)
Kroschewski, R., Hall, A. & Mellman, I. Cdc42 controls secretory and endocytic transport to the basolateral plasma membrane of MDCK cells. Nature Cell Biol. 1, 8–13 (1999)
Zhang, X. et al. Cdc42 interacts with the exocyst and regulates polarized secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 46745–46750 (2001)
Sugihara, K. et al. The exocyst complex binds the small GTPase RalA to mediate filopodia formation. Nature Cell Biol. 4, 73–78 (2001)
Moskalenko, S. et al. The exocyst is a Ral effector complex. Nature Cell Biol. 4, 66–72 (2002)
Luo, L. Rho GTPases in neuronal morphogenesis. Nature Rev. Neurosci. 1, 173–180 (2000)
Lee, T., Winter, C., Marticke, S. S., Lee, A. & Luo, L. Essential role of Drosophila RhoA in the regulation of neuroblast proliferation and dendritic but not axonal morphogenesis. Neuron 25, 307–316 (2000)
Ozdinler, P. H. & Erzurumlu, R. S. Regulation of neurotrophin-induced axonal responses via Rho GTPases. J. Comp. Neurol. 438, 377–387 (2001)
Li, Z., Van Aelst, L. & Cline, H. T. Rho GTPases regulate distinct aspects of dendritic arbor growth in Xenopus central neurons in vivo. Nature Neurosci. 3, 217–225 (2000)
Wong, W. T., Faulkner-Jones, B., Sanes, J. R. & Wong, R. O. Rapid dendritic remodeling in the developing retina: dependence on neurotransmission and reciprocal regulation by Rac and Rho. J. Neurosci. 20, 5024–5036 (2000)
Ridley, A. Rho GTPases and cell migration. J. Cell Sci. 114, 2713–2722 (2001)
Small, J. V., Stradal, T., Vignal, E. & Rottler, K. The lamellipodium: where motility begins. Trends Cell Biol. 12, 112–120 (2002)
Condeelis, J. How is actin polymerization nucleated in vivo? Trends Cell Biol. 11, 288–293 (2001)
Kraynov, V. S. et al. Localized Rac activation dynamics visualized in living cells. Science 290, 333–337 (2000)
Gupta, T. & Schupbach, T. Two signals are better than one: border cell migration in Drosophila. Dev. Cell 1, 443–445 (2001)
Duchek, P., Somogyi, K., Jekely, G., Beccari, S. & Rorth, P. Guidance of cell migration by the Drosophila PDGF/VEGF receptor. Cell 107, 17–26 (2001)
Reddien, P. W. & Horvitz, H. R. CED-2/CrkII and CED-10/Rac control phagocytosis and cell migration in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature Cell Biol. 2, 131–136 (2000)
Albert, M. L., Kim, J. I. & Birge, R. B. αvβ5 integrin recruites the CrkII-Dock180-rac1 complex for phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. Nature Cell Biol. 2, 899–905 (2000)
Worthylake, R. A., Lemoine, S., Watson, J. M. & Burridge, K. RhoA is required for monocyte tail retraction during transendothelial migration. J. Cell Biol. 154, 147–160 (2001)
Allen, W. E., Zicha, D., Ridley, A. J. & Jones, G. E. A role for Cdc42 in macrophage chemotaxis. J. Cell Biol. 141, 1147–1157 (1998)
Wittmann, T. & Waterman-Storer, C. M. Cell motility: can Rho GTPases and microtubules point the way? J. Cell Sci. 114, 3795–3803 (2001)
Liu, B. P. & Strittmatter, S. M. Semaphorin-mediated axonal guidance via Rho-related G proteins. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 13, 619–626 (2001)
Ng, J. et al. Rac GTPases control axon growth, guidance and branching. Nature 416, 442–447 (2002)
Lundquist, E. A., Reddien, P. W., Hartwieg, E., Horvitz, H. R. & Bargmann, C. I. Three C. elegans Rac proteins and several alternative Rac regulators control axon guidance, cell migration and apoptotic cell phagocytosis. Development 128, 4475–4488 (2001)
Brock, J., Midwinter, K., Lewis, J. & Martin, P. Healing of incisional wounds in the embryonic chick wing bud: characterization of the actin purse-string and demonstration of a requirement for Rho activation. J. Cell Biol. 135, 1097–1107 (1996)
Lu, Y. & Settleman, J. The Drosophila Pkn protein kinase is a Rho/Rac effector _target required for dorsal closure during embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 13, 1168–1180 (1999)
Stronach, B. E. & Perrimon, N. Stress signaling in Drosophila. Oncogene 18, 6172–6182 (1999)
Knust, E. Drosophila morphogenesis: movements behind the edge. Curr. Biol. 7, R558–R561 (1997)
Nobes, C. D. & Hall, A. Rho GTPases control polarity, protrusion and adhesion during cell movement. J. Cell Biol. 144, 1235–1244 (1999)
Etienne-Manneville, S. & Hall, A. Integrin-mediated Cdc42 activation controls cell polarity in migrating astrocytes through PKCζ. Cell 106, 489–498 (2001)
Palazzo, A. F. et al. Cdc42, dynein, and dynactin regulate MTOC reorientation independent of Rho-regulated microtubule stabilization. Curr. Biol. 11, 1536–1541 (2001)
Ishizaki, T. et al. Coordination of microtubules and actin cytoskeleton by the Rho effector mDial. Nature Cell Biol. 3, 8–14 (2001)
Ridely, A. J. Rho family proteins: coordinating cell responses. Trends Cell Biol. 11, 471–477 (2001)
Fukata, Y., Amano, M. & Kaibuchi, K. Rho-Rho-kinase pathway in smooth muscle contraction and cytoskeletal reorganization of non-muscle cells. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 22, 32–39 (2001)
Sakurada, S., Okamoto, H., Takuwa, N., Sugimoto, N. & Takuwa, Y. Rho activation in excitatory agonist-stimulated vascular smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 281, C571–C578 (2001)
Uehata, M. et al. Calcium sensitization of smooth muscle mediated by Rho-associated protein kinase in hypertension. Nature 389, 990–994 (1997)
van Nieuw Amerongen, G. P., van Delft, S., Vermeer, M. A., Collard, J. G. & van Hinsbergh, V. W. Activation of RhoA by thrombin in endothelial hypermeability: role of Rho kinase and protein tyrosine kinases. Circ. Res. 87, 335–340 (2000)
Wojciak-Stothard, B., Potempa, S., Eichholtz, T. & Ridley, A. J. Rho and Rac but not Cdc42 regulate endothelial cell permeability. J. Cell Sci. 114, 1343–1355 (2001)
Caron, E. & Hall, A. Identification of two distinct mechanisms of phagocytosis controlled by different Rho GTPases. Science 282, 1717–1721 (1998)
Caron, E. Rac and roll over the corpses. Curr. Biol. 10, R489–R491 (2000)
Bokoch, G. M. Regulation of cell function by Rho family GTPases. Immunol. Res. 21, 139–148 (2000)
Nobes, C. & Marsh, M. Dendritic cells: new roles for Cdc42 and Rac in antigen uptake? Curr. Biol. 10, R739–R741 (2000)
Aktories, K., Schmidt, G. & Just, I. Rho GTPases as _targets of bacterial protein toxins. Biol. Chem. 381, 421–426 (2000)
Galan, J. E. Salmonella interactions with host cells: Type III secretion at work. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 17, 53–86 (2001)
Cantrell, D. Lymphocyte signalling: a coordinating role for Vav? Curr. Biol. 8, R535–R538 (1998)
Glassford, J. et al. Vav is required for cyclin D2 induction and proliferation of mouse B lymphocytes activated via the antigen receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 41040–41048 (2001)
Olson, M. F., Ashworth, A. & Hall, A. An essential role for Rho, Rac and CDC42 GTPases in cell cycle progression through G1. Science 269, 1270–1272 (1995)
Welsh, C. F. et al. Timing of cyclin D1 expression within G1 phase is controlled by Rho. Nature Cell Biol. 3, 950–957 (2001)
Olson, M. F., Paterson, H. F. & Marshall, C. J. Signals from Ras and Rho GTPases interact to regulate expression of p21Waf1/Cip1. Nature 394, 295–299 (1998)
Mettouchi, A. et al. Integrin-specific activation of Rac controls progression through the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Mol. Cell 8, 115–127 (2001)
Glotzer, M. Animal cell cytokinesis. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 17, 351–386 (2001)
Stowers, L., Yelon, D., Berg, L. J. & Chant, J. Regulation of the polarization of T cells towards antigen-presenting cells by Ras-related GTPase CDC42. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 5027–5031 (1995)
Pinxteren, J. A., O'Sullivan, A. J., Larbi, K. Y., Tatham, P. E. R. & Gomperts, B. D. Thirty years of stimulus-secretion coupling: from Ca2+ to GTP in the regulation of exocytosis. Biochimie 82, 385–393 (2000)
Chiang, S. H. et al. Insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation requires the CAP-dependent activation of TC10. Nature 410, 944–948 (2001)
Kanzaki, M. & Pessin, J. E. Insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation in adipocytes is dependent upon cortical actin remodeling. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 42436–42444 (2001)
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for support from Cancer Research UK and the Medical Research Council. S.E.-M. is supported by an EMBO long-term fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Etienne-Manneville, S., Hall, A. Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature 420, 629–635 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01148
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01148
This article is cited by
-
Emerging roles of prominin-1 (CD133) in the dynamics of plasma membrane architecture and cell signaling pathways in health and disease
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2024)
-
Potential role of RhoA GTPase regulation in type interferon signaling in systemic lupus erythematosus
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2024)
-
BCG immunization induces CX3CR1hi effector memory T cells to provide cross-protection via IFN-γ-mediated trained immunity
Nature Immunology (2024)
-
ROCK1 inhibition improves wound healing in diabetes via RIPK4/AMPK pathway
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2024)
-
Differential functions of RhoGDIβ in malignant transformation and progression of urothelial cell following N-butyl-N-(4-hydmoxybutyl) nitrosamine exposure
BMC Biology (2023)