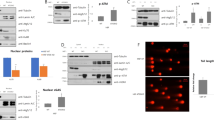
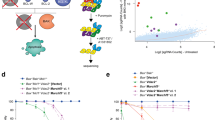
Abstract
Autophagy-related gene (Atg) 5 is a gene product required for the formation of autophagosomes. Here, we report that Atg5, in addition to the promotion of autophagy, enhances susceptibility towards apoptotic stimuli. Enforced expression of Atg5-sensitized tumour cells to anticancer drug treatment both in vitro and in vivo. In contrast, silencing the Atg5 gene with short interfering RNA (siRNA) resulted in partial resistance to chemotherapy. Apoptosis was associated with calpain-mediated Atg5 cleavage, resulting in an amino-terminal cleavage product with a relative molecular mass of 24,000 (Mr 24K). Atg5 cleavage was observed independent of the cell type and the apoptotic stimulus, suggesting that calpain activation and Atg5 cleavage are general phenomena in apoptotic cells. Truncated Atg5 translocated from the cytosol to mitochondria, associated with the anti-apoptotic molecule Bcl-xL and triggered cytochrome c release and caspase activation. Taken together, calpain-mediated Atg5 cleavage provokes apoptotic cell death, therefore, represents a molecular link between autophagy and apoptosis — a finding with potential importance for clinical anticancer therapies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
We are sorry, but there is no personal subscription option available for your country.
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levine, B. & Klionsky, D. J. Development by self-digestion: Molecular mechanisms and biological functions of autophagy. Dev. Cell 6, 463–477 (2004).
Gozuacik, D. & Kimchi, A. Autophagy as a cell death and tumor suppressor mechanism. Oncogene 23, 2891–2906 (2004).
Blommaart, E. F., Luiken, J. J. & Meijer, A. J. Autophagic proteolysis: control and specificity. Histochem. J. 29, 365–385 (1997).
Yu, L. et al. Regulation of an ATG7–beclin 1 program of autophagic cell death by caspase-8. Science 304, 1500–1502 (2004).
Shimizu, S. et al. Role of Bcl-2 family proteins in a non-apoptotic programmed cell death dependent on autophagy genes. Nature Cell Biol. 6, 1221–1228 (2004).
Mizushima, N. et al. Dissection of autophagosome formation using Apg5-deficient mouse embryonic stem cells. J. Cell. Biol. 152, 657–667 (2001).
Qu, X. et al. Promotion of tumorigenesis by heterozygous disruption of the beclin 1 gene. J. Clin. Invest. 112, 1809–1820 (2003).
Yue, Z., Jin, S., Yang, C., Levine, A. J. & Heintz, N. Beclin 1, an autophagy gene essential for early embryonic development, is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 100, 15077–15082 (2003).
Goldstein, J. C., Waterhouse, N. J., Juin, P., Evan, G. I. & Green, D. R. The coordinate release of cytochrome c during apoptosis is rapid, complete and kinetically invariant. Nature Cell Biol. 2, 156–162 (2000).
Simon, H.-U. Neutrophil apoptosis pathways and their modifications in inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 193, 101–110 (2003).
Gao, G. & Dou, Q. P. N-terminal cleavage of Bax by calpain generates a potent proapoptotic 18-kDa fragment that promotes Bcl-2-independent cytochrome c release and apoptotic cell death. J. Cell Biochem. 80, 53–72 (2000).
Altznauer, F., Conus, S., Cavalli, A., Folkers, G. & Simon, H.-U. Calpain-1 regulates Bax and subsequent Smac-dependent caspase-3 activation in neutrophil apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 5947–5957 (2004).
Arthur, J. S., Elce, J. S., Hegadorn, C., Williams, K. & Greer, P. A. Disruption of the murine calpain small subunit gene, Capn4: calpain is essential for embryonic development but not for cell growth and division. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 4474–4481 (2000).
Martin, S. J. et al. Early redistribution of plasma membrane phosphatidylserine is a general feature of apoptosis regardless of the initiating stimulus: Inhibition by overexpression of Bcl-2 and Abl. J. Exp. Med. 182, 1545–1556 (1995).
Strasser, A. The role of BH3-only proteins in the immune system. Nature Rev. Immunol. 5, 189–200 (2005).
Marchenko, N. D., Zaika, A. & Moll, U. M. Death signal-induced localization of p53 protein to mitochondria: A potential role in apoptotic signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 16202–16212 (2000).
Mihara, M. et al. p53 has a direct apoptogenic role at the mitochondria. Mol. Cell 11, 577–590 (2003).
Chipuk, J. E. et al. Direct activation of Bax by p53 mediates mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and apoptosis. Science 303, 1010–1014 (2004).
Leu, J. I., Dumont, P., Hafey, M., Murphy, M. E. & George, D. L. Mitochondrial p53 activates Bak and causes disruption of a Bak-Mcl1 complex. Nature Cell Biol. 6, 443–450 (2004).
Li, H. et al. Cytochrome c release and apoptosis induced by mitochondrial _targeting of nuclear orphan receptor TR3. Science 289, 1159–1164 (2000).
Karuman, P. et al. The Peutz-Jegher gene product LKB1 is a mediator of p53-dependent cell death. Mol. Cell 7, 1307–1319 (2001).
Chua, B. T. et al. Mitochondrial translocation of cofilin is an early step in apoptosis induction. Nature Cell Biol. 5, 1083–1089 (2003).
Daigle, I., Yousefi, S., Colonna, M., Green, D. R. & Simon, H.-U. Death receptors bind SHP-1 and block cytokine-induced anti-apoptotic signaling in neutrophils. Nature Med. 8, 61–67 (2002).
Simon, H.-U. et al. Eosinophils maintain their capacity to signal and release eosinophil cationic protein upon repetitive stimulation with the same agonist. J. Immunol. 165, 4069–4075 (2000).
Altznauer, F. et al. Inflammation-associated cell cycle-independent block of apoptosis by survivin in terminally differentiated neutrophils. J. Exp. Med. 199, 1343–1354 (2004).
Martinelli, S. et al. Induction of genes mediating interferon-dependent extracellular trap formation during neutrophil differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 44123–44132 (2004).
Adrain, C., Creagh, E. M. & Martin, S. J. Apoptosis-associated release of Smac/DIABLO from mitochondria requires active caspases and is blocked by Bcl-2. EMBO J. 20, 6627–6636 (2001).
Yousefi, S., Green, D. R., Blaser, K. & Simon, H.-U. Protein-tyrosine phosphorylation regulates apoptosis in human eosinophils and neutrophils. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 91, 10868–10872 (1994).
von Gunten, S. et al. Siglec-9 transduces apoptotic and nonapoptotic death signals into neutrophils depending on the proinflammatory cytokine environment. Blood 106, 1423–1431 (2005).
Takeuchi, H., Kanzawa, T., Kondo, Y. & Kondo, S. Inhibition of platelet-derived growth factor signalling induces autophagy in malignant glioma cells. Br. J. Cancer 90, 1069–1075 (2004).
Wolf, B. B. et al. Calpain functions in a caspase-independent manner to promote apoptosis-like events during platelet activation. Blood 94, 1683–1692 (1999).
Bovia, F. et al. Efficient transduction of primary human B lymphocytes and nondividing myeloma B cells with HIV-1-derived lentiviral vectors. Blood 101, 1727–1733 (2003).
Wiznerowicz, M. & Trono, D. Conditional suppression of cellular genes: lentivirus vector-mediated drug-inducible RNA interference. J. Virol. 77, 8957–8961 (2003).
Costes, S. V. et al. Automatic and quantitative measurement of protein-protein colocalization in live cells. Biophys. J. 86, 3993–4003 (2004).
Uren, R. T. et al. Mitochondrial release of pro-apoptotic proteins: electrostatic interactions can hold cytochrome c but not Smac/DIABLO to mitochondrial membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 2266–2274 (2005).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (grant No. 310000-107526 and 310000-112078).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figures S1, S2, S3 and Supplementary Information (PDF 783 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yousefi, S., Perozzo, R., Schmid, I. et al. Calpain-mediated cleavage of Atg5 switches autophagy to apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol 8, 1124–1132 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1482
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1482
This article is cited by
-
N-acetylcysteine and Hydroxychloroquine Ameliorate ADMA-Induced Fetal Growth Restriction in Mice via Regulating Oxidative Stress and Autophagy
Reproductive Sciences (2024)
-
The new insights into autophagy in thyroid cancer progression
Journal of Translational Medicine (2023)
-
Autophagy restricts Mycobacterium tuberculosis during acute infection in mice
Nature Microbiology (2023)
-
Moschus ameliorates glutamate-induced cellular damage by regulating autophagy and apoptosis pathway
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
_targeted Inhibition of Hsp90 in Combination with Metformin Modulates Programmed Cell Death Pathways in A549 Lung Cancer Cells
Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (2023)