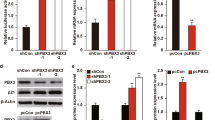
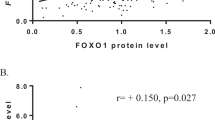
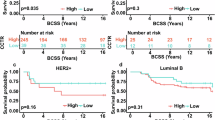
Abstract
Mutations in certain genes that regulate the cell cycle, such as p16 and p53, are frequently found in human cancers1. However, tumor-specific mutations are uncommon in genes encoding cyclin E and the CDK inhibitor p27Kip1, two cell-cycle regulators that are also thought to contribute to tumor progression2–8. It is now known that levels of both cyclin E and p27 can be controlled by posttranscriptional mechanisms, indicating that expression of these proteins can be altered by means other than simply mutation of their respective genes9,10. Thus, changes in p27 and cyclin E protein levels in tumors might be more common than previously anticipated and may be indicators of tumor behavior.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
We are sorry, but there is no personal subscription option available for your country.
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clurman, B. & Roberts, J. cellcycle and cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 87, 1499–1501 (1995).
Pietenpol, J. et al. Assignment of the human p27Kip1 gene to 12p13 and its analysis in leukemias. Cancer Res. 55, 1206–1210 (1995).
Ponce-Castaneda, M. et al. p27Kip1: Chromosomal mapping to 12p12–l2p13 and absence of mutations in human tumors. Cancer Res. 55, 1211–1214 (1995).
Konstantin, S. et al. p27/Kip1 mutation found in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 56, 2400–2404 (1996).
Leach, F. et al. Amplification of cyclin genes in colorectal carcinomas. Cancer Res. 53, 1986–1989 (1993).
Keyomarsi, K. et al. Cyclin E, a potential prognostic marker for breast cancer. Cancer Res. 54, 380–385 (1994).
Said, T. & Medina, D. Cell cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinase activities in mouse mammary tumor development. Carcinogenesls 16, 823–830 (1995).
Fero, M.L. et al. A syndrome of multi-organ hyperplasia with features of gigantism, tumorigenesis and female sterility in p27Kip1–deficient mice. Cell 85, 733–744 (1996).
Clurman, B., Sheaff, R., Thress, K., Groudine, M. & Roberts, J. Turnover of cyclin E by the ubiquitin-proteosome pathway is regulated by CDK2 binding and cyclin phosphorylation. Genes Dev. 10, 1979–1990 (1996).
Pagano, M. et al. Role of the ubiquitin-proteosome pathway in regulating abundance of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27. Science 269, 682–685 (1995).
Dulic, V., Lees, E. & Reed, S. Association of human cyclin E with a periodic G1–S phase protein kinase. Science 257, 1958–1961 (1992).
Koff, A. et al. Human cyclin E, a new cyclin that interacts with two members of the CDC2 gene family. Cell 66, 1217–1228 (1991).
Nourse, J. et al. lnterleukin-2-mediated elimination of p27Kip1 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor prevented by rapamycin. Nature 372, 570–573 (1994).
Coats, S., Flannagan, W., Nourse, J. & Roberts, J. Requirement of p27Kip1 for restriction point control of the fibroblast cell cycle. Science 272, 877–880 (1996).
McGuire, W. & Clark, G. Prognostic factors and treatment decisions in axillarynode negative breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 326, 1756–1761 (1992).
Dutta, A., Chandra, R., Leiter, L. & Lester, S. Cyclins as markers of tumor proliferation: Immunocytochemical studies in breast cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 5386–5390 (1995).
Ohtsubo, M., Theodoras, A., Schumacher, J., Roberts, J. & Pagano, M. Human cyclin E, a nuclear protein essential for the Gl-to-S phase transition. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 2612–2624 (1995).
Ohtsubo, M. & Roberts, J. Cyclin-dependent regulation of G1 in mammalian fibroblasts. Science 259, 1908–1912 (1993).
Gerdes, J., Becker, M. & Key, G. Immunohistological detection of tumour growth fraction (Ki-67 antigen) in formalin-fixed and routinely processed tissues J. Pathol. 168, 85–86 (1992).
Lin, D. & Ying, Z. Cox regression with incomplete covariate measurements. J. Am. Statist. Assoc. 88, 1341–1349 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Porter, P., Malone, K., Heagerty, P. et al. Expression of cell-cycle regulators p27Kip1 and cyclin E, alone and in combination, correlate with survival in young breast cancer patients. Nat Med 3, 222–225 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0297-222
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0297-222
This article is cited by
-
Bacterial protein MakA causes suppression of tumour cell proliferation via inhibition of PIP5K1α/Akt signalling
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
A prospective phase II clinical trial identifying the optimal regimen for carboplatin plus standard backbone of anthracycline and taxane-based chemotherapy in triple negative breast cancer
Medical Oncology (2022)
-
Novel B, C-ring truncated deguelin derivatives reveals as potential inhibitors of cyclin D1 and cyclin E using molecular docking and molecular dynamic simulation
Molecular Diversity (2022)
-
The inhibitory effect of silencing CDCA3 on migration and proliferation in bladder urothelial carcinoma
Cancer Cell International (2021)
-
Algae-meditated route to cuprous oxide (Cu2O) nanoparticle: differential expression profile of MALAT1 and GAS5 LncRNAs and cytotoxic effect in human breast cancer
Cancer Nanotechnology (2020)