Abstract
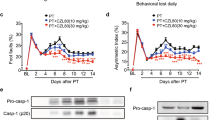
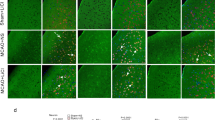
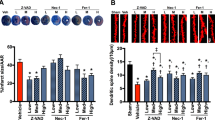
Neuronal death in cerebral ischemia is largely due to excitotoxic mechanisms, which are known to activate the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway. We have evaluated the neuroprotective power of a cell-penetrating, protease-resistant peptide that blocks the access of JNK to many of its _targets. We obtained strong protection in two models of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO): transient occlusion in adult mice and permanent occlusion in 14-d-old rat pups. In the first model, intraventricular administration as late as 6 h after occlusion reduced the lesion volume by more than 90% for at least 14 d and prevented behavioral consequences. In the second model, systemic delivery reduced the lesion by 78% and 49% at 6 and 12 h after ischemia, respectively. Protection correlated with prevention of an increase in c-Jun activation and c-Fos transcription. In view of its potency and long therapeutic window, this protease-resistant peptide is a promising neuroprotective agent for stroke.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
We are sorry, but there is no personal subscription option available for your country.
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 333, 1581–1587 (1995).
Namura, S. et al. Activation and cleavage of caspase-3 in apoptosis induced by experimental cerebral ischemia. J. Neurosci. 18, 3659–3668 (1998).
Hara, H. et al. Inhibition of interleukin 1beta converting enzyme family proteases reduces ischemic and excitotoxic neuronal damage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 2007–2012 (1997).
Morris, D.C. et al. Extension of the therapeutic window for recombinant tissue plasminogen activator with argatroban in a rat model of embolic stroke. Stroke 32, 2635–2640 (2001).
Iadecola, C. & Alexander, M. Cerebral ischemia and inflammation. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 14, 89–94 (2001).
Fink, K. et al. Prolonged therapeutic window for ischemic brain damage caused by delayed caspase activation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 18, 1071–1076 (1998).
Gladstone, D.J., Black, S.E. & Hakim, A.M. Toward wisdom from failure: lessons from neuroprotective stroke trials and new therapeutic directions. Stroke 33, 2123–2136 (2002).
Brott, T. & Bogousslavsky, J. Treatment of acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 343, 710–722 (2000).
Petty, M.A. & Wettstein, J.G. White matter ischaemia. Brain Res. Rev. 31, 58–64 (1999).
Imai, H., McCulloch, J., Graham, D.I., Masayasu, H. & Macrae, I.M. New method for the quantitative assessment of axonal damage in focal cerebral ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 22, 1080–1089 (2002).
Dirnagl, U., Iadecola, C. & Moskowitz, M.A. Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: an integrated view. Trends Neurosci. 22, 391–397 (1999).
Zipfel, G.J., Babcock, D.J., Lee, J.M. & Choi, D.W. Neuronal apoptosis after CNS injury: the roles of glutamate and calcium. J. Neurotrauma 17, 857–869 (2000).
Yam, P.S., Dunn, L.T., Graham, D.I., Dewar, D. & McCulloch, J. NMDA receptor blockade fails to alter axonal injury in focal cerebral ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 20, 772–779 (2000).
Wu, D.C., Ye, W., Che, X.M. & Yang, G.Y. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases after permanent cerebral artery occlusion in mouse brain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 20, 1320–1330 (2000).
Saporito, M.S. et al. Preservation of cholinergic activity and prevention of neuron death by CEP-1347/KT-7515 following excitotoxic injury of the nucleus basalis magnocellularis. Neuroscience 86, 461–472 (1998).
Savinainen, A., Garcia, E.P., Dorow, D., Marshall, J. & Liu, Y.F. Kainate receptor activation induces mixed lineage kinase-mediated cellular signaling cascades via post-synaptic density protein 95. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 11382–11386 (2001).
Yang, D.D. et al. Absence of excitotoxicity-induced apoptosis in the hippocampus of mice lacking the Jnk3 gene. Nature 389, 865–870 (1997).
Kuan, C.Y. et al. The Jnk1 and Jnk2 protein kinases are required for regional specific apoptosis during early brain development. Neuron 22, 667–676 (1999).
Behrens, A., Sibilia, M. & Wagner, E.F. Amino-terminal phosphorylation of c-Jun regulates stress-induced apoptosis and cellular proliferation. Nat. Genet. 21, 326–329 (1999).
Bonny, C., Oberson, A., Negri, S., Sauser, C. & Schorderet, D.F. Cell-permeable peptide inhibitors of JNK novel blockers of β-cell death. Diabetes 50, 77–82 (2001).
Barr, R.K., Kendrick, T.S. & Bogoyevitch, M.A. Identification of the critical features of a small peptide inhibitor of JNK activity. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 10987–10997 (2002).
Vives, E., Brodin, P. & Lebleu, B. A truncated HIV-1 Tat protein basic domain rapidly translocates through the plasma membrane and accumulates in the cell nucleus. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 16010–16017 (1997).
Steiner, D.F., Smeekens, S.P., Ohagi, S. & Chan, S.J. The new enzymology of precursor processing endoproteases. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 23435–23438 (1992).
Brugidou, J., Legrand, C., Mery, J. & Rabie, A. The retro-inverso form of a homeobox-derived short peptide is rapidly internalised by cultured neurones: a new basis for an efficient intracellular delivery system. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 214, 685–693 (1995).
Bennett, B.L. et al. SP600125, an anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of Jun N-terminal kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 13681–13686 (2001).
Ko, H.W. et al. Ca2+-mediated activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and nuclear factor kappa B by NMDA in cortical cell cultures. J. Neurochem. 71, 1390–1395 (1998).
Coffey, E.T., Hongisto, V., Dickens, M., Davis, R.J. & Courtney, M.J. Dual roles for c-Jun N-terminal kinase in developmental and stress responses in cerebellar granule neurons. J. Neurosci. 20, 7602–7613 (2000).
Cavigelli, M., Dolfi, F., Claret, F.X. & Karin, M. Induction of c-fos expression through JNK-mediated TCF/Elk-1 phosphorylation. EMBO J. 14, 5957–5964 (1995).
Schwarze, S.R., Ho, A., Vocero-Akbani, A. & Dowdy, S.F. In vivo protein transduction: delivery of a biologically active protein into the mouse. Science 285, 1569–1572 (1999).
Dawson, D.A., Wadsworth, G. & Palmer, A.M. A comparative assessment of the efficacy and side-effect liability of neuroprotective compounds in experimental stroke. Brain Res. 892, 344–350 (2001).
Iadecola, C., Zhang, F. & Xu, X. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase ameliorates cerebral ischemic damage. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 268, R286–R292 (1995).
Hossmann, K.A. Glutamate-mediated injury in focal cerebral-ischemia - the excitotoxin hypothesis revised. Brain Pathol. 4, 23–36 (1994).
Hardingham, G.E. & Bading, H. The yin and yang of NMDA receptor signalling. Trends Neurosci. 26, 81–89 (2003).
Hirosumi, J. et al. A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature 420, 333–336 (2002).
Curtis, J. & Finkbeiner, S. Sending signals from the synapse to the nucleus: possible roles for CaMK, Ras/ERK, and SAPK pathways in the regulation of synaptic plasticity and neuronal growth. J. Neurosci. Res. 58, 88–95 (1999).
Schauwecker, P.E. Seizure-induced neuronal death is associated with induction of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and is dependent on genetic background. Brain Res. 884, 116–128 (2000).
Zhu, X. et al. Activation and redistribution of c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress activated protein kinase in degenerating neurons in Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurochem. 76, 435–441 (2001).
Kim, H.S. et al. Carboxyl-terminal fragment of Alzheimer's APP destabilizes calcium homeostasis and renders neuronal cells vulnerable to excitotoxicity. FASEB J. 14, 1508–1517 (2000).
Chomczynski, P. & Sacchi, N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate- phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 162, 156–159 (1987).
Huang, Z. et al. Effects of cerebral ischemia in mice deficient in neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Science 265, 1883–1885 (1994).
Ma, J., Qiu, J., Hirt, L., Dalkara, T. & Moskowitz, M.A. Synergistic protective effect of caspase inhibitors and bFGF against brain injury induced by transient focal ischaemia. Br. J. Pharmacol. 133, 345–350 (2001).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants 31-50598.97, 32-54119.98, 31-61736.00, 32-65139.01 and 3200-68306.02 from the Swiss National Science Foundation, the San Paolo Bank (Italy) and the Alzheimer Project (Italian Ministry of Health). We are particularly grateful to P. Nicod and the Botnar Foundation for human and financial support. We thank E. Bernardi, I. Favre, V. Mottier and A. Oberson for assistance; R. Kraftsik for help with computation and statistics; and J.-Y. Chatton and A. Volterra for critical comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
C.B. receives partial remuneration from the vendor, Alexis, for the sale of D-JNKI-1 and L-JNKI-1.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borsello, T., Clarke, P., Hirt, L. et al. A peptide inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase protects against excitotoxicity and cerebral ischemia. Nat Med 9, 1180–1186 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm911
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm911
This article is cited by
-
Cell-permeable PI3 kinase competitive peptide inhibits KIT mutant mediated tumorigenesis of gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST)
Molecular Biology Reports (2024)
-
Proteomic association with age-dependent sex differences in Wisconsin Card Sorting Test performance in healthy Thai subjects
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Cerebrolysin reduces excitotoxicity by modulation of cell-death proteins in delayed hours of ischemic reperfusion injury
Metabolic Brain Disease (2023)
-
Examining the role of astrogliosis and JNK signaling in post-traumatic epilepsy
Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery (2022)
-
Delayed Therapeutic Administration of Melatonin Enhances Neuronal Survival Through AKT and MAPK Signaling Pathways Following Focal Brain Ischemia in Mice
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2022)