Abstract
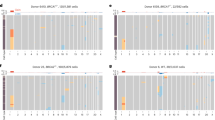
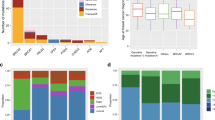
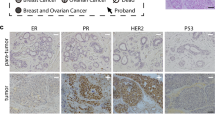
The status of p53 was investigated in breast tumours arising in germ-line carriers of mutant alleles of BRCA1 and BRCA2 and in a control series of sporadic breast tumours. p53 expression was detected in 20/26 (77%) BRCA1-, 10/22 (45%) BRCA2-associated and 25/72 (35%) grade-matched sporadic tumours. Analysis of p53 sequence revealed that the gene was mutant in 33/50 (66%) BRCA-associated tumours, whereas 7/20 (35%) sporadic grade-matched tumours contained p53 mutation (P<0.05). A number of the mutations detected in the BRCA-associated tumours have not been previously described in human cancer databases, whilst others occur extremely rarely. Analysis of additional genes, p16INK4, Ki-ras and β-globin revealed absence or very low incidence of mutations, suggesting that the higher frequency of p53 mutation in the BRCA-associated tumours does not reflect a generalized increase in susceptibility to the acquisition of somatic mutation. Furthermore, absence of frameshift mutations in the polypurine tracts present in the coding sequence of the TGF β type II receptor (TGF β IIR) and Bax implies that loss of function of BRCA1 or BRCA2 does not confer a mutator phenotype such as that found in tumours with microsatellite instability (MSI). p21Waf1 was expressed in BRCA-associated tumours regardless of p53 status and, furthermore, some tumours expressing wild-type p53 did not express detectable p21Waf1. These data do not support, therefore, the simple model based on studies of BRCA−/− embryos, in which mutation of p53 in BRCA-associated tumours results in loss of p21Waf1 expression and deregulated proliferation. Rather, they imply that proliferation of such tumours will be subject to multiple mechanisms of growth regulation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
We are sorry, but there is no personal subscription option available for your country.
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crook, T., Brooks, L., Crossland, S. et al. p53 mutation with frequent novel codons but not a mutator phenotype in BRCA1- and BRCA2-associated breast tumours. Oncogene 17, 1681–1689 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202106
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202106