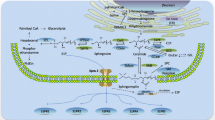
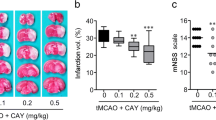
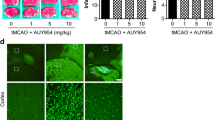
Abstract
Stroke is a major cause of long-term disability, the severity of which is directly related to the numbers of neurons that succumb to the ischemic insult. The signaling cascades activated by cerebral ischemia that may either promote or protect against neuronal death are not well-understood. One injury-responsive signaling pathway that has recently been characterized in studies of non-neural cells involves cleavage of membrane sphingomyelin by acidic and/or neutral sphingomyelinase (ASMase) resulting in generation of the second messenger ceramide. We now report that transient focal cerebral ischemia induces large increases in ASMase activity, ceramide levels, and production of inflammatory cytokines in wild-type mice, but not in mice lacking ASMase. The extent of brain tissue damage is decreased and behavioral outcome improved in mice lacking ASMase. Neurons lacking ASMase exhibit decreased vulnerability to excitotoxicity and hypoxia, which is associated with decreased levels of intracellular calcium and oxyradicals. Treatment of mice with a drug that inhibits ASMase activity and ceramide production reduces ischemic neuronal injury and improves behavioral outcome, suggesting that drugs that inhibit this signaling pathway may prove beneficial in stroke patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajjalieh S. and Batchelor R. (2000) Ceramide kinase. Methods Enzymol. 311, 207–215.
Ballou L. R., Laulederkind S. J., Rosloniec E. F., and Raghow R. (1996) Ceramide signalling and the immune response. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1301, 273–287.
Barone F. C., Arvin B., White R. F., Miller A., Webb C. L., Willette R. N., et al. (1997) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha. A mediator of focal ischemic brain injury. Stroke 28, 1233–1244.
Bruce A. J., Boling W., Kindy M. S., Peschon J., Kraemer P. J., Carpenter M. K., et al. (1996) Altered neuronal and microglial responses to excitotoxic and ischemic brain injury in mice lacking TNF receptors. Nature Med. 2, 788–794.
Brugg B., Michel P. P., Agid Y., and Ruberg M. (1996) Ceramide induces apoptosis in cultured mesencephalic neurons. J. Neurochem. 66, 733–739.
Chen J., Nikolova-Karakashian M., Merrill A. H., and Morgan E. T. (1995) Regulation of cytochrome p450 2C11 (CYP2C11) gene expression by interleukin-1, sphingomyelin hydrolysis, and ceramides in rat hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 25,233–25,236.
Cifone M. G., Roncaioli P., De Maria R., Camarda G., Santoni A., Ruberti G., and Testi R. (1995) Multiple pathways originate at the Fas/APO-1 (CD95) receptor: sequential involvement of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C and acidic sphingomyelinase in the propagation of the apoptotic signal. EMBO J. 14, 5859–5868.
Cifone M. G., Migliorati G., Parroni R., Marchetti C., Millimaggi D., Santoni A., and Riccardi C. (1999) Dexamethasone-induced thymocyte apoptosis: apoptotic signal involves the sequential activation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C, acidic sphingomyelinase, and caspases. Blood 93, 2282–2296.
Crumrine R. C., Thomas A. L., and Morgan P. F. (1994) Attenuation of p53 expression protects against focal ischemic damage in transgenic mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 14, 887–891.
Degli Esposti M. and McLennan H. (1998) Mitochondria and cells produce reactive oxygen species in virtual anaerobiosis: relevance to ceramide-induced apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 430, 338–342.
DeGraba T. J. (1998) The role of inflammation after acute stroke: utility of pursuing anti-adhesion molecule therapy. Neurology 51, S62-S68.
Dirnagl U., Iadecola C. and Moskowitz M. A. (1999) Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: an integrated view. Trends Neurosci. 22, 391–397.
Endres M., Fink K., Zhu J., Stagliano N. E., Bondada V., Geddes J. W., et al. (1999) Neuroprotective effects of gelsolin during murine stroke. J. Clin. Invest. 103, 347–354.
Fedoroff S., Berezovskaya O., and Maysinger D. (1997) Role of colony stimulating factor-1 in brain damage caused by ischemia. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 21, 187–191.
Fink K., Zhu J., Namura S., Shimizu-Sasamata M., Endres M., Ma J., et al. (1998) Prolonged therapeutic window for ischemic brain damage caused by delayed caspase activation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 18, 1071–1076.
France-Lanord V., Brugg B., Michel P. P., Agid Y., and Ruberg M. (1997) Mitochondrial free radical signal in ceramide-dependent apoptosis: a putative mechanism for neuronal death in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 69, 1612–1621.
Garcia-Ruiz C., Colell A., Mari M., Morales A., and Fernandez-Checa J. C. (1997) Direct effect of ceramide on the mitochondrial electron transport chain leads to generation of reactive oxygen species. Role of mitochondrial glutathione. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 11,369–11,377.
Gary D. S., Bruce-Keller A. J., Kindy M. S., and Mattson M. P. (1998) Ischemic and excitotoxic brain injury is enhanced in mice lacking the p55 tumor necrosis factor receptor. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 18, 1283–1287.
Goodman Y. and Mattson M. P. (1996) Ceramide protects hippocampal neurons against excitotoxic and oxidative insults, and amyloid beta-peptide toxicity. J. Neurochem. 6, 869–872.
Guo Q., Sebastian L., Sopher B. L., Miller M. W., Glazner G. W., Ware C. B., et al. (1999) Neurotrophic factors [activity-dependent neurotrophic factor (ADNF) and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF)] interrupt excitotoxic neurodegenerative cascades promoted by a PS1 mutation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 4125–4130.
Hannun Y. A. and Obeid L. M. (1997) Ceramide and the eukaryotic stress response. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 25, 1171–1175.
Hara H., Fink K., Endres M., Friedlander R. M., Gagliardini V., Yuan J., and Moskowitz M. A. (1997) Attenuation of transient focal cerebral ischemic injury in transgenic mice expressing a mutant ICE inhibitory protein. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 17, 370–375.
Hartfield P. J., Mayne G. C., and Murray A. W. (1997) Ceramide induces apoptosis in PC12 cells. FEBS Lett. 401, 148–152.
Herr I., Martin-Villalba A., Kurz E., Roncaioli P., Schenkel J., Cifone M. G., and Debatin K. M. (1999) FK506 prevents stroke-induced generation of ceramide and apoptosis signaling. Brain Res. 826, 210–219.
Hida H., Takeda M., and Soliven B. (1998) Ceramide inhibits inwardly rectifying K+ currents via a Ras- and Raf-1-dependent pathway in cultured oligodendrocytes. J. Neurosci. 18, 8712–8719.
Hofmann K. and Dixit V. M. (1998) Ceramide in apoptosis: does it really matter? Trends Biochem. Sci. 23, 374–377.
Horinouchi K., Erlich S., Perl D. P., Ferlinz K., Bisgaier C. L., Sandhoff K., et al. (1995) Acid sphingomyelinase deficient mice: a model of types A and B Niemann-Pick disease. Nat. Gen. 10, 288–293.
Jarvis W. D., Kolesnick R. N., Fornari F. A., Traylor R. S., Gewirtz D. A., and Grant S. (1994) Induction of apoptotic DNA damage and cell death by activation of the sphingomyelin pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 73–77.
Keller J. N., Kindy M. S., Holtsberg F. W., St Clair D. K., Yen H. C., Germeyer A., et al. (1998) Mitochondrial manganese superoxide dismutase prevents neural apoptosis and reduces ischemic brain injury: suppression of peroxynitrite production, lipid peroxidation, and mitochondrial dysfunction. J. Neurosci. 18, 687–697.
Kobrinsky E., Spielman A. I., Rosenzweig S., and Marks A. R. (1999) Ceramide triggers intracellular calcium release via the IP(3) receptor in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Am. J. Physiol. 277, C665–672.
Kubota M., Kitahara S., Shimasaki H., and Ueta N. (1989) Accumulation of ceramide in ischemic human brain of an acute case of cerebral occlusion. Jpn. J. Exp. Med. 59, 59–64.
Loddick S. A., Turnbull A. V., and Rothwell N. J. (1998) Cerebral interleukin-6 is neuroprotective during permanent focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 18, 176–179.
Long S. D. and Pekala P. H. (1996) Lipid mediators of insulin resistance: ceramide signalling down-regulates GLUT4 gene transcription in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem. J. 319, 179–184.
Love S. (1998) Oxidative stress in brain ischemia. Brain Pathol. 9, 119–131.
Mansat-de Mas V., Bezombes C., Quillet-Mary A., Bettaieb A., D’orgeix A. D., Laurent G., and Jaffrezou J. P. (1999) Implication of radical oxygen species in ceramide generation, c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation and apoptosis induced by daunorubicin. Mol. Pharmacol. 56, 867–874.
Mathias S., Pena L. A., and Kolesnick R. N. (1998) Signal transduction of stress via ceramide. Biochem. J. 335, 465–480.
Mattson M. P. (1997) Neuroprotective signal transduction: relevance to stroke. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 21, 193–206.
Mattson M. P., Goodman Y., Luo H., Fu W., and Furukawa K. (1997) Activation of NF-κB protects hippocampal neurons against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis: evidence for induction of manganese superoxide dismutase and suppression of peroxynitrite production and protein tyrosine nitration. J. Neurosci. Res. 49, 681–697.
Merrill, A. H. Jr., Wang E., Mullins R. E., Jamison W. C., Nimkar S., and Liotta D. (1988) Quantitation of free sphingosine in liver by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 171, 373–381.
Nikolova-Karakashian M. N., Morgan E. T., Alexander C., Liotta D. C., and Merrill A. H. (1997) Biomdal regulation of ceramidase by interleukin-1β: Implication for the regulation of cytochrome P450 2C11 (CYP2C11). J. Biol. Chem. 272, 18,718–18,724.
Pruschy M., Resch H., Shi Y. Q., Aalame N., Glanzmann C., and Bodis S. (1999) Ceramide triggers p53-dependent apoptosis in genetically defined fibrosarcoma tumour cells. Br. J. Cancer 80, 693–698.
Relton J. K. and Rothwell N. J. (1992) Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist inhibits ischaemic and excitotoxic neuronal damage in the rat. Brain Res. Bull. 29, 243–246.
Santana P., Pena L. A., Haimovitz-Friedman A., Martin S., Green D., McLoughlin M., et al. (1996) Acid sphingomyelinase-deficient human lymphoblasts and mice are defective in radiation-induced apoptosis. Cell 86, 189–199.
Scheid M. P., Foltz I. N., Young P. R., Schrader J. W., and Duronio V. (1999) Ceramide and cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) induce cAMP response element binding protein phosphorylation via distinct signaling pathways while having opposite effects on myeloid cell survival. Blood 93, 217–225.
Schielke G. P., Yang G. Y., Shivers B. D., and Betz A. L. (1998) Reduced ischemic brain injury in interleukin-1β converting enzyme-deficient mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 18, 180–185.
Schutze S., Potthoff K., Machleidt T., Berkovic D., Wiegmann K., and Kronke M. (1992) TNF activates NF-κB by phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C-induced acidic sphingomyelin breakdown. Cell 71, 765–776.
Shioda S., Ozawa H., Dohi K., Mizushima H., Matsumoto K., Nakajo S., et al. (1998) PACAP protects hippocampal neurons against apoptosis: involvement of JNK/SAPK signaling pathway. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 865, 111–117.
Wang Y. M., Seibenhener M. L., Vandenplas M. L., and Wooten M. W. (1999) Atypical PKC zeta is activated by ceramide, resulting in coactivation of NF-κB/JNK kinase and cell survival. J. Neurosci. Res. 55, 293–302.
Yoshimura S., Banno Y., Nakashima S., Hayashi K., Yamakawa H., Sawada M., et al. (1999) Inhibition of neutral sphingomyelinase activation and ceramide formation by glutathione in hypoxic PC12 cell death. J. Neurochem. 73, 675–683.
Yu Z., Zhou D., Bruce-Keller A. J., Kindy M. S., and Mattson M. P. (1999) Lack of the p50 subunit of nuclear factor-κB increases the vulnerability of hippocampal neurons to excitotoxic injury. J. Neurosci. 19, 8856–8865.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Z.F., Nikolova-Karakashian, M., Zhou, D. et al. Pivotal role for acidic sphingomyelinase in cerebral ischemia-induced ceramide and cytokine production, and neuronal apoptosis. J Mol Neurosci 15, 85–97 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:15:2:85
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:15:2:85