Convolutional Neural Networks–Based Image Analysis for the Detection and Quantification of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps
Abstract
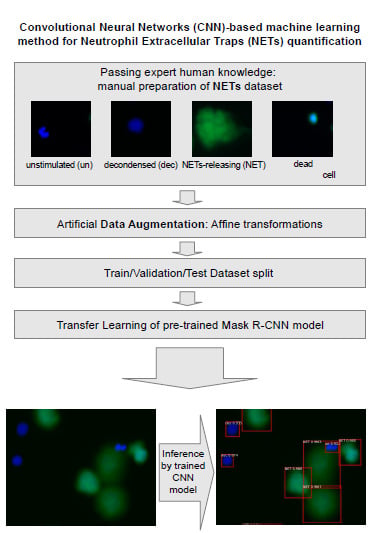
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Procedures for Isolation and Stimulation of Neutrophils; Visualization of NETs
2.1.1. Reagents
2.1.2. Isolation of Human Neutrophils and Stimulation of NETs Release
2.1.3. Microscopic Live Imaging of NETs
2.1.4. Immunofluorescence Staining of NETs
2.2. Open NETs Dataset for Image Analysis Models
- Training data set: images from 15 individuals, 5–27 images (mean ± SEM: 12.5 ± 1.9) and 65–473 labeled objects (mean ± SEM: 210.6 ± 37.3) per each individual;
- Validation data set: images from four individuals, 2–22 images (mean ± SEM: 15.0 ± 4.5) and 27–438 labeled objects (mean ± SEM: 332.5 ± 101.8) per each individual;
- Test data set: images from six individuals, 6–12 images (mean ± SEM: 12.5 ± 1.0) and 122–271 labeled objects (mean ± SEM: 169.3 ± 22.8) per each individual.
2.3. CNN Quantification Method
2.3.1. Model Training
2.3.2. Performance Metrics for the CNN Model
2.4. Quantification by Measurement of Extracellular DNA Release
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Adopted Model Detects Objects with Quality Comparable to Manual Counting
3.2. The CNN Model is Superior to NETs Quantification Based on Extracellular DNA Release
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dale, D.C.; Boxer, L.; Liles, W.C. The phagocytes: Neutrophils and monocytes. Blood 2008, 112, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacy, P. Mechanisms of degranulation in neutrophils. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2006, 2, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yipp, B.G.; Kubes, P. NETosis: How vital is it? Blood 2013, 122, 2784–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, S.; Mihalache, C.; Kozlowski, E.; Schmid, I.; Simon, H.U. Viable neutrophils release mitochondrial DNA to form neutrophil extracellular traps. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilsczek, F.H.; Salina, D.; Poon, K.K.; Fahey, C.; Yipp, B.G.; Sibley, C.D.; Robbins, S.M.; Green, F.H.; Surette, M.G.; Sugai, M.; et al. A novel mechanism of rapid nuclear neutrophil extracellular trap formation in response to Staphylococcus aureus. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 7413–7425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasler, P.; Giaglis, S.; Hahn, S. Neutrophil extracellular traps in health and disease. Swiss. Med. Wkly. 2016, 146, w14352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, S.; Kaplan, M.J. The role of neutrophils and NETosis in autoimmune and renal diseases. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naccache, P.H.; Fernandes, M.J. Challenges in the characterization of neutrophil extracellular traps: The truth is in the details. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Buhr, N.; von Kockritz-Blickwede, M. How Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Become Visible. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 4604713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hakkim, A.; Fuchs, T.A.; Martinez, N.E.; Hess, S.; Prinz, H.; Zychlinsky, A.; Waldmann, H. Activation of the Raf-MEK-ERK pathway is required for neutrophil extracellular trap formation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, V.; Goosmann, C.; Kuhn, L.I.; Zychlinsky, A. Automatic quantification of in vitro NET formation. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rebernick, R.; Fahmy, L.; Glover, C.; Bawadekar, M.; Shim, D.; Holmes, C.L.; Rademacher, N.; Potluri, H.; Bartels, C.M.; Shelef, M.A. DNA Area and NETosis Analysis (DANA): A High-Throughput Method to Quantify Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Fluorescent Microscope Images. Biol. Proced. Online 2018, 20, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coelho, L.P.; Pato, C.; Friaes, A.; Neumann, A.; von Kockritz-Blickwede, M.; Ramirez, M.; Carrico, J.A. Automatic determination of NET (neutrophil extracellular traps) coverage in fluorescent microscopy images. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2364–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohanty, T.; Sorensen, O.E.; Nordenfelt, P. NETQUANT: Automated Quantification of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elsherif, L.; Sciaky, N.; Metts, C.A.; Modasshir, M.; Rekleitis, I.; Burris, C.A.; Walker, J.A.; Ramadan, N.; Leisner, T.M.; Holly, S.P.; et al. Machine Learning to Quantitate Neutrophil NETosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.H.; Schaekel, K.; Gaiser, M.R.; Enk, A.H.; Hadaschik, E.N. Interindividual variation of NETosis in healthy donors: Introduction and application of a refined method for extracellular trap quantification. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 25, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, V.; Laube, B.; Abu Abed, U.; Goosmann, C.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps: How to generate and visualize them. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Linden, M.; Westerlaken, G.H.A.; van der Vlist, M.; van Montfrans, J.; Meyaard, L. Differential Signalling and Kinetics of Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Release Revealed by Quantitative Live Imaging. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ginley, B.G.; Emmons, T.; Lutnick, B.; Urban, C.F.; Segal, B.H.; Sarder, P. Computational detection and quantification of human and mouse neutrophil extracellular traps in flow cytometry and confocal microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.; Fogg, D.K.; Kaplan, M.J. A novel image-based quantitative method for the characterization of NETosis. J. Immunol. Methods 2015, 423, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hubel, D.H.; Wiesel, T.N. Receptive fields and functional architecture of monkey striate cortex. J. Physiol. 1968, 195, 215–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, K. Neocognitron: A self organizing neural network model for a mechanism of pattern recognition unaffected by shift in position. Biol. Cybern. 1980, 36, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. GradientBased Learning Applied to Document Recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 25: 26th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2012, 3–6 December, 2012, Lake Tahoe, Nevada, United States; Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation, Inc. (NIPS): La Jolla, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fisch, D.; Yakimovich, A.; Clough, B.; Wright, J.; Bunyan, M.; Howell, M.; Mercer, J.; Frickel, E. Defining host-pathogen interactions employing an artificial intelligence workflow. Elife 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, A.; Lombardi, S.; Signoroni, A. Bacterial colony counting by Convolutional Neural Networks. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2015, 2015, 7458–7461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusumoto, D.; Yuasa, S. The application of convolutional neural network to stem cell biology. Inflamm. Regen. 2019, 39, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 Qctober 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Manda-Handzlik, A.; Bystrzycka, W.; Wachowska, M.; Sieczkowska, S.; Stelmaszczyk-Emmel, A.; Demkow, U.; Ciepiela, O. The influence of agents differentiating HL-60 cells toward granulocyte-like cells on their ability to release neutrophil extracellular traps. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, F.A.; Hsu, P.D.; Wright, J.; Agarwala, V.; Scott, D.A.; Zhang, F. Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2281–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Everingham, M.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.I.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The PASCAL Visual Object Classes (VOC) Challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2010, 88, 303–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2014; Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 8693. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulla, W. Mask R-CNN for Object Detection and Instance Segmentation on Keras and Tensorflow. Available online: https://github.com/matterport/Mask_RCNN (accessed on 19 December 2019).
- Johnson, J.W. Adapting Mask-RCNN for Automatic Nucleus Segmentation Preprint. 2018. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1805.00500.pdf (accessed on 19 December 2019).
- Danielczuk, M.; Matl, M.; Gupta, S.; Li, A.; Lee, A.; Mahler, J.; Goldberg, K. Segmenting Unknown 3D Objects from Real Depth Images Using Mask R-CNN Trained on Synthetic Point Clouds. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1809.05825.pdf (accessed on 19 December 2019).
- Singh, J.; Shekhar, S. Road Damage Detection and Classification in Smartphone Captured Images Using Mask R-CNN. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1811.04535.pdf (accessed on 19 December 2019).
- Zhu, Y.; Aoun, M.; Krijn, M.; Vanschoren, J.; Campus, H.T. Data Augmentation Using Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks for Leaf Counting in Arabidopsis Plants. BMVC 2018 Workshop on Computer Vision Problems in Plant Phenotyping. Available online: http://bmvc2018.org/contents/workshops/cvppp2018/0014.pdf (accessed on 19 December 2019).
- Zhou, G.; Bescos, B.; Dymczyk, M.; Pfeiffer, M.; Neira, J.; Siegwart, R. Dynamic objects Segmentation for Visual Localization in Urban Environments. 2018. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1807.02996.pdf (accessed on 19 December 2019).
- Zimmermann, R.S.; Siems, J.N. Faster Training of Mask R-CNN by Focusing on Instance Boundaries. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1809.07069.pdf (accessed on 19 December 2019).
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. The 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Available online: https://www.cv-foundation.org/openaccess/content_cvpr_2016/papers/He_Deep_Residual_Learning_CVPR_2016_paper.pdf (accessed on 19 December 2019).
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 28 (NIPS 2015), Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1804.02767.pdf (accessed on 19 December 2019).
- Patel, S.; Kumar, S.; Jyoti, A.; Srinag, B.S.; Keshari, R.S.; Saluja, R.; Verma, A.; Mitra, K.; Barthwal, M.K.; Krishnamurthy, H.; et al. Nitric oxide donors release extracellular traps from human neutrophils by augmenting free radical generation. Nitric Oxide 2010, 22, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshari, R.S.; Jyoti, A.; Kumar, S.; Dubey, M.; Verma, A.; Srinag, B.S.; Krishnamurthy, H.; Barthwal, M.K.; Dikshit, M. Neutrophil extracellular traps contain mitochondrial as well as nuclear DNA and exhibit inflammatory potential. Cytometry A 2012, 81, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manda-Handzlik, A.; Bystrzycka, W.; Cieloch, A.; Glodkowska-Mrowka, E.; Jankowska-Steifer, E.; Heropolitanska-Pliszka, E.; Skrobot, A.; Muchowicz, A.; Ciepiela, O.; Wachowska, M.; et al. Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite trigger and enhance release of neutrophil extracellular traps. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, A.C.; Kubes, P. Platelets, neutrophils, and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in sepsis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Hasler, P.; Gebhardt, S.; Holzgreve, W.; Hahn, S. Occurrence of neutrophil extracellular DNA traps (NETs) in pre-eclampsia: A link with elevated levels of cell-free DNA? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1075, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu-Velez, A.M.; Smith, J.G., Jr.; Howard, M.S. Presence of neutrophil extracellular traps and antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies associated with vasculitides. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2009, 1, 309–313. [Google Scholar]
- Logters, T.; Paunel-Gorgulu, A.; Zilkens, C.; Altrichter, J.; Scholz, M.; Thelen, S.; Krauspe, R.; Margraf, S.; Jeri, T.; Windolf, J.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of neutrophil-derived circulating free DNA (cf-DNA/NETs) for septic arthritis. J. Orthopaed. Res. 2009, 27, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnado, A.; Crofford, L.J.; Oates, J.C. At the Bedside: Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) as _targets for biomarkers and therapies in autoimmune diseases. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 99, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicca, I.J.; Milward, M.R.; Chapple, I.L.C.; Griffiths, G.; Benson, R.; Dietrich, T.; Cooper, P.R. Development and Application of High-Content Biological Screening for Modulators of NET Production. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppenbrouwers, T.; Autar, A.S.A.; Sultan, A.R.; Abraham, T.E.; van Cappellen, W.A.; Houtsmuller, A.B.; van Wamel, W.J.B.; van Beusekom, H.M.M.; van Neck, J.W.; de Maat, M.P.M. In vitro induction of NETosis: Comprehensive live imaging comparison and systematic review. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tadie, J.M.; Bae, H.B.; Jiang, S.; Park, D.W.; Bell, C.P.; Yang, H.; Pittet, J.F.; Tracey, K.; Thannickal, V.J.; Abraham, E.; et al. HMGB1 promotes neutrophil extracellular trap formation through interactions with Toll-like receptor 4. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2013, 304, L342–L349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Su, X.; Pan, P.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Tan, H.; Wu, D.; Liu, B.; Li, H.; Li, H.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps are indirectly triggered by lipopolysaccharide and contribute to acute lung injury. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schechter, M.C.; Buac, K.; Adekambi, T.; Cagle, S.; Celli, J.; Ray, S.M.; Mehta, C.C.; Rada, B.; Rengarajan, J. Neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) levels in human plasma are associated with active TB. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gavillet, M.; Martinod, K.; Renella, R.; Harris, C.; Shapiro, N.I.; Wagner, D.D.; Williams, D.A. Flow cytometric assay for direct quantification of neutrophil extracellular traps in blood samples. Am. J. Hematol. 2015, 90, 1155–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Subset | Images | Cell Type | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unstimulated | Decondensed | NET | Dead | |||
| Split | Total | 305 | 3017 | 638 | 1919 | 581 |
| Train | 188 | 1918 | 492 | 1241 | 193 | |
| Val | 60 | 701 | 69 | 374 | 182 | |
| Test | 57 | 398 | 77 | 304 | 206 | |
| Metric | Area | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small | Medium | Large | All | |
| AP @ IoU = 0.50:0.95 (MS CoCo) | 0.380 | 0.593 | 0.213 | 0.593 |
| AP @ IoU = 0.50 (Pascal VOC) | 0.580 | 0.930 | 0.305 | 0.906 |
| AP @ IoU = 0.10 | 0.619 | 0.930 | 0.316 | 0.913 |
| AR @ IoU 0.50:0.95 | 0.467 | 0.673 | 0.235 | 0.666 |
| AR @ IoU = 0.50 | 0.625 | 0.946 | 0.317 | 0.925 |
| AR @ IoU = 0.10 | 0.656 | 0.947 | 0.325 | 0.931 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manda-Handzlik, A.; Fiok, K.; Cieloch, A.; Heropolitanska-Pliszka, E.; Demkow, U. Convolutional Neural Networks–Based Image Analysis for the Detection and Quantification of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Cells 2020, 9, 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020508
Manda-Handzlik A, Fiok K, Cieloch A, Heropolitanska-Pliszka E, Demkow U. Convolutional Neural Networks–Based Image Analysis for the Detection and Quantification of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Cells. 2020; 9(2):508. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020508
Chicago/Turabian StyleManda-Handzlik, Aneta, Krzysztof Fiok, Adrianna Cieloch, Edyta Heropolitanska-Pliszka, and Urszula Demkow. 2020. "Convolutional Neural Networks–Based Image Analysis for the Detection and Quantification of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps" Cells 9, no. 2: 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020508
APA StyleManda-Handzlik, A., Fiok, K., Cieloch, A., Heropolitanska-Pliszka, E., & Demkow, U. (2020). Convolutional Neural Networks–Based Image Analysis for the Detection and Quantification of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Cells, 9(2), 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020508