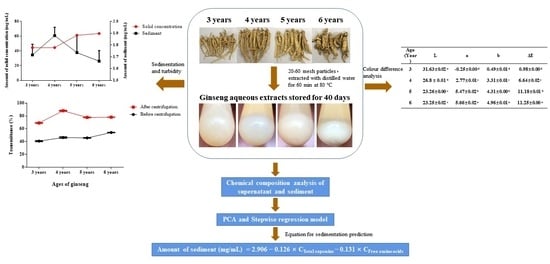
Analysis of Key Chemical Components in Aqueous Extract Sediments of Panax Ginseng at Different Ages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Ginseng Extracts
2.3. Sediment Formation Observations
2.4. Preparation of Sediment and Determination of Solids
2.5. Measurement of Clarity
2.6. Chromatic Aberration Analysis
2.7. Chemical Composition Analysis
2.7.1. Free Amino Acid and Protein Analysis
2.7.2. Total Sugar Analysis
2.7.3. Total Saponin Analysis
2.7.4. Mineral Analysis
2.7.5. Analysis of Individual Ginsenosides
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sediment Formation of Ginseng Extract at Different Ages
3.2. Analysis of the Chemical Composition
3.3. Colour Difference Analysis
3.4. Analysis of Key Chemical Components
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Byong-Kyu, S.; Sung, W.K.; Jeong, H.P. Chemical diversity of ginseng saponins from Panax ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2015, 39, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, S.; Xu, X.; Lu, Z. Effect of azoxystrobin fungicide on the physiological and biochemical indices and ginsenoside contents of ginseng leaves. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, T.; Qiu, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, D. Inhibitory effects of Panax ginseng glycoproteins in models of doxorubicin-induced cardiac toxicity in vivo and in vitro. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 10862–10874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.C.; Lee, H.Y.; Cho, D.Y.; Jung, J.G.; Kang, D.; Kang, S.S.; Cho, K.M. Changes in nutritional compositions of processed mountain-cultivated ginseng sprouts (Panax ginseng) and screening for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 86, 104668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ren, H.; Li, K.; Xie, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, L.; Xia, J.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Wang, J. Therapeutic effect of various ginsenosides on rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Dai, X.; Zhu, R.; Chen, B.; Xia, B.; Ye, Z.; Zhao, D.; Gao, S.; Orekhov, A.N.; et al. A comprehensive review on the phytochemistry, pharmacokinetics, and antidiabetic effect of Ginseng. Phytomedicine 2021, 92, 153717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, J.-F.; Tang, F.; Chen, L.; Tan, Y.-Z.; Rao, C.-L.; Ao, H.; Peng, C. Panax ginseng and its ginsenosides: Potential candidates for the prevention and treatment of chemotherapy-induced side effects. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, K.; Wang, Y.; Hua, H.; Qin, S.; Yang, A.; Shao, J. Ginsenoside Rg3 combined with oxaliplatin inhibits the proliferation and promotes apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via downregulating PCNA and cyclin D1. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 42, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Wang, Y.-S.; Zhang, E.-T.; Li, G.-A.; Liu, W.-Y.; Li, Y.; Jin, Y.-H. (20S) ginsenoside Rh2 exerts its anti-tumor effect by disrupting the HSP90A-Cdc37 system in human liver cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yan, X.; Sun, G.; Jia, G.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Su, H.; Li, Y. Application of lipidomics strategy to explore aging-related biomarkers and potential anti-aging mechanisms of ginseng. Biogerontology 2021, 22, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Xia, H.; Guo, Y.; Qian, X.; Zou, X.; Yang, H.; Yin, M.; Liu, H. Ginsenoside Rb1 retards aging process by regulating cell cycle, apoptotic pathway and metabolism of aging mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 255, 112746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, C. Recent advances in panax ginseng C.A. Meyer as a herb for anti-fatigue: An effects and mechanisms review. Foods 2021, 10, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, I.-S.; Kim, D.-H.; Jang, E.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Yoo, H.-S. Anti-fatigue properties of cultivated wild ginseng distilled extract and its active component panaxydol in rats. J. Pharmacopunct. 2019, 22, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, C.; Pu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Bao, Y. Structure characteristics and immunomodulatory activities of a polysaccharide RGRP-1b from radix ginseng Rubra. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 189, 980–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, M.; Liu, Z.; Sha, J.; Li, S.; Dong, L.; Sun, Y. Effects of ginseng soluble dietary fiber on serum antioxidant status, immune factor levels and cecal health in healthy rats. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Ding, L.; Li, J.; Qu, C.-L.; Chen, L.-G.; Jin, H.-Y.; Zhang, H.-Q. Determination of Seven Major Ginsenosides in Different Parts of Panax quinquefolius L. (American Ginseng) with Different Ages. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2008, 24, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, J.-Y.; Xiao, X.-Y.; Lin, R.-C.; Cheng, Y.-Y. Simultaneous determination of ginsenosides in Panax ginseng with different growth ages using high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Phytochem. Anal. 2006, 17, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.G.S.; Rebellato, A.P.; Caramês, E.T.D.S.; Greiner, R.; Pallone, J.A.L. In vitro digestion effect on mineral bioaccessibility and antioxidant bioactive compounds of plant-based beverages. Food Res. Int. 2019, 130, 108993. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0963996920300181?via%3Dihub (accessed on 10 January 2020). [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.E.; Mousavi, M.; Kiani, H. Characterization and identification of sediment forming agents in barberry juice. Food Chem. 2019, 312, 126056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Xu, Y.-J.; Wu, J.-J.; Yu, Y.-S.; Xiao, G.-S. Phenolic compounds participating in mulberry juice sediment formation during storage. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2017, 18, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jasentuliyana, N.; Toma, R.B.; Klavons, J.A.; Medora, N. Beverage cloud stability with isolated soy protein. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1998, 78, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Ding, L. Investigation of ginsenosides in different parts and ages of Panax ginseng. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Kim, K.; Choi, B.Y.; Lee, D.; Shin, Y.S.; Bang, K.H.; Cha, S.W.; Lee, J.W.; Choi, H.K.; Jang, D.S.; et al. Metabolomic approach for age discrimination of Panax ginseng using UPLC-Q-Tof MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 10435–10441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Song, W.; Hou, Z.; Wang, Z. Classification of ginseng according to plant species, geographical origin, and age using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and hyperspectral imaging. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2021, 36, 1704–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LiXue, C.; Di, Q.; Mei, H.; Kun, G.; YinShi, S. A comparative study of effective components in ginseng samples from different parts and ages. Food Sci. 2019, 40, 124–129. Available online: http://www.spkx.net.cn (accessed on 30 January 2019). [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.-L.; Qiao, M.-D.; Yu, P.; Zheng, F.; Yue, H.; Liu, S.-Y. Comparing eight types of ginsenosides in ginseng of different plant ages and regions using RRLC-Q-TOF MS/MS. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 44, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Hua, M.; Chen, J.-B.; Li, S.-S.; Wen, L.-K.; Sun, Y.-S. Formation and characterization of irreversible sediment of ginseng extract. Foods 2021, 10, 2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Huo, X.-H.; Li, Z.-M.; Hua, M.; Lu, Y.-S.; Chen, J.-B.; Li, S.-S.; Wen, L.-K.; Sun, Y.-S. Sediment formation and analysis of the main chemical components of aqueous extracts from different parts of ginseng roots. Food Chem. 2022, 379, 132146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagalakshmi, S.; Ramaswamy, M.; Natarajan, C.; Seshadri, R. The rôle of added carbohydrates in tea ‘cream’ solubilisation. Food Chem. 1984, 13, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, K. Haze formation in beverages. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 39, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Li, K.; Li, J.; Shang, Y.; Cui, F.; Hou, C.; Wang, Q.; Hang, F.; Li, W.; Shi, C.; et al. Understanding the pathways for irreversible aggregate clusters formation in concentrated sugarcane juice derived from the membrane clarification process. LWT 2021, 151, 112204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaClair, C.E.; Etzel, M.R. Ingredients and pH are Key to Clear Beverages that Contain Whey Protein. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, C21–C27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaClair, C.E.; Etzel, M.R. Turbidity and Protein Aggregation in Whey Protein Beverages. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, C526–C535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stounbjerg, L.; Vestergaard, C.; Andreasen, B.; Ipsen, R. Beverage clouding agents: Review of principles and current manufacturing. Food Rev. Int. 2018, 34, 613–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeb, B.; Mi-Yeon, L.; Gibis, M.; Weiss, J. Growth phenomena in biopolymer complexes composed of heated WPI and pectin. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 74, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.F.; Nasirpour, A.G.; Sayed Amir, H.; Riahi, E. Effect of heat treatment and solution preparation procedure on colloidal stability of whey protein sour cherry beverage. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2018, 71, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santipanichwong, R.; Suphantharika, M.; Weiss, J.; McClements, D.J. Core-shell biopolymer nanoparticles produced by electrostatic deposition of beet pectin onto heat-denatured β-lactoglobulin aggregates. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, N23–N30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fei, S.; Wang, Y.; Zan, L.; Zhu, J. Comparative study on the self-assembly of pectin and alginate molecules regulated by calcium ions investigated by atomic force microscopy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 231, 115673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ürüncüoğlu, Ş.; Alba, K.; Morris, G.A.; Kontogiorgos, V. Influence of cations, pH and dispersed phases on pectin emulsification properties. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2019, 4, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Zhao, S.; Lian, Y.; Yang, Y.; Tian, G.; Zhao, C.; Gao, W.; Zheng, J. Effects of hydrosoluble calcium ions and organic acids on citrus oil emulsions stabilized with citrus pectin. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 100, 105413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paduret, S.; Norocel, L. Physico-chemical and sensorial properties of a new beverages obtained from wild mountain cranberry (Vacciniumvitis-idaea). Rev. Chim. 2020, 71, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakauma, M.; Funami, T.; Fang, Y.; Nishinari, K.; Draget, K.I.; Phillips, G.O. Calcium binding and calcium-induced gelation of normal low-methoxyl pectin modified by low molecular-weight polyuronate fraction. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 69, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abramova, I.M.; Medrish, M.E.; Savelieva, V.B.; Romanova, A.G.; Gavrilova, D.A.; Zhirova, V.V. The ionic composition of distilled beverages and its effect on their stability during storage. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 640, 062026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafoor, K.; Kim, S.O.; Lee, D.U.; Seong, K.; Park, J. Effects of high hydrostatic pressure on structure and colour of red ginseng (Panax ginseng). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 2975–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Piao, X.; Zheng, P.; Zhang, H.; Pang, S.; Qu, Z.; Wang, Y. Changes of 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furfural in fresh and processed ginsengs. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 2068–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Chemical Components (mg/mL) | Supernatant | Sediment | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 Years | 4 Years | 5 Years | 6 Years | 3 Years | 4 Years | 5 Years | 6 Years | |
| Free amino acid | 4.88 ± 0.17 b | 3.93 ± 0.10 a | 4.54 ± 0.16 b | 4.12 ± 0.34 a | 0.24 ± 0.01 b | 0.23 ± 0.03 b | 0.21 ± 0.01 ab | 0.19 ± 0.01 a |
| Protein | 3.30 ± 0.48 a | 3.14 ± 0.41 a | 3.61 ± 0.25 a | 3.37 ± 0.14 a | 0.82 ± 0.03 b | 0.81 ± 0.01 b | 0.61 ± 0.11 a | 0.51 ± 0.09 a |
| Total sugar | 32.47 ± 4.95 a | 29.16 ± 2.83 a | 53.13 ± 1.78 b | 54.51 ± 3.31 b | 2.18 ± 0.06 b | 1.95 ± 0.11 a | 2.18 ± 0.21 ab | 2.26 ± 0.05 b |
| Total saponins | 4.25 ± 0.10 a | 4.043 ± 0.14 a | 4.783 ± 0.55 ab | 5.542 ± 0.66 b | 1.04 ± 0.33 b | 0.121 ± 0.11 a | 0 a | 0.05 ± 0.08 a |
| Rg1 | 0.16 ± 0.00 a | 0.31 ± 0.00 c | 0.29 ± 0.00 b | 0.33 ± 0.01 d | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a |
| Re | 0.28 ± 0.00 c | 0.31 ± 0.00 d | 0.19 ± 0.00 a | 0.23 ± 0.00 b | 0.03 ± 0.00 c | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a |
| Rf | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 0.10 ± 0.00 d | 0.07 ± 0.00 b | 0.09 ± 0.01 c | 0 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 0 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 b |
| Rb1 | 0.23 ± 0.01 a | 0.47 ± 0.01 c | 0.36 ± 0.00 b | 0.51 ± 0.01 d | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.01 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 b |
| Rc | 0.12 ± 0.03 a | 0.21 ± 0.02 bc | 0.18 ± 0.02 b | 0.23 ± 0.01 c | 0.03 ± 0.00 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a |
| Rb2 | 0.13 ± 0.01 a | 0.27 ± 0.01 d | 0.15 ± 0.00 b | 0.19 ± 0.00 c | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a |
| Rb3 | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 c | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0 a | 0 a | 0 a | 0 a |
| Rd | 0.13 ± 0.02 c | 0.31 ± 0.01 d | 0.07 ± 0.00 a | 0.12 ± 0.00 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.03 ± 0.00 c | 0 a | 0 a |
| Total ginsenoside | 1.10 ± 0.04 a | 2.01 ± 0.03 d | 1.33 ± 0.04 b | 1.71 ± 0.04 c | 0.12 ± 0.01 b | 0.13 ± 0.02 b | 0.07 ± 0.01 a | 0.08 ± 0.00 a |
| Mineral Elements (μg/mL) | Supernatant | Sediment | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 Years | 4 Years | 5 Years | 6 Years | 3 Years | 4 Years | 5 Years | 6 Years | |
| Al | 0.92 ± 0.23 a | 1.00 ± 0.24 a | 0.76 ± 0.10 a | 1.23 ± 0.22 a | 0.72 ± 0.23 a | 0.91 ± 0.27 a | 0.95 ± 0.20 a | 0.70 ± 0.11 a |
| Ba | 0.23 ± 0.08 a | 0.16 ± 0.01 a | 0.20 ± 0.01 a | 0.15 ± 0.01 a | 0.14 ± 0.03 b | 0.03 ± 0.03 a | 0.04 ± 0.01 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a |
| Ca | 49.60 ± 6.53 b | 35.78 ± 0.75 a | 43.49 ± 1.74 ab | 42.13 ± 1.04 ab | 28.98 ± 8.70 b | 12.68 ± 1.62 a | 11.14 ± 2.95 a | 11.04 ± 0.70 a |
| Cu | 0.43 ± 0.06 b | 0.12 ± 0.01 a | 0.44 ± 0.08 b | 0.40 ± 0.07 b | 0.41 ± 0.04 b | 0.06 ± 0.02 a | 0.06 ± 0.01 a | 0.08 ± 0.05 a |
| Fe | 0.93 ± 0.31 a | 1.24 ± 0.11 a | 1.02 ± 0.13 a | 1.33 ± 0.15 a | 0.48 ± 0.11 c | 0.27 ± 0.15 bc | 0.228 ± 0.060 a | 0.22 ± 0.02 a |
| Mg | 106.67 ± 4.96 b | 80.50 ± 0.75 a | 76.34 ± 0.57 a | 78.22 ± 1.61 a | 49.30 ± 7.92 b | 6.02 ± 1.50 a | 4.15 ± 1.08 a | 4.43 ± 0.22 a |
| Mn | 1.72 ± 0.22 ab | 2.43 ± 0.03 b | 2.70 ± 0.03 b | 3.88 ± 0.04 c | 1.42 ± 0.38 b | 0.06 ± 0.04 a | 0.15 ± 0.03 a | 0.22 ± 0.02 a |
| Na | 25.88 ± 1.84 c | 16.17 ± 0.25 a | 18.36 ± 0.57 ab | 19.98 ± 1.76 b | 19.88 ± 1.33 b | 14.17 ± 3.15 a | 10.90 ± 0.93 a | 9.82 ± 1.03 a |
| Ni | 0.07 ± 0.01 b | 0.03 ± 0.01 a | 0.09 ± 0.01 bc | 0.11 ± 0.02 c | 0.01 ± 0.02 a | 0.02 ± 0.01 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.01 a |
| Sr | 0.37 ± 0.06 c | 0.26 ± 0.00 a | 0.30 ± 0.00 bc | 0.27 ± 0.01 b | 0.17 ± 0.06 b | 0.06 ± 0.01 a | 0.05 ± 0.01 a | 0.05 ± 0.01 a |
| Zn | 1.32 ± 0.19 b | 0.72 ± 0.04 a | 0.67 ± 0.03 a | 0.86 ± 0.12 a | 0.45 ± 0.27 b | 0.05 ± 0.03 a | 0.04 ± 0.022 a | 0.06 ± 0.02 a |
| K | 556.14 ± 12.16 b | 505.22 ± 1.62 b | 470.83 ± 14.70 b | 466.86 ± 25.94 a | 60.67 ± 3.12 b | 54.21 ± 7.48 a | 30.40 ± 7.31 a | 32.34 ± 3.37 a |
| Total | 744.28 ± 26.65 c | 643.61 ± 3.81 b | 615.19 ± 17.96 a | 615.40 ± 30.99 a | 162.63 ± 22.19 c | 88.54 ± 14.29 b | 58.08 ± 12.61 a | 58.99 ± 5.55 a |
| Age (Year) | L | a | b | ΔE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 31.63 ± 0.02 c | −0.25 ± 0.00 a | 0.49 ± 0.01 a | 0.98 ± 0.00 a |
| 4 | 26.8 ± 0.01 b | 2.77 ± 0.01 b | 3.31 ± 0.01 b | 6.64 ± 0.02 b |
| 5 | 23.26 ± 0.00 a | 5.47 ± 0.02 c | 4.31 ± 0.00 c | 11.18 ± 0.01 c |
| 6 | 23.25 ± 0.02 a | 5.66 ± 0.02 d | 4.96 ± 0.01 d | 11.25 ± 0.00 d |
| Chemical Components | Component | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Free amino acid | 0.912 | 0.131 | −0.069 | −0.007 |
| Protein | 0.465 | 0.230 | −0.119 | −0.019 |
| Total sugar | −0.107 | 0.980 | −0.007 | −0.034 |
| Total saponins | −0.122 | 0.834 | 0.235 | 0.392 |
| Rg1 | −0.937 | 0.334 | 0.024 | −0.080 |
| Re | −0.057 | −0.924 | 0.327 | 0.176 |
| Rf | −0.973 | −0.015 | 0.113 | −0.007 |
| Rb1 | −0.931 | 0.236 | 0.242 | 0.078 |
| Rc | −0.853 | 0.322 | 0.264 | −0.128 |
| Rb2 | −0.853 | −0.459 | 0.217 | −0.034 |
| Rb3 | −0.901 | −0.306 | 0.255 | −0.025 |
| Rd | −0.550 | −0.804 | 0.183 | 0.028 |
| Total ginsenoside | −0.938 | −0.229 | 0.249 | 0.016 |
| Al | −0.169 | 0.167 | 0.765 | 0.332 |
| Ba | 0.661 | −0.044 | 0.360 | −0.605 |
| Ca | 0.842 | 0.261 | 0.379 | −0.243 |
| Cu | 0.632 | 0.623 | −0.162 | 0.093 |
| Fe | −0.485 | 0.164 | 0.711 | −0.271 |
| Mg | 0.841 | −0.424 | 0.296 | 0.091 |
| Mn | 0.132 | 0.570 | 0.759 | 0.035 |
| Na | 0.884 | 0.013 | 0.280 | 0.298 |
| Ni | 0.234 | 0.906 | 0.097 | 0.085 |
| Sr | 0.852 | −0.015 | 0.389 | −0.316 |
| Zn | 0.799 | −0.189 | 0.502 | 0.163 |
| K | 0.609 | −0.679 | 0.093 | 0.073 |
| Total minerals | 0.792 | −0.561 | 0.136 | 0.166 |
| Cumulative variance (%) | 49.82 | 74.84 | 86.78 | 91.00 |
| Model | R | R2 | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | Sig | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | SE | β | ||||||
| 1 | 0.754 | 0.568 | (constant) | 2.352 | 0.169 | 13.985 | 0.000 | |
| Total saponins | −0.13 | 0.36 | −754 | −3.628 | 0.005 | |||
| 2 | 0.882 | 0.777 | (constant) | 2.906 | 0.229 | 12.686 | 0.000 | |
| Total saponins | −0.126 | 0.027 | −0.731 | −4.643 | 0.001 | |||
| Free amino acid | −0.131 | 0.045 | −0.458 | −2.908 | 0.017 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, D.; Bo, P.; Wen, L.; Sun, Y. Analysis of Key Chemical Components in Aqueous Extract Sediments of Panax Ginseng at Different Ages. Foods 2022, 11, 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11081161
Qu D, Bo P, Wen L, Sun Y. Analysis of Key Chemical Components in Aqueous Extract Sediments of Panax Ginseng at Different Ages. Foods. 2022; 11(8):1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11081161
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Di, Panpan Bo, Liankui Wen, and Yinshi Sun. 2022. "Analysis of Key Chemical Components in Aqueous Extract Sediments of Panax Ginseng at Different Ages" Foods 11, no. 8: 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11081161
APA StyleQu, D., Bo, P., Wen, L., & Sun, Y. (2022). Analysis of Key Chemical Components in Aqueous Extract Sediments of Panax Ginseng at Different Ages. Foods, 11(8), 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11081161