Surface Water Impacted by Rural Activities Induces Genetic Toxicity Related to Recombinagenic Events in Vivo
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
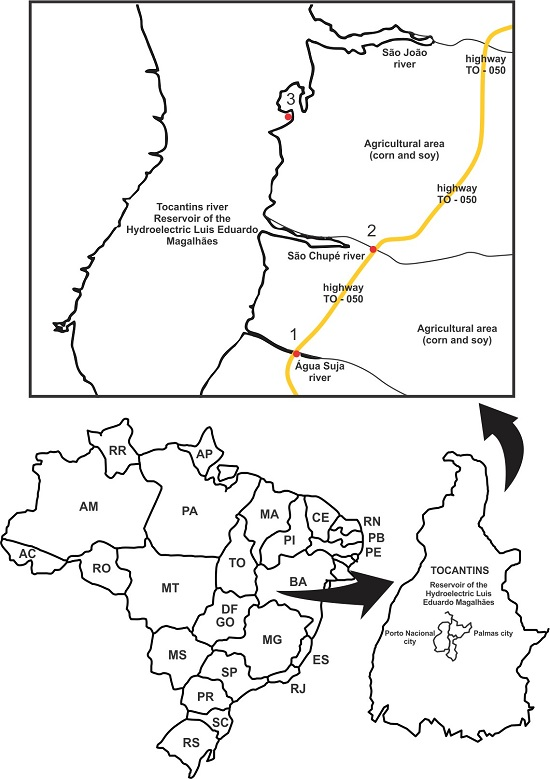
2.1. Collection Sites and Physical-Chemical Analysis in Situ
2.2. Quantification of Inorganic Chemicals
2.3. Somatic Mutation and Recombination Test (SMART)
2.3.1. Wing Spot Analysis
2.3.2. Statistical Evaluation
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Georgellis, A.; Kolmodin-Hedman, B.; Kourestas, D. Can traditional epidemiology detect cancer risk caused by occupation exposure to pesticides? J. Exp. Clin. Cancer 1999, 18, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Purdue, M.P.; Hoppin, J.A.; Blair, A.; Dosemeci, M.; Alavanja, M.C. Occupational exposure to organochlorine insecticides and cancer incidence in the agricultural health study. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khuder, S.A.; Mutgi, A.B. Meta-analyses of multiple myeloma and farming. Am. J. Ind. Med. 1997, 32, 510–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourad, T.A. Adverse impact of insecticides on the health of Palestinian farm workers in the Gaza Strip: A hematologic biomarker study. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2005, 11, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adad, L.M.M.; de Andrade, H.H.R.; Kvitko, K.; Lehmann, M.; Cavalcante, A.A.C.M.; Dihl, R.R. Occupational exposure of workers to pesticides: Toxicogenetics and susceptibility gene polymorphisms. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2015, 38, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaham, J.; Kaufman, Z.; Gurvich, R.; Levi, Z. Frequency of sister-chromatid exchange among greenhouse farmers exposed to pesticides. Mutat. Res. 2001, 491, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendetti, D.; Alves, J.; Silva, F.R.D.; Silva, J.D. An evaluation of occupational exposures to pesticides in Brazil. Occup. Med. Health Aff. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, C. Genotoxicity of pesticides: A review of human biomonitoring studies. Mutat. Res. 2003, 543, 251–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). The WHO Recommended Classification of Pesticides and Guidelines to Classification; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009; p. 81. [Google Scholar]
- White, P.A.; Rasmussen, J.B. The genotoxic hazards of domestic wastes in surface waters. Mutat. Res. 1998, 410, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacociunas, L.V.; Dihl, R.R.; Lehmann, M.; Reguly, M.L.; de Andrade, H.H.R. Recombinagenic activity of water and sediment from Sinos River and Araçá and Garças Streams Canoas, Brazil, in the Drosophila wing spot test. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares Neto, J.L. Variações Espaço-Temporais da Ictiofauna a Montante e a Jusante da Usina Hidroelétrica do Lajeado. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal do Tocantins, Palmas, Brazil, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Graf, U.; Wurgler, F.E.; Katz, A.J.; Frei, H.; Juon, H.; Hall, C.B.; Kale, P.G. Somatic mutation and recombination test in Drosophila melanogaster. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 1984, 6, 153–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bier, E. Drosophila, the golden bug, emerges as a tool for human genetics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benford, D.J.; Hanley, A.B.; Bottrill, K.; Oehlschlager, S.; Balls, M.; Brance, F.; Castegnara, J.J.; Descotes, J.; Hemminiky, K.; Lindsay, D.; et al. Biomarkers as predictive tools in toxicity testing. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2000, 28, 119–131. [Google Scholar]
- Vargas, V.M.F.; Motta, V.E.P.; Henriques, J.A.P. Mutagenic activity detected by the Ames test in river water under the influence of petrochemical industries. Mutat. Res. 1993, 319, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, S.A.E.; Campbel, J.L.; Malmqvist, K.G. Particle Induced X-ray Emission Spectrometry (PIXE), 4th ed.; John Willey & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Santos, C.E.I.; Da Silva, L.R.M.; Boufleur, L.A.; Debastiani, R.; Stefenon, C.A.; Amaral, L. Elemental characterisation of Cabernet Sauvignon wines using Particle-Induced X-ray Emission (PIXE). Food Chem. 2010, 121, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.L.; Hopman, T.L.; Maxwell, J.A.; Nejedly, Z. The Guelph PIXE software package III: Alternative proton database. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 2000, 170, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, H.H.R.; Reguly, M.L.; Lehmann, M. Wing Somatic Mutation and Recombination Test SMART. In Drosophila Cytogenetics Protocols; Henderson, D.S., Ed.; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 389–412. [Google Scholar]
- Frölich, A.; Würgler, F.E. New tester strains with improved bioactivation capacity for the Drosophila wing-spot test. Mutat. Res. 1989, 216, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, U.; van Schaik, N. Improved high bioactivation cross for the wing somatic mutation and recombination test in Drosophila melanogaster. Mutat. Res. 1992, 271, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastenbaum, M.A.; Bowman, K.O. Tables for determining the statistical significance of mutation frequencies. Mutat. Res. 1970, 9, 527–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dihl, R.R.; Bereta, M.S.; do Amaral, V.S.; Lehmann, M.; Reguly, M.L.; de Andrade, H.H.R. Nitropolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are inducers of mitotic homologous recombination in the wing-spot test of Drosophila melanogaster. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 2344–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomé, S.; Bizarro, C.R.; Lehmann, M.; De Abreu, B.R.; De Andrade, H.H.R.; Cunha, K.S.; Dihl, R.R. Recombinagenic and mutagenic activities of fluoroquinolones in Drosophila melanogaster. Mutat. Res. 2012, 742, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, R.A.; Dihl, R.R.; Nascimento e Santos, D.; De Abreu, B.R.; De Lima, A.; De Andrade, H.H.; Lehmann, M. Evaluation of antioxidant and mutagenic activities of honey-sweetened cashew apple nectar. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frei, H.; Würgler, E. Statistical methods to decide whether mutagenicity test data from Drosophila assays indicate positive, negative or inconclusive. Mutat. Res. 1988, 203, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, H.; Würgler, E. Induction of somatic mutation and recombination by four inhibitors of eukaryotic topoisomerases assayed in the wing spot test of Drosophila melanogaster. Mutagenesis 1996, 11, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohe, T.; Watanabe, T.; Wakabayashi, K. Mutagens in surface water: A review. Mutat. Res. 2004, 567, 109–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, H.; Hayatsu, T.; Hietsch, G.; Steinkellner, H.; Nishioka, S.; Narimatsu, S.; Knasmüller, S.; Hayatsu, H. Identification of mutagenic heterocyclic amines IQ, Trp-P-1 and AC in the water of the Danube River. Mutat. Res. 2006, 466, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, Y.; Somiya, I.; Oda, S. Identification of a carcinogenic heterocyclic amine in river water. Water Res. 2000, 34, 890–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Nukaya, H.; Terao, Y.; Hirayma, T.; Wakabayashi, K. Seasonal fluctuation of the mutagenicity of river water in Funkui, Japan, and the contribution of 2-phenylbenzotriazole-type mutagens. Mutat. Res. 2002, 519, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabias-Martinez, R.; Rodríguez-Gonzalo, E.; Fernández-Laespada, M.E.; Calvo-Seronero, L.; Sánchez-San Román, F.J. Evolution over time of the agricultural pollution of waters in an area of Salamanca and Zamora Spain. Water Pollut. 2003, 37, 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, T.; Yamano, S.; Waxman, D.J.; Lapenson, D.P.; Meyer, V.A.; Fisher, V.; Tyndale, R.R.; Inaba, T.; Kalow, W.; Gelbion, H.V.; et al. Cytochrome P450 hPCN3, a novel cytochrome P450 IIIA gene product that is differentially expressed in adult human liver. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 10388–10395. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amaral, V.S.; Sinigaglia, M.; Reguly, M.L.; Andrade, H.H.R. Genetic toxicity in surface water from Guaíba Hydrographic Region under the influence of industrial, urban and agricultural sewage in the Drosophila Wing-Spot Test. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 139, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.P. Cellular defenses against damage from reactive oxygen species. Physiol. Rev. 1994, 74, 139–162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beyersmann, D.; Hartwig, A. Carcinogenic metal compounds: Recent insight into molecular and cellular mechanisms. Arch. Toxicol. 2008, 82, 493–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, M.; Chen, F.; Shi, X.; Yucesoy, B.; Mossman, B.; Vallyathan, V. Diseases caused by silica: Mechanisms of injury and disease development. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2002, 2, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulini, B.; Hubbard, A. Reactive oxygen species ROS and reactive nitrogen species RNS generation by silica in inflammation and fibrosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, B.D.; Seth, V.; Ahmed, R.S. Pesticide-induced oxidative stress: Perspectives and trends. Rev. Environ. Health 2001, 16, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdollahi, M.; Ranjbar, A.; Shadnia, S.; Nikfar, S.; Rezaie, A. Pesticides and oxidative stress: A review. Med. Sci. Monit. 2004, 10, RA141–RA147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Villarini, M.; Moretti, M.; Pasquini, R.; Scassellati-Sforzolini, G.; Fatigoni, C.; Marcarelli, M.; Monarca, S.; Rodriguez, A.V. In vitro genotoxic effects of the insecticide deltamethrin in human peripheral blood leukocytes: DNA damage “comet” assay in relation to the induction of sister-chromatid exchanges and micronuclei. Toxicology 1998, 130, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlastos, D.; Stivaktakis, P.; Matthopoulos, D. Pesticide exposure and genotoxicity correlations within a Greek farmers’ group. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2006, 86, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, J.; Cabral-de-Mello, D.C.; Marin-Morales, M.A. Toxicogenetic effects of low concentrations of the pesticides imida-cloprid and sulfentrazone individually and in combination in in vitro tests with Hep G2 cells and Salmonella typhimurium. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 120, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahden-Staron, I.; Czeczot, H.; Szumilo, M. Induction of rat liver cytochrome P450 isoenzymes CYP 1A and CYP 2B by different fungicides, nitrofurans, and quercetin. Mutat. Res. 2001, 498, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roustan, A.; Aye, M.; De Meo, M.; Di Giorgio, C. Genotoxicity of mixtures of glyphosate and atrazine and their environmental transformation products before and after photoactivation. Chemosphere 2014, 108, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrelia, P.; Maffei, F.; Fimognari, C.; Vigagni, F.; Cantelli-Forti, G. Cytogenetic effects of Metalaxyl on human and animal chromosomes. Mutat. Res. 1996, 369, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Thai, S.F.; Tully, D.B.; Lambert, G.R.; Goetz, A.K.; Wolf, D.C.; Dix, D.J.; Nesnow, S. Propiconazole-induced cytochrome P450 gene expression and enzymatic activities in rat and mouse liver. Toxicol. Lett. 2005, 155, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delescluse, C.; Ledirac, N.; De Sousa, G.; Pralavorio, M.; Lesca, P.; Rahmani, R. Cytotoxic effects and induction of cytochromes P450 1A1/2 by insecticides, in hepatic or epidermal cells: Binding capability to the Ah receptor. Toxicol. Lett. 1998, 96–97, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisari, M.; Long, M.; Tabbo, A.; Bonefeld-Jørgensen, E.C. Effects of currently used pesticides and their mixtures on the function of thyroid hormone and aryl hydrocarbon receptor in cell culture. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 284, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetti, D.; Nunes, E.; Sarmento, M.; Porto, C.; Santos, C.E.; Dias, J.F.; da Silva, J. Genetic damage in soybean workers exposed to pesticides: Evaluation with the comet and buccal micronucleus cytome assays. Mutat. Res. 2013, 752, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, A.J.; Schiestl, R.H. Role of homologous recombination in carcinogenesis. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2003, 74, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kok, T.M.C.M.; Driece, H.A.L.; Hogervorst, J.G.F.; Briedé, J.J. Toxicological assessment of ambient and traffic-related particulate matter: A review of recent studies. Mutat. Res. 2006, 613, 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Site | Anthropic Influence | Coordinates |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Soy and maize plantations | 10°26′18′′ 48°22′35′′ |
| 2 | Soy and maize plantations | 10°29′45′′ 48°21′05′′ |
| 3 | Fruit orchards | 10°32′02′′ 48°22′37′′ |
| Elements | Rainy Season | Dry Season | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collection Sites | Collection Sites | |||||
| Site 1 | Site 2 | Site 3 | Site 1 | Site 2 | Site 3 | |
| Mg | 330 ± 25 | 136± 45 | 265 ± 28 | 215 ± 26 | 104 ± 48 | 106 ± 46 |
| Al | 12,639 ± 4 | 9511 ± 4 | 4404 ± 6 | 8381 ± 3 | 4385 ± 4 | 2554 ± 5 |
| Si | 135,647 ± 2 | 91,237 ± 2 | 137,609 ± 2 | 41,295 ± 2 | 34,218 ± 2 | 40,605 ± 2 |
| P | 334 ± 43 | 98 ± 117 | ND | ND | 61 ± 133 | ND |
| S | 203 ± 24 | 141 ± 24 | 19 ± 39 | 224 ± 31 | 105 ± 61 | 98 ± 65 |
| Cl | ND | 49 ± 35 | 135 ± 29 | 430 ± 17 | 307 ± 22 | 315 ± 21 |
| K | 560 ± 18 | 250 ± 28 | 479 ± 20 | 389 ± 14 | 206 ± 21 | 156 ± 26 |
| Ca | 1160 ± 6 | 1270 ± 6 | 6286 ± 4 | 2230 ± 4 | 2026 ± 4 | 2090 ± 4 |
| Ti | 1784 ± 5 | 1136 ± 6 | 393 ± 9 | 1298 ± 4 | 1359 ± 4 | 189 ± 10 |
| Mn | ND | 745 ± 4 | 215 ± 10 | ND | 88 ± 13 | 65 ± 15 |
| Fe | 26,175 ± 1 | 34,109 ± 1 | 8400 ± 1 | 16,150 ± 1 | 8952 ± 1 | 5854 ± 1 |
| Zn | 41 ± 33 | 16 ± 65 | 16 ± 53 | 35 ± 25 | 30 ± 26 | 14 ± 45 |
| Seasons and Genotypes | Sites of Collection and Controls | No. of Flies (N) | Spots per Fly (No. of Spots)/Statistical Diagnosis a | Total Mwh Clones c (n) | Clone Induction Frequencies (per 105 Cells per Cell Division) e (n/NC*) d,f | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small Single Spots b (1–2 Cells) (m = 2) | Large Single Spots b (>2 Cells) (m = 5) | Twin Spots (m = 5) | Total Spots (m = 2) | |||||
| Rainy | ||||||||
| mwh/flr3 | PC | 10 | 2.80 (28) + | 0.80 (08) + | 0,00 (00) + | 3.60 (36) + | 35 | 7.17 {5.89} |
| NC | 40 | 0.60 (24) | 0.03 (01) | 0.10 (04) | 0.73 (29) | 25 | 1.28 | |
| Site 1 | 40 | 0.70 (28) − | 0.08 (03) i | 0.00 (00) − | 0.78 (31) − | 31 | 1.59 {0.31} | |
| Site 2 | 40 | 0.75 (30) i | 0.13 (05) i | 0.03 (01) − | 0.90 (36) − | 35 | 1.79 {0.51} | |
| Site 3 | 40 | 0.68 (27) − | 0.15 (06) i | 0.05 (02) i | 0.88 (35) − | 33 | 1.69 {0.41} | |
| Dry | ||||||||
| mwh/flr3 | PC | 10 | 2.80 (28) + | 0.80 (08) + | 0.00 (00) + | 3.60 (36) + | 35 | 7.17 {5.89} |
| NC | 40 | 0.60 (24) | 0.03 (01) | 0.10 (04) | 0.73 (29) | 25 | 1.28 | |
| Site 1 | 40 | 0.55 (22) − | 0.23 (09) + | 0.03 (01) − | 0.80 (32) − | 30 | 1.54 {0.26} | |
| Site 2 | 40 | 0.63 (25) − | 0.20 (08) + | 0.10 (04) i | 0.93 (37) − | 37 | 1.90 {0.61} | |
| Site 3 | 40 | 0.63 (25) − | 0.20 (08) + | 0.00 (00) − | 0.83 (33) − | 32 | 1.64 {0.36} | |
| Seasons and Genotypes | Sites of Collection and Controls | No. of Flies (N) | Spots per Fly (No. of Spots)/Statistical Diagnosis a | Total Mwh Clones c (n) | Clone Induction Frequencies (per 105 Cells per Cell Division) e (n/NC*) d,f | Recombination (%) h | Mutation (%) h | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small Single Spots b (1–2 Cells) (m = 2) | Large Single Spots b (>2 Cells) (m = 5) | Twin Spots (m = 5) | Total Spots (m = 2) | |||||||
| Rainy | ||||||||||
| mwh/flr3 | PC | 10 | 23.10 (231) + | 4.10 (41) + | 3.00 (30) + | 30.20 (302) + | 298 | 61.07 {59.22} | ||
| NC | 40 | 0.75 (30) | 0.15 (06) | 0.03 (01) | 0.93 (37) | 36 | 1.84 | |||
| Site 1 | 40 | 1.08 (43) i | 0.20 (08) i | 0.08 (03) i | 1.35 (54) + | 54 | 2.77 {0.92} | 88.89 | 11.11 | |
| Site 2 | 40 | 1.35 (54) + | 0.18 (07) i | 0.08 (03) i | 1.60 (64) + | 62 | 3.18 {1.33} | 73.08 | 26.92 | |
| Site 3 | 40 | 0.90 (36) − | 0.28 (11) i | 0.00 (00) i | 1.18 (47) − | 47 | 2.41 {0.56} | |||
| mwh/TM3 | PC | 10 | 8.50 (85) + | 1.80 (18) + | g | 10.30 (103) + | 103 | 21.11 {19.83} | ||
| NC | 40 | 0.63 (25) | 0.00 (00) | 0.63 (25) | 25 | 1.28 | ||||
| Site 1 | 40 | 0.63 (25) − | 0.05 (02) i | 0.68 (27) − | 27 | 1.38 {0.10} | ||||
| Site 2 | 40 | 0.75 (30) − | 0.05 (02) i | 0.80 (32) i | 32 | 1.64 {[0.36} | ||||
| Dry | ||||||||||
| mwh/flr3 | PC | 10 | 23.10 (231) + | 4.10 (41) + | 3.00 (30) + | 30.20 (302) + | 298 | 61.07 {59.22} | ||
| NC | 40 | 0.75 (30) | 0.15 (06) | 0.03 (01) | 0.93 (37) | 36 | 1.84 | |||
| Site 1 | 40 | 1.18 (47) + | 0.18 (07) i | 0.03 (01) i | 1.38 (55) + | 55 | 2.82 {0.97} | 94.74 | 5.26 | |
| Site 2 | 40 | 1.48 (59) + | 0.13 (05) i | 0.05 (02) i | 1.65 (66) + | 64 | 3.28 {1.43} | 92.86 | 7.14 | |
| Site 3 | 40 | 1.00 (40) − | 0.10 (04) i | 0.05 (02) i | 1.15 (46) − | 46 | 2.36 {0.51} | |||
| mwh/TM3 | PC | 10 | 8.50 (85) + | 1.80 (18) + | g | 10.30 (103) + | 103 | 21.11 {19.83} | ||
| NC | 40 | 0.63 (25) | 0.00 (00) | 0.63 (25) | 25 | 1.28 | ||||
| Site 1 | 40 | 0.90 (36) i | 0.00 (00) i | 0.90 (36) i | 36 | 1.33 {0.05} | ||||
| Site 2 | 40 | 0.68 (27) − | 0.00 (00) i | 0.68 (27) − | 27 | 1.38 {0.10} | ||||
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soares Neto, J.L.; De Carli, R.F.; Kotzal, Q.S.G.; Latroni, F.B.; Lehmann, M.; Dias, J.F.; De Souza, C.T.; Niekraszewicz, L.A.B.; Da Silva, F.R.; Da Silva, J.; et al. Surface Water Impacted by Rural Activities Induces Genetic Toxicity Related to Recombinagenic Events in Vivo. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13080827
Soares Neto JL, De Carli RF, Kotzal QSG, Latroni FB, Lehmann M, Dias JF, De Souza CT, Niekraszewicz LAB, Da Silva FR, Da Silva J, et al. Surface Water Impacted by Rural Activities Induces Genetic Toxicity Related to Recombinagenic Events in Vivo. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2016; 13(8):827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13080827
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoares Neto, José Lopes, Raíne Fogliati De Carli, Queila Susana Gambim Kotzal, Francine Bolico Latroni, Mauricio Lehmann, Johnny Ferraz Dias, Cláudia Telles De Souza, Liana Appel Boufleur Niekraszewicz, Fernanda Rabaioli Da Silva, Juliana Da Silva, and et al. 2016. "Surface Water Impacted by Rural Activities Induces Genetic Toxicity Related to Recombinagenic Events in Vivo" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 13, no. 8: 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13080827
APA StyleSoares Neto, J. L., De Carli, R. F., Kotzal, Q. S. G., Latroni, F. B., Lehmann, M., Dias, J. F., De Souza, C. T., Niekraszewicz, L. A. B., Da Silva, F. R., Da Silva, J., & Dihl, R. R. (2016). Surface Water Impacted by Rural Activities Induces Genetic Toxicity Related to Recombinagenic Events in Vivo. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 13(8), 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13080827