The Synergistic Anti-Cancer Effects of NVP-BEZ235 and Regorafenib in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. BEZ235 Increased the Regorafenib-Induced Inhibition of Cell Viability in HCC Cells
2.2. BEZ235 Enhances the Regorafenib-Induced Apoptosis in HCC Cells
2.3. BEZ235 Increases the Regorafenib-Induced Inhibition of Cell Migration and Invasion in HCC Cells
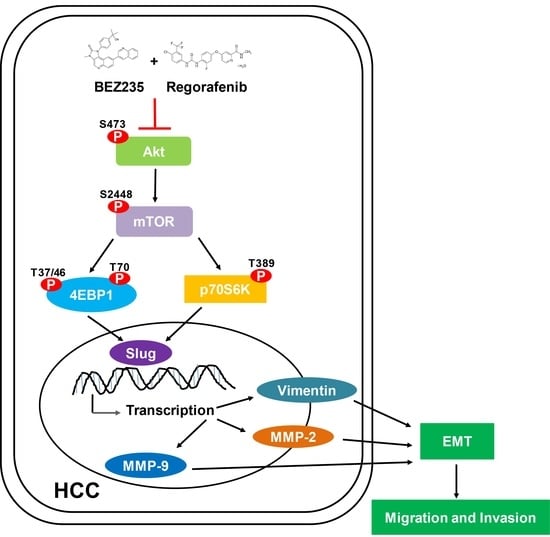
2.4. Combined Drug Treatment Affects the Expression of EMT-Associated Proteins in HCC Cells
2.5. Regorafenib and BEZ235 Suppress the Akt/mTOR Pathway in the HCC Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Antibodies
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. MTT Assay
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Cell Migration and Invasion Assay
4.6. Flow Cytometric Analysis
4.7. Gelatin Zymography
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, L.C.; Hsu, C.H.; Hsu, C.; Cheng, A.L. Tumor Heterogeneity in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Facing the Challenges. Liver Cancer 2016, 5, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psyrri, A.; Arkadopoulos, N.; Vassilakopoulou, M.; Smyrniotis, V.; Dimitriadis, G. Pathways and _targets in hepatocellular carcinoma. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2012, 12, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, H.M.; Chu, Q.; Karlitz, J.J.; Stevens, J.L.; Harlan, L.C. Adoption of Sorafenib for the Treatment of Advanced-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Oncology Practices in the United States. Liver Cancer 2017, 6, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abou-Elkacem, L.; Arns, S.; Brix, G.; Gremse, F.; Zopf, D.; Kiessling, F.; Lederle, W. Regorafenib inhibits growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis in a highly aggressive, orthotopic colon cancer model. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strumberg, D.; Scheulen, M.E.; Schultheis, B.; Richly, H.; Frost, A.; Buchert, M.; Christensen, O.; Jeffers, M.; Heinig, R.; Boix, O.; et al. Regorafenib (BAY 73-4506) in advanced colorectal cancer: A phase I study. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 1722–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilhelm, S.M.; Dumas, J.; Adnane, L.; Lynch, M.; Carter, C.A.; Schutz, G.; Thierauch, K.H.; Zopf, D. Regorafenib (BAY 73-4506): A new oral multikinase inhibitor of angiogenic, stromal and oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinases with potent preclinical antitumor activity. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regorafenib Approved for Liver Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 660.
- Chen, J.; Wang, J. Risk of regorafenib-induced cardiovascular events in patients with solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e12705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.L.; Cantley, L.C. PI3K pathway alterations in cancer: Variations on a theme. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5497–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, J.; Manning, B.D.; Cantley, L.C. _targeting the PI3K-Akt pathway in human cancer: Rationale and promise. Cancer Cell 2003, 4, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matter, M.S.; Decaens, T.; Andersen, J.B.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. _targeting the mTOR pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma: Current state and future trends. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. mTOR Signaling in Cancer and mTOR Inhibitors in Solid Tumor _targeting Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Gao, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Fan, Y.; Ma, W.; Yang, D.; Yang, A.; Yu, Y. Antitumor activity of curcumin by modulation of apoptosis and autophagy in human lung cancer A549 cells through inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 1523–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, S.; She, Q.B. AKT inhibition overcomes rapamycin resistance by enhancing the repressive function of PRAS40 on mTORC1/4E-BP1 axis. Onco_target 2015, 6, 13962–13977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denaro, N.; Russi, E.G.; Adamo, V.; Merlano, M.C. State-of-the-art and emerging treatment options in the management of head and neck cancer: News from 2013. Oncology 2014, 86, 212–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Shi, G.; Jin, J.; Guo, H.; Guo, X.; Luo, F.; Song, Y.; Jia, X. Dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BEZ235-induced apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines is enhanced by inhibitors of autophagy. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 31, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogers-Broadway, K.R.; Kumar, J.; Sisu, C.; Wander, G.; Mazey, E.; Jeyaneethi, J.; Pados, G.; Tsolakidis, D.; Klonos, E.; Grunt, T.; et al. Differential expression of mTOR components in endometriosis and ovarian cancer: Effects of rapalogues and dual kinase inhibitors on mTORC1 and mTORC2 stoichiometry. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqurashi, N.; Hashimi, S.M.; Alowaidi, F.; Ivanovski, S.; Wei, M.Q. Dual mTOR/PI3K inhibitor NVPBEZ235 arrests colorectal cancer cell growth and displays differential inhibition of 4EBP1. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar]
- Bahrami, A.; Khazaei, M.; Hasanzadeh, M.; ShahidSales, S.; Joudi Mashhad, M.; Farazestanian, M.; Sadeghnia, H.R.; Rezayi, M.; Maftouh, M.; Hassanian, S.M.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of _targeting PI3K/AKT Pathway in Treatment of Colorectal Cancer: Rational and Progress. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 2460–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatehi, D.; Soltani, A.; Ghatrehsamani, M. SRT1720, a potential sensitizer for radiotherapy and cytotoxicity effects of NVB-BEZ235 in metastatic breast cancer cells. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2018, 214, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, G.; Que, H.; Sun, J.; Jin, T. Inhibitory effect of BEZ235 on human prostate carcinoma in vitro. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2017, 42, 869–873. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Civallero, M.; Cosenza, M.; Marcheselli, L.; Pozzi, S.; Sacchi, S. NVP-BEZ235 alone and in combination in mantle cell lymphoma: An effective therapeutic strategy. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2012, 21, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Chandrasekaran, G.; de Gooijer, M.C.; Beijnen, J.H.; van Tellingen, O. Determination of NVP-BEZ235, a dual PI3K and mTOR inhibitor, in human and mouse plasma and in mouse tissue homogenates by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2012, 901, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise-Draper, T.M.; Moorthy, G.; Salkeni, M.A.; Karim, N.A.; Thomas, H.E.; Mercer, C.A.; Beg, M.S.; O’Gara, S.; Olowokure, O.; Fathallah, H.; et al. A Phase Ib Study of the Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor Dactolisib (BEZ235) Combined with Everolimus in Patients with Advanced Solid Malignancies. _target Oncol. 2017, 12, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsu, C.M.; Lin, P.M.; Tsai, Y.T.; Tsai, M.S.; Tseng, C.H.; Lin, S.F.; Yang, M.Y. NVP-BEZ235, a dual PI3K-mTOR inhibitor, suppresses the growth of FaDu hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma and has a synergistic effect with Cisplatin. Cell Death Discov. 2018, 4, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, A.; Li, H.; Li, R.; Lu, L.; Wu, X. Co-treatment with BEZ235 enhances chemosensitivity of A549/DDP cells to cisplatin via inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling and downregulation of ERCC1 expression. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 2353–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakouny, Z.; Assi, T.; El Rassy, E.; Nasr, F. Second-line Treatments of Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettrich, T.J.; Seufferlein, T. Regorafenib. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2018, 211, 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Kirstein, M.M.; Boukouris, A.E.; Pothiraju, D.; Buitrago-Molina, L.E.; Marhenke, S.; Schutt, J.; Orlik, J.; Kuhnel, F.; Hegermann, J.; Manns, M.P.; et al. Activity of the mTOR inhibitor RAD001, the dual mTOR and PI3-kinase inhibitor BEZ235 and the PI3-kinase inhibitor BKM120 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2013, 33, 780–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Wu, H.C.; Wu, J.E.; Huang, K.Y.; Yang, S.C.; Chen, S.X.; Tsao, C.J.; Hsu, K.F.; Chen, Y.L.; Hong, T.M. The dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor BEZ235 restricts the growth of lung cancer tumors regardless of EGFR status, as a potent accompanist in combined therapeutic regimens. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piperigkou, Z.; Manou, D.; Karamanou, K.; Theocharis, A.D. Strategies to _target Matrix Metalloproteinases as Therapeutic Approach in Cancer. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1731, 325–348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meyer, S.N.; Galvan, J.A.; Zahnd, S.; Sokol, L.; Dawson, H.; Lugli, A.; Zlobec, I. Co-expression of cytokeratin and vimentin in colorectal Cancer highlights a subset of tumor buds and an atypical Cancer-associated stroma. Hum. Pathol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horejs, C.M. Basement membrane fragments in the context of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 95, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.M.; Stone, A.M.; Shields, J.D.; Huntley, S.; Paterson, I.C.; Prime, S.S. Functional significance of MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression by human malignant oral keratinocyte cell lines. Arch. Oral Biol. 2003, 48, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Feng, L.; Meng, F.; Yu, Z. Dual blocking of PI3K and mTOR signaling by NVP-BEZ235 inhibits proliferation in cervical carcinoma cells and enhances therapeutic response. Cancer Lett. 2017, 388, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, S.; Xie, D.; Chen, H.; Zheng, X.; Pan, D. Dual inhibitor of PI3K and mTOR (NVP-BEZ235) augments the efficacy of fluorouracil on gastric cancer chemotherapy. Onco _targets Ther. 2018, 11, 6111–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.C.; Wu, R.H.; Wang, W.S. Regorafenib diminishes the expression and secretion of angiogenesis and metastasis associated proteins and inhibits cell invasion via NF-kappaB inactivation in SK-Hep1 cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joannes, A.; Grelet, S.; Duca, L.; Gilles, C.; Kileztky, C.; Dalstein, V.; Birembaut, P.; Polette, M.; Nawrocki-Raby, B. Fhit regulates EMT _targets through an EGFR/Src/ERK/Slug signaling axis in human bronchial cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, O.; Hwang, H.S.; Lee, B.S.; Oh, Y.T.; Kim, C.H.; Chun, M. Met inactivation by S-allylcysteine suppresses the migration and invasion of nasopharyngeal cancer cells induced by hepatocyte growth factor. Radiat. Oncol. J. 2015, 33, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocana, A.; Vera-Badillo, F.; Al-Mubarak, M.; Templeton, A.J.; Corrales-Sanchez, V.; Diez-Gonzalez, L.; Cuenca-Lopez, M.D.; Seruga, B.; Pandiella, A.; Amir, E. Activation of the PI3K/mTOR/AKT pathway and survival in solid tumors: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, H.; Qing, X.; Li, S.; Cui, X.; Lou, Q.; Ma, Y.; Pu, H.; Hu, Y. Glucose regulates heat shock factor 1 transcription activity via mTOR pathway in HCC cell lines. Cell Biol. Int. 2015, 39, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Dong, X.; Yu, D.; Shen, Z.; Yu, J.; Yan, S. Natural product pectolinarigenin inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, and causes G2/M phase arrest of HCC via PI3K/AKT/mTOR/ERK signaling pathway. Onco _targets Ther. 2018, 11, 8633–8642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huynh, H.; Ngo, V.C.; Koong, H.N.; Poon, D.; Choo, S.P.; Thng, C.H.; Chow, P.; Ong, H.S.; Chung, A.; Soo, K.C. Sorafenib and rapamycin induce growth suppression in mouse models of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 2673–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Refolo, M.G.; Lippolis, C.; Carella, N.; Cavallini, A.; Messa, C.; D’Alessandro, R. Chlorogenic Acid Improves the Regorafenib Effects in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, R.; Li, S. Regorafenib delays the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma by inducing autophagy. Pharmazie 2018, 73, 218–222. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.M.; Lin, P.M.; Lin, H.C.; Tsai, Y.T.; Tsai, M.S.; Li, S.H.; Wu, C.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Lin, S.F.; Yang, M.Y. NVP-BEZ235 Attenuated Cell Proliferation and Migration in the Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Oral Cavities and p70S6K Inhibition Mimics its Effect. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, B.R.; Michael, H.T.; Halsey, C.H.; Peer, C.J.; Adhikari, A.; Dwyer, J.E.; Hoover, S.B.; El Meskini, R.; Kozlov, S.; Weaver Ohler, Z.; et al. Synergistic _targeted inhibition of MEK and dual PI3K/mTOR diminishes viability and inhibits tumor growth of canine melanoma underscoring its utility as a preclinical model for human mucosal melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2016, 29, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, H.; Li, L.; Garcia Carcedo, I.; Xu, Z.P.; Monteiro, M.; Gu, W. Synergistic inhibition of colon cancer cell growth with nanoemulsion-loaded paclitaxel and PI3K/mTOR dual inhibitor BEZ235 through apoptosis. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 1947–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, D.L.; Lee, B.S.; Lin, L.I.; Liou, J.Y.; Liao, S.C.; Hsu, C.; Cheng, A.L. Vertical blockade of the IGFR- PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: The role of survivin. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serra, V.; Markman, B.; Scaltriti, M.; Eichhorn, P.J.; Valero, V.; Guzman, M.; Botero, M.L.; Llonch, E.; Atzori, F.; Di Cosimo, S.; et al. NVP-BEZ235, a dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, prevents PI3K signaling and inhibits the growth of cancer cells with activating PI3K mutations. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8022–8030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.; Lin, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, B.; Hu, Y.; Dong, B.; et al. Dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor BEZ235 as a promising therapeutic strategy against paclitaxel-resistant gastric cancer via _targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roulin, D.; Waselle, L.; Dormond-Meuwly, A.; Dufour, M.; Demartines, N.; Dormond, O. _targeting renal cell carcinoma with NVP-BEZ235, a dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, in combination with sorafenib. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiu, S.C.; Chiu, T.L.; Huang, S.Y.; Chang, S.F.; Chen, S.P.; Pang, C.Y.; Hsieh, T.F. Potential therapeutic effects of N-butylidenephthalide from Radix Angelica Sinensis (Danggui) in human bladder cancer cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.Y.; Chang, S.F.; Liao, K.F.; Chiu, S.C. Tanshinone IIA Inhibits Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Bladder Cancer Cells via Modulation of STAT3-CCL2 Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |






| Concentration | Hep3B | DRI | |||
| BEZ235 (nM) | Regorafenib (μM) | fa | CI | BEZ235 | Regorafenib |
| 125 | 5 | 0.46 | 1.04 | 3.46 | 1.34 |
| 250 | 5 | 0.54 | 0.99 | 2.53 | 1.68 |
| 500 | 5 | 0.59 | 1.13 | 1.61 | 1.94 |
| Concentration | HepG2 | DRI | |||
| BEZ235 (nM) | Regorafenib (μM) | fa | CI | BEZ235 | Regorafenib |
| 250 | 1 | 0.52 | 0.43 | 8.59 | 3.16 |
| 500 | 1 | 0.56 | 0.48 | 4.75 | 3.70 |
| 1000 | 1 | 0.69 | 0.45 | 3.38 | 6.42 |
| Concentration | Huh7 | DRI | |||
| BEZ235 (nM) | Regorafenib (μM) | fa | CI | BEZ235 | Regorafenib |
| 10 | 2.5 | 0.44 | 0.88 | 3.13 | 1.77 |
| 20 | 2.5 | 0.55 | 0.74 | 2.67 | 2.74 |
| 40 | 2.5 | 0.67 | 0.63 | 2.47 | 4.53 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, C.-C.; Huang, S.-Y.; Chang, S.-F.; Liao, K.-F.; Chiu, S.-C. The Synergistic Anti-Cancer Effects of NVP-BEZ235 and Regorafenib in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Molecules 2020, 25, 2454. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102454
Yu C-C, Huang S-Y, Chang S-F, Liao K-F, Chiu S-C. The Synergistic Anti-Cancer Effects of NVP-BEZ235 and Regorafenib in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Molecules. 2020; 25(10):2454. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102454
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Cheng-Chan, Sung-Ying Huang, Shu-Fang Chang, Kuan-Fu Liao, and Sheng-Chun Chiu. 2020. "The Synergistic Anti-Cancer Effects of NVP-BEZ235 and Regorafenib in Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Molecules 25, no. 10: 2454. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102454
APA StyleYu, C. -C., Huang, S. -Y., Chang, S. -F., Liao, K. -F., & Chiu, S. -C. (2020). The Synergistic Anti-Cancer Effects of NVP-BEZ235 and Regorafenib in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Molecules, 25(10), 2454. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102454