Vitamin K in Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
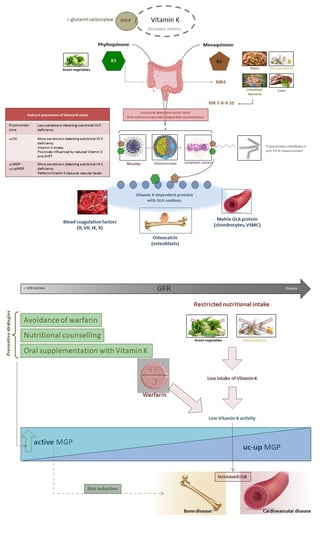
:1. Introduction
2. Vitamin K Deficiency
3. Vitamin K Status in CKD Patients
4. Anti-Vitamin K Treatment and Effects—Warfarin
4.1. Bone Fracture
4.2. Cardiovascular Calcification
4.3. Calciphylaxis
4.4. Arteriovenous Fistula Failure
5. New Oral Anticoagulant vs. Warfarin
6. Phosphate Binders
7. Drug and Vitamin K-Dependent Protein (VKDP)
8. Vitamin K Supplementation
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shearer, M.J.; Newman, P. Metabolism and cell biology of vitamin K. Thromb Haemost 2008, 100, 530–547. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Booth, S.L. Vitamin K: Food composition and dietary intakes. Food Nutr. Res. 2012, 56, 5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elder, S.J.; Haytowitz, D.B.; Howe, J.; Peterson, J.W.; Booth, S.L. Vitamin K contents of meat, dairy, and fast food in the US diet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakano, T.; Nagaoka, T.; Morimoto, A.; Hirauchi, K. Measurement of K vitamins in human and animal feces by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorometric detection. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1986, 34, 4322–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Li, X.; Tso, P. Intestinal fatty acid absorption. Immununol. Endocr. Metab. Agents Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusaro, M.; Gallieni, M.; Rizzo, M.A.; Stucchi, A.; Delanaye, P.; Cavalier, E.; Moysés, R.M.A.; Jorgetti, V.; Iervasi, G.; Giannini, S.; et al. Vitamin K plasma levels determination in human health. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 55, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fusaro, M.; Crepaldi, G.; Maggi, S.; Galli, F.; D’Angelo, A.; Calò, L.; Giannini, S.; Miozzo, D.; Gallieni, M. Vitamin K, bone fractures, and vascular calcifications in chronic kidney disease: An important but poorly studied relationship. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2011, 34, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buranasinsup, S.; Bunyaratavej, N. The intriguing correlation between undercarboxylated osteocalcin and vitamin D. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2015, 98 (Suppl. 8), S16–S20. [Google Scholar]
- Caluwé, R.; Vandecasteele, S.; Van Vlem, B.; Vermeer, C.; De Vriese, A.S. Vitamin K2 supplementation in haemodialysis patients: A randomized dose-finding study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxma, P.Y.; van den Berg, E.; Geleijnse, J.M.; Laverman, G.D.; Schurgers, L.J.; Vermeer, C.; Kema, I.P.; Muskiet, F.A.; Navis, G.; Bakker, S.J.; et al. Vitamin K intake and plasma desphospho-uncarboxylated matrix Gla-protein levels in kidney transplant recipients. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westenfeld, R.; Krueger, T.; Schlieper, G.; Cranenburg, E.C.; Magdeleyns, E.J.; Heidenreich, S.; Holzmann, S.; Vermeer, C.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Ketteler, M.; et al. Effect of vitamin K2 supplementation on functional vitamin K deficiency in hemodialysis patients: A randomized trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2012, 59, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cranenburg, E.C.; Koos, R.; Schurgers, L.J.; Magdeleyns, E.J.; Schoonbrood, T.H.; Landewé, R.B. Characterisation and potential diagnostic value of circulating matrix Gla protein (MGP) species. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 104, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanaye, P.; Dubois, B.E.; Lukas, P.; Peters, P.; Krzesinski, J.M.; Pottel, H.; Cavalier, E. Impact of stopping vitamin K antagonist therapy on concentrations of dephospho-uncarboxylated Matrix Gla protein. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2015, 53, e191-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cranenburg, E.C.M.; Schurgers, L.J.; Uiterwijk, H.H.; Beulens, J.W.; Dalmeijer, G.W.; Westerhuis, R.; Magdeleyns, E.J.; Herfs, M.; Vermeer, C.; Laverman, G.D. Vitamin K intake and status are low in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellasi, A.; Raggi, P. Vascular imaging in chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2012, 21, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlieper, G.; Westenfeld, R.; Krüger, T.; Cranenburg, E.C.; Magdeleyns, E.J.; Brandenburg, V.M.; Djuric, Z.; Damjanovic, T.; Ketteler, M.; Vermeer, C.; et al. Circulating nonphosphorylated carboxylated matrix gla protein predicts survival in ESRD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shea, M.K.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Vermeer, C.; Magdeleyns, E.J.; Crosier, M.D.; Gundberg, C.M.; Ordovas, J.M.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Booth, S.L. Circulating uncarboxylated matrix gla protein is associated with vitamin K nutritional status, but not coronary artery calcium, in older adults. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 1529–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurgers, L.J.; Barreto, D.V.; Barreto, F.C.; Liabeuf, S.; Renard, C.; Magdeleyns, E.J.; Vermeer, C.; Choukroun, G.; Massy, Z.A. The circulating inactive form of matrix gla protein is a surrogate marker for vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease: A preliminary report. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, K.; Booth, S.; Fu, X.; Shobeiri, N.; Pang, J.; Adams, M.; Holden, R. Dietary vitamin K and therapeutic warfarin alter the susceptibility to vascular calcification in experimental chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, R.M.; Morton, A.R.; Garland, J.S.; Pavlov, A.; Day, A.G.; Booth, S.L. Vitamins K and D status in stages 3–5 chronic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, K.M.; Adams, M.A.; Holden, R.M. Vitamin K status in chronic kidney disease. Nutrients 2013, 5, 4390–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voong, K.; Harrington, D.; Goldsmith, D. Vitamin K status in chronic kidney disease: A report of a study and a mini-review. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2013, 45, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stankowiak-Kulpa, H.; Krzyzanowska, P.; Koziol, L.; Grzymislawski, M.; Wanic-Kossowska, M.; Moczko, J.; Walkowiak, J. Vitamin K status in peritoneally dialyzed patients with chronic kidney disease. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2011, 58, 617–620. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holden, R.M.; Iliescu, E.; Morton, A.R.; Booth, S.L. Vitamin K status of canadian peritoneal dialysis patients. Perit. Dial. Int. 2008, 28, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jansz, T.T.; Neradova, A.; van Ballegooijen, A.J.; Verhaar, M.C.; Vervloet, M.G.; Schurgers, L.J.; van Jaarsveld, B.C. The role of kidney transplantation and phosphate binder use in vitamin K status. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tantisattamo, E.; Han, K.H.; O’Neill, W.C. Increased vascular calcification in patients receiving warfarin. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Garcia, M.; Gomez-Alonso, C.; Naves-Diaz, M.; Díaz López, J.B.; Megido, J.; Gago, E.; Forascepi, R.; Cannata Andía, J.B. Prevalence of vertebral fractures and aortic calcifications in hemodialysis patients: Comparison with a population of the same age and sex. Nefrologia 2003, 23 (Suppl. 2), 106–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jamal, S.A.; Gilbert, J.; Gordon, C.; Bauer, D.C. Cortical pQCT measures are associated with fractures in dialysis patients. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2006, 21, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Garcia, M.; Gomez-Alonso, C.; Naves-Diaz, M.; Diaz-Lopez, J.B.; Diaz-Corte, C.; Cannata-Andia, J.B.; Asturias Study Group. Vascular calcifications, vertebral fractures and mortality in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alem, A.M.; Sherrard, D.J.; Gillen, D.L.; Weiss, N.S.; Beresford, S.A.; Heckbert, S.R.; Wong, C.; Stehman-Breen, C. Increased risk of hip fracture among patients with end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kohlmeier, M.; Saupe, J.; Shearer, M.J.; Schaefer, K.; Asmus, G. Bone health of adult hemodialysis patients is related to vitamin K status. Kidney Int. 1997, 51, 1218–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fusaro, M.; Noale, M.; Viola, V.; Galli, F.; Tripepi, G.; Vajente, N.; Plebani, M.; Zaninotto, M.; Guglielmi, G.; Miotto, D.; et al. VItamin K Italian (VIKI) dialysis study investigators. Vitamin K, vertebral fractures, vascular calcifications, and mortality: Vitamin K Italian (VIKI) dialysis study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2012, 27, 2271–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusaro, M.; Tripepi, G.; Noale, M.; Plebani, M.; Zaninotto, M.; Piccoli, A.; Naso, A.; Miozzo, D.; Giannini, S.; Avolio, M.; et al. Prevalence of vertebral fractures, vascular calcifications, and mortality in warfarin treated hemodialysis patients. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2013, 13, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockayne, S.; Adamson, J.; Lanham-New, S.; Shearer, M.J.; Gilbody, S.; Torgerson, D.J. Vitamin K and prevention of fractures: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schurgers, L.J.; Aebert, H.; Vermeer, C.; Bultmann, B.; Janzen, J. Oral anticoagulant treatment: Friend or foe in cardiovascular disease? Blood 2004, 104, 3231–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koos, R.; Mahnken, A.H.; Muhlenbruch, G.; Brandenburg, V.; Pflueger, B.; Wildberger, J.E.; Kuhl, H.P. Relation of oral anticoagulation to cardiac valvular and coronary calcium assessed by multislice spiral computed tomography. Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 96, 747–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hristova, M.; van Beek, C.; Schurgers, L.J.; Lanske, B.; Danziger, J. Rapidly progressive severe vascular calcification sparing the kidney allograft following warfarin initiation. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010, 56, 1158–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennenberg, R.J.; van Varik, B.J.; Schurgers, L.J.; Hamulyak, K.; Ten Cate, H.; Leiner, T.; Vermeer, C.; de Leeuw, P.W.; Kroon, A.A. Chronic coumarin treatment is associated with increased extracoronary arterial calcification in humans. Blood 2010, 115, 5121–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weijs, B.; Blaauw, Y.; Rennenberg, R.J.; Schurgers, L.J.; Timmermans, C.C.; Pison, L.; Nieuwlaat, R.; Hofstra, L.; Kroon, A.A.; Wildberger, J.; et al. Patients using vitamin K antagonists show increased levels of coronary calcification: An observational study in low-risk atrial fibrillation patients. Eur. Heart J. 2011, 32, 2555–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatrou, M.L.L.; Winckers, K.; Hackeng, T.M.; Reutelingsperger, C.P.; Schurgers, L.J. Vascular calcification: The price to pay for anticoagulation therapy with vitamin K-antagonists. Blood Rev. 2012, 26, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; Takamatsu, I.; Kanno, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Abe, T.; Sato, Y.; Japanese Calciphylaxis Study Group. A case-control study of calciphylaxis in Japanese end-stage renal disease patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 1580–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigwekar, S.U.; Bloch, D.B.; Nazarian, R.M.; Vermeer, C.; Booth, S.L.; Xu, D.; Thadhani, R.I.; Malhotra, R. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation of matrix Gla protein influences the risk of calciphylaxis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, T.; Westenfeld, R.; Schurgers, L.; Brandenburg, V. Coagulation meets calcification: The vitamin K system. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2009, 32, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisoni, R.L.; Young, E.W.; Dykstra, D.M.; Greenwood, R.N.; Hecking, E.; Gillespie, B.; Wolfe, R.A.; Goodkin, D.A.; Held, P.J. Vascular access use in Europe and the United States: Results from the DOPPS. Kidney Int. 2002, 61, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwab, S.J.; Harrington, J.T.; Singh, A.; Roher, R.; Shohaib, S.A.; Perrone, R.D.; Meyer, K.; Beasley, D. Vascular access for hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 1999, 55, 2078–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lemson, M.S.; Tordoir, J.H.; Daemen, M.J.A.P.; Kitslaar, P.J.E.H.M. Intimal hyperplasia in vascular grafts. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2000, 19, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, W.G.; Goldin, J.; Kuizon, B.D.; Yoon, C.; Gales, B.; Sider, D.; Wang, Y.; Chung, J.; Emerick, A.; Greaser, L.; et al. Coronary-artery calcification in young adults with end-stage renal disease who are undergoing dialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1478–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balci, M.; Kirkpantur, A.; Turkvatan, A.; Mandıroglu, S.; Ozturk, E.; Afsar, B. Sclerostin as a new key player in arteriovenous fistula calcification. Herz 2013, 40, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, H.C.; Hajjar, K.; Frank, B.; Perrey, M. New anticoagulants for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation. Herz 2012, 37, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cario-Toumaniantz, C.; Boularan, C.; Schurgers, L.J.; Le Cunff, M.; Léger, J.; Loirand, G.; Pacaud, P. Identification of differentially expressed genes in human varicose veins: Involvement of matrix gla protein in extracellular matrix remodeling. J. Vasc. Res. 2007, 44, 444–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaragatski, E.; Grommes, J.; Schurgers, L.J.; Langer, S.; Kennes, L.; Tamm, M.; Koeppel, T.A.; Kranz, J.; Hackhofer, T.; Arakelyan, K.; et al. Vitamin K antagonism aggravates aggravates chronic kidney disease-induced neointimal hyperplasia and calcification in arterialized veins: Role of vitamin K tratment? Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, S.J.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Yusuf, S.; Eikelboom, J.; Oldgren, J.; Parekh, A.; Pogue, J.; Reilly, P.A.; Themeles, E.; Varrone, J.; et al. Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.R.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Garg, J.; Pan, G.; Singer, D.E.; Hacke, W.; Breithardt, G.; Halperin, J.L.; Hankey, G.J.; Piccini, J.P.; et al. Rivaroxaban versus warfarin in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.E.; Edelman, E.R.; Wenger, J.B.; Thadhani, R.I.; Maddux, F.W. Dabigatran and rivaroxaban use in atrial fibrillation patients on hemodialysis. Circulation 2015, 131, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siontis, K.C.; Zhang, X.; Eckard, A.; Bhave, N.; Schaubel, D.E.; He, K.; Tilea, A.; Stack, A.G.; Balkrishnan, R.; Yao, X.; et al. Outcomes Associated with Apixaban Use in End-Stage Kidney Disease Patients with Atrial Fibrillation in the United States. Circulation 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozzolino, M.; Mangano, M.; Magagnoli, L.; Di Lullo, L.; Galassi, A.; Brancaccio, D.; Bellasi, A. Iron-based Phosphate Binders for ESRD Patients G Ital Nefrol. Giornale italiano di nefrologia: Organo ufficiale della Societa italiana di nefrologia 2016, 33, 27545638. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, S.C.; Gardner, S.; Tonelli, M.; Mavridis, D.; Johnson, D.W.; Craig, J.C.; French, R.; Ruospo, M.; Strippoli, G.F. Phosphate-binding agents in adults with CKD: A network meta-analysis of randomized trials. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 68, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtake, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Oka, M.; Furuya, R.; Iwagami, M.; Tsutsumi, D.; Mochida, Y.; Maesato, K.; Ishioka, K.; Moriya, H.; et al. Lanthanum carbonate delays progression of coronary artery calcification compared with calcium-based phosphate binders in patients on hemodialysis: A pilot study. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 18, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raggi, P.; Bommer, J.; Chertow, G.M. Valvular calcification in hemodialysis patients randomized to calcium-based phosphorus binders or sevelamer. J. Heart Valve Dis. 2004, 13, 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- Chertow, G.M.; Burke, S.K.; Raggi, P.; Treat to Goal Working Group. Sevelamer attenuates the progression of coronary and aortic calcification in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neradova, A.; Schumacher, S.P.; Hubeek, I.; Lux, P.; Schurgers, L.J.; Vervloet, M.G. Phosphate binders affect vitamin K concentration by undesired binding, an in vitro study. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusaro, M.; Giannini, S.; Gallieni, M.; Noale, M.; Tripepi, G.; Rossini, M.; Messa, P.; Rigotti, P.; Pati, T.; Barbisoni, F.; et al. Calcimimetic and vitamin D analog use in hemodialyzed patients is associated with increasedlevels of vitamin K dependent proteins. Endocrine 2016, 51, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, M.; Aguilera-Tejero, E.; Mendoza, F.J.; Guerrero, F.; López, I. Effects of calcimimetics on extraskeletal calcifications in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2008, 74 (Suppl. 111), S50–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza, F.J.; Martinez-Moreno, J.; Almaden, Y.; Rodriguez-Ortiz, M.E.; Lopez, I.; Estepa, J.C.; Henley, C.; Rodriguez, M.; Aguilera-Tejero, E. Effect of calcium and the calcimimetic AMG 641 on matrix-GIa protein in vascular smooth musclecells. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2011, 88, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torbergsen, A.C.; Watne, L.O.; Wyller, T.B.; Frihagen, F.; Strømsøe, K.; Bøhmer, T.; Mowe, M. Vitamin K1 and 25(OH)D are independently and synergistically associated with a risk for hipfracture in an elderly population: A case control study. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geleijnse, J.M.; Vermeer, C.; Grobbee, D.E.; Schurgers, L.J.; Knapen, M.H.; van der Meer, I.M.; Hofman, A.; Witteman, J.C. Dietary intake of menaquinone is associated with a reduced risk of coronary heart disease: The Rotterdam Study. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 3100–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shea, M.K.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Hoffmann, U.; Dallal, G.E.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Ordovas, J.M.; Price, P.A.; Williamson, M.K.; Booth, S.L. Vitamin K supplementation and progression of coronary artery calcium in older men and women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 1799–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keyzer, C.A.; Vermeer, C.; Joosten, M.M.; Knapen, M.H.; Drummen, N.E.; Navis, G.; Bakker, S.J.; de Borst, M.H. Vitamin K status and mortality after kidney transplantation: A cohort study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 65, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cozzolino, M.; Mangano, M.; Galassi, A.; Ciceri, P.; Messa, P.; Nigwekar, S. Vitamin K in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010168
Cozzolino M, Mangano M, Galassi A, Ciceri P, Messa P, Nigwekar S. Vitamin K in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients. 2019; 11(1):168. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010168
Chicago/Turabian StyleCozzolino, Mario, Michela Mangano, Andrea Galassi, Paola Ciceri, Piergiorgio Messa, and Sagar Nigwekar. 2019. "Vitamin K in Chronic Kidney Disease" Nutrients 11, no. 1: 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010168
APA StyleCozzolino, M., Mangano, M., Galassi, A., Ciceri, P., Messa, P., & Nigwekar, S. (2019). Vitamin K in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients, 11(1), 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010168