A Stimuli-Responsive Biosensor of Glucose on Layer-by-Layer Films Assembled through Specific Lectin-Glycoenzyme Recognition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Film Assembly
2.3. Apparatus and Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fabrication of {Con A/GOD}n LbL Films
3.2. Stimuli-Responsive Behavior of {Con A/GOD}5 Films Controlled by Solution pH
3.3. Influence of Film Thickness
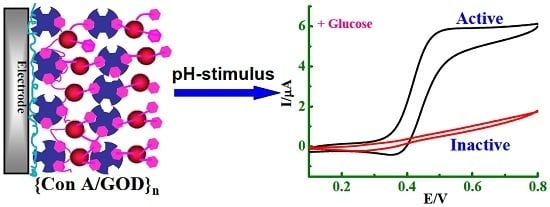
3.4. Stimuli-Responsive Bioelectrocatalysis for {Con A/GOD}5 Films
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mendes, P.M. Stimuli-responsive surfaces for bio-applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 2512–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Xie, R.; Ju, X.J.; Chu, L.Y. Stimuli-responsive smart gating membranes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 460–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Sai, H.; Spoth, K.A.; Tan, K.W.; Werner-Zwanziger, U.; Zwanziger, J.; Gruner, S.M.; Kourkoutis, L.F.; Wiesner, U. Stimuli-responsive shapeshifting mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parlak, O.; Turner, A.P.F.; Tiwari, A. pH-induced on/off-switchable graphene bioelectronics. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 7434–7439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratto, B.E.; Katz, E. Controlled logic gates–switch gate and fredkin gate based on enzyme-biocatalyzed reactions realized in flow cells. ChemPhysChem 2016, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailloux, S.; Gerasimova, Y.V.; Guz, N.; Kolpashchikov, D.M.; Katz, E. Bridging the two worlds: A universal interface between enzymatic and DNA computing systems. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 6562–6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Lian, W.; Yao, H.; Liu, H. Multiple-stimuli responsive bioelectrocatalysis based on reduced graphene oxide/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) composite films and its application in the fabrication of logic gates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 5168–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, E.; Fernandez, V.M.; Pita, M. Switchable bioelectrocatalysis controlled by pH changes. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 2063–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Chen, X. Stimuli-responsive supramolecular interfaces for controllable bioelectrocatalysis. ChemElectroChem 2014, 1, 1602–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio, T.R.T.A.; Cabral, M.F.; Cesarino, I.; Machado, S.A.S.; Pedrosa, V.A. Toward pH-controllable bioelectrocatalysis for hydrogen peroxide based on polymer brushes. Electrochem. Commun. 2013, 29, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Hu, N.; Liu, H. pH-switchable bioelectrocatalysis based on weak polyelectrolyte multilayers. Electroanalysis 2011, 23, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decher, G.; Schneloff, J.B. Multilayer Thin Films: Sequential Assembly of Nanocomposite Materials; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Eisenberg, A.; Liu, G.J.; Zhang, X. Macromolecular Self-Assembly; Scientific Press: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 30–40. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, K.T.; Turner, T.A.; Preast, C.E. Rational design of novel glycomimetics: Inhibitors of concanavalin A. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 6573–6580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, J.W.; Reeke, G.N., Jr.; Cunningcham, B.A.; Edelman, G.M. New evidence on the location of the saccharide-binding site of concanavalin A. Nature 1976, 259, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konishi, M.; Imura, T.; Fukuoka, T.; Morita, T.; Kitamoto, D. A yeast glycolipid biosurfactant, mannosylerythritol lipid, shows high binding affinity towards lectins on a self-assembled monolayer system. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Hu, N. pH-switchable bioelectrocatalysis of hydrogen peroxide on layer-by-layer films assembled by concanavalin A and horseradish peroxidase with electroactive mediator in solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 3380–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleemuddin, M.; Husain, Q. Concanavalin A: A useful ligand for glycoenzyme immobilization—A review. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1991, 13, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, K. A Glucose-selective surface plasmon resonance sensor based on self-assembled multilayers. Acta Chim. Sin. 2007, 65, 1185–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.; Guo, X.; Hu, N. Loading of myoglobin into layer-by-layer films assembled by concanavalin A and dextran based on their biospecific recognition: An electrochemical study. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 7330–7337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Anzai, J. Preparation and optimization of bienzyme multilayer films using lectin and glyco-enzymes for biosensor applications. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2001, 507, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Lian, W.; Liu, H.; Li, C. Logic gate system with three outputs and three inputs based on switchable electrocatalysis of glucose by glucose oxidase entrapped in chitosan films. Chem. Asian J. 2015, 10, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, H.A.O. Bio-electrochemistry. Pure Appl. Chem. 1987, 59, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, Y.; Ariga, K.; Ichinose, I.; Kunitake, T. Molecular film assembly via layer-by-layer adsorption of oppositely charged macromolecules (linear polymer, protein and clay) and concanavalin A and glycogen. Thin Solid Films 1996, 284–285, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, Y.M.; Lu, Z.; Schenkman, J.B.; Zu, X.; Rusling, J.F. Direct electrochemistry of myoglobin and cytochrome P450cam in alternate layer-by-layer films with DNA and other polyions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 4073–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Hu, N. Salt-induced swelling and electrochemical property change of hyaluronic acid/myoglobin multilayer films. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 1984–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lvov, Y.; Aviga, K.; Ichinose, I.; Kunitake, T. Assembly of multicomponent protein films by means of electrostatic layer-by-layer adsorption. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 6117–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, N. Study on direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase stabilized by cross-linking and immobilized in silica nanoparticle films. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooten, M.; Karra, S.; Zhang, M.; Gorski, W. On the direct electron transfer, sensing, and enzyme activity in the glucose oxidase/carbon nanotubes system. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karuppiah, C.; Palanisamy, S.; Chen, S.; Veeramani, V.; Periakaruppan, P. Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase and sensing glucose using a screen-printed carbon electrode modified with graphite nanosheets and zinc oxide nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 1843–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, R.W. Electroanalytical Chemistry; Bard, A.J., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1984; Volume 13, pp. 191–368. [Google Scholar]
- Pazur, J.H.; Kleppe, K. The oxidation of glucose and related compounds by glucose oxidase from Aspergillus niger. Biochemistry 1964, 3, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Hu, N. pH-controllable bioelectrocatalysis based on “on-off” switching redox property of electroactive probes for spin-assembled layer-by-layer films containing branched poly(ethyleneimine). J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 3648–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decher, G. Fuzzy nanoassemblies: Toward layered polymeric multicomposites. Science 1997, 277, 1232–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Electrochemical glucose biosensors. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, K.; Hu, N. Triply switchable bioelectrocatalysis based on poly(N,N-diethylacrylamide-co-4-vinylpyridine) copolymer hydrogel films with immobilized glucose oxidase. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 60, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cass, A.E.G.; Davis, G.; Francis, G.D.; Hill, H.A.O.; Aston, W.J.; Higgins, I.J.; Plotkin, E.V.; Scott, L.D.L.; Turner, A.P.F. Ferrocene-mediated enzyme electrode for amperometric determination of glucose. Anal. Chem. 1984, 56, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.J.; Hill, H.A.O. Amperometric enzyme electrodes. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. I 1986, 82, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Imoto, Y.; Sugama, J.; Seki, S.; Inoue, H.; Odagiri, T.; Hoshi, T.; Anzai, J. Sugar-induced disintegration of layer-by-layer assemblies composed of concanavalin A and glycogen. Langmuir 2005, 21, 797–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandel, D.K.; Kishore, N.; Brewer, C.F. Thermodynamics of lectin-carbohydrate interactions. titration microcalorimetry measurements of the binding of N-linked carbohydrates and ovalbumin to concanavalin A. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradkar, V.M.; Sordick, J.S. Purification of glycoproteins by selective transport using concanavalin-mediated reverse micellar extraction. Biotechnol. Prog. 1991, 7, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koneke, R.; Menzel, C.; Ulber, R.; Schügerl, K.; Scheper, T. Reversible coupling of glucoenzymes on fluoride-sensitive FET biosensors based on lectin-glucoprotein binding. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1996, 11, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, N.; Yang, C.; Yang, X. One-step synthesis of amino-dextran-protected gold and silver nanoparticles and its application in biosensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 382, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslan, K.; Lakowicz, J.R.; Geddes, C.D. Nanogold-plasmon-resonance-based glucose sensing. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 330, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Naim, A.Y. Cooperativity and Regulation in Biochemical Processes; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Tam, T.K.; Zhou, J.; Pita, M.; Ornatska, M.; Minko, S.; Katz, E. Biochemically controlled bioelectrocatalytic interface. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10888–10889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, H.; Gan, Q.; Peng, J.; Huang, S.; Zhu, M.; Shi, K. A Stimuli-Responsive Biosensor of Glucose on Layer-by-Layer Films Assembled through Specific Lectin-Glycoenzyme Recognition. Sensors 2016, 16, 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040563
Yao H, Gan Q, Peng J, Huang S, Zhu M, Shi K. A Stimuli-Responsive Biosensor of Glucose on Layer-by-Layer Films Assembled through Specific Lectin-Glycoenzyme Recognition. Sensors. 2016; 16(4):563. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040563
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Huiqin, Qianqian Gan, Juan Peng, Shan Huang, Meilin Zhu, and Keren Shi. 2016. "A Stimuli-Responsive Biosensor of Glucose on Layer-by-Layer Films Assembled through Specific Lectin-Glycoenzyme Recognition" Sensors 16, no. 4: 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040563
APA StyleYao, H., Gan, Q., Peng, J., Huang, S., Zhu, M., & Shi, K. (2016). A Stimuli-Responsive Biosensor of Glucose on Layer-by-Layer Films Assembled through Specific Lectin-Glycoenzyme Recognition. Sensors, 16(4), 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040563