Figure 1.
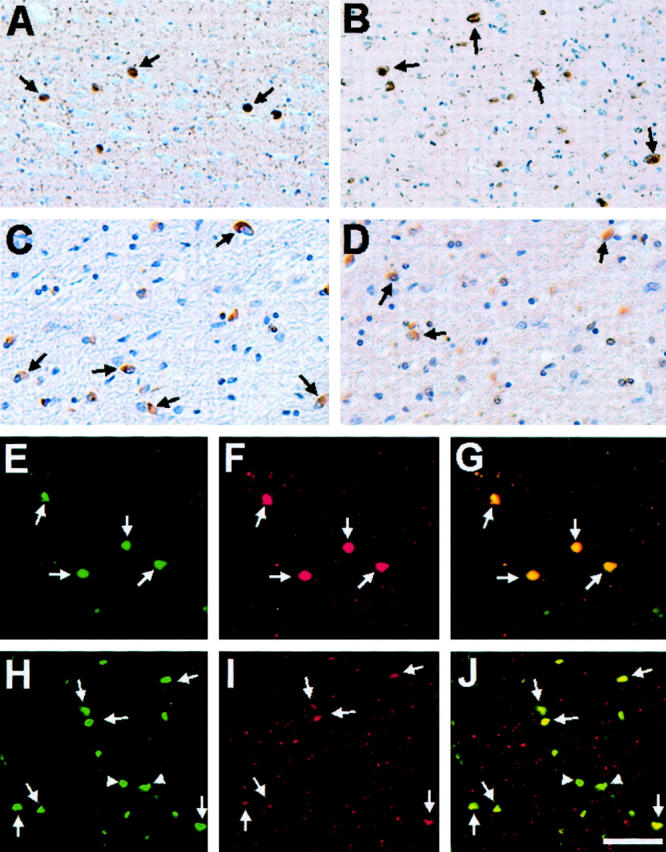
Ubiquitin immunostaining of α-syn pathological inclusions in DLB and MSA. Immunohistochemistry of cingulate cortex from a DLB patient (DLB-2) (A and B) and cerebellum from a MSA patient (MSA-6) (C and D) stained using monoclonal anti-α-syn antibodies Syn303 (A and C) and monoclonal anti-ubiquitin antibody mAb 1510 (B and D). In A and B, arrows highlight immunoreactive cortical LBs, whereas in C and D arrows indicate stained GCIs. Double-label immunofluorescence of cortical LBs in the cingulate cortex of a patient with DLB (DLB-5) (E–G) and GCIs in the cerebellum of a patient with MSA (MSA-8) (H–J) with rabbit anti-α-syn antibody SNL-4 (green, E and H) and murine anti-ubiquitin antibody mAb 1510 (red, F and I). The overlays of staining with both antibodies are shown in G and J. In H to J, arrows indicate inclusions stained with antibodies to both α-syn and ubiquitin, whereas arrowheads depict inclusions stained only with antibodies to α-syn. Scale bars: 80 μm (A, B, E–J), 40 μm (C, D).
