Abstract
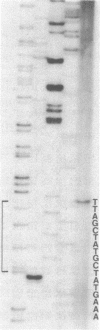
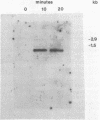
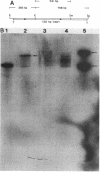
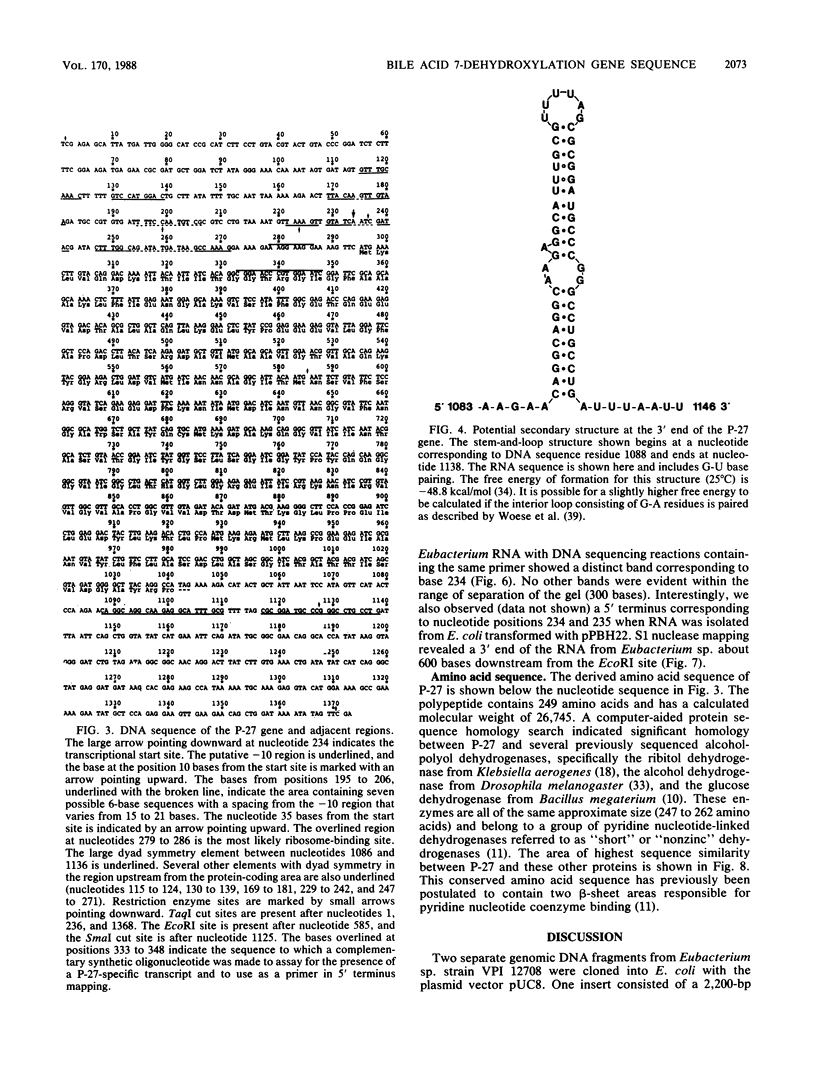
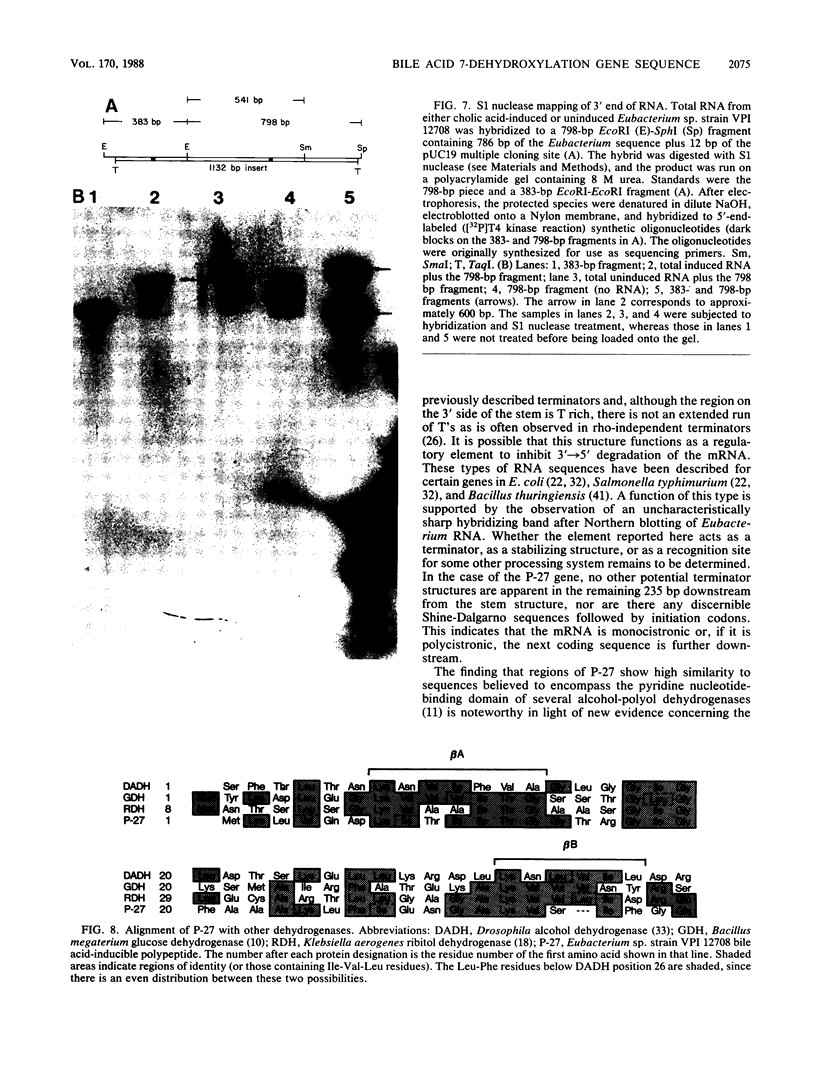
Eubacterium sp. strain VPI 12708 is an anaerobic intestinal bacterium that has inducible bile acid 7-dehydroxylation activity. At least four new polypeptides were synthesized after addition of primary bile acids to the growth medium. One of these, of molecular weight 27,000 (P-27), was shown to be involved in the 7-dehydroxylation reaction sequence. The gene coding for P-27 was cloned, and the entire DNA sequence for the protein-coding region was determined. In addition, sequence information was obtained for 294 bases upstream from the translational start codon and 329 bases downstream from the stop codon. Induction studies with a synthetic oligonucleotide probe (16-mer) revealed the presence of a cholic acid-inducible mRNA species approximately 900 bases long. A 5' terminus of this mRNA was detected by primer extension analysis, and the location of the 3' terminus of the mRNA was estimated by using S1 nuclease mapping. The 3' terminus of the mRNA contained a large element with dyad symmetry of unknown function. The open reading frame contained 249 codons, and the corresponding polypeptide had a calculated molecular weight of 26,745. The amino acid sequence of P-27 showed significant homology to several previously described alcohol-polyol dehydrogenases ("nonzinc" dehydrogenases), especially in the region believed to contain a pyridine nucleotide-binding domain. The implications of this homology and the possible function of P-27 in bile acid 7-dehydroxylation are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagheri S. A., Bolt M. G., Boyer J. L., Palmer R. H. Stimulation of thymidine incorporation in mouse liver and biliary tract epithelium by lithocholate and deoxycholate. Gastroenterology. 1978 Feb;74(2 Pt 1):188–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. P., White W. B., Egestad B., Sjövall J., Hylemon P. B. Biosynthesis of a novel bile acid nucleotide and mechanism of 7 alpha-dehydroxylation by an intestinal Eubacterium species. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4701–4707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. P., White W. B., Hylemon P. B. Molecular cloning of bile acid 7-dehydroxylase from Eubacterium sp. strain VPI 12708. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1516–1521. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1516-1521.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari A., Beretta L. Activity on bile acids of a Clostridium bifermentans cell-free extract. FEBS Lett. 1977 Mar 15;75(1):163–165. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves M. C., Rabinowitz J. C. In vivo and in vitro transcription of the Clostridium pasteurianum ferredoxin gene. Evidence for "extended" promoter elements in gram-positive organisms. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11409–11415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYAKAWA S., SAMUELSSON B. TRANSFORMATION OF CHOLIC ACID IN VITRO BY CORYNEBACTERIUM SIMPLEX. BILE ACIDS AND STEROIDS. 132. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:94–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa S., Kanematsu Y., Fujiwara T. Microbiological degradation of bile acids. Ring A cleavage and 7alpha, 12alpha-dehydroxylation of cholic acid by Arthrobacter simplex. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(2):249–256. doi: 10.1042/bj1150249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jany K. D., Ulmer W., Fröschle M., Pfleiderer G. Complete amino acid sequence of glucose dehydrogenase from Bacillus megaterium. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jan 2;165(1):6–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörnvall H., von Bahr-Lindström H., Jany K. D., Ulmer W., Fröschle M. Extended superfamily of short alcohol-polyol-sugar dehydrogenases: structural similarities between glucose and ribitol dehydrogenases. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jan 9;165(2):190–196. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80167-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsey M. I., Pienta R. J. Transformation of hamster embryo cells by cholesterol-alpha-epoxide and lithocholic acid. Cancer Lett. 1979 Mar;6(3):143–149. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(79)80025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni M. S., Heidepriem P. M., Yielding K. L. Production by lithocholic acid of DNA strand breaks in L1210 cells. Cancer Res. 1980 Aug;40(8 Pt 1):2666–2669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. C., Roeder R. G. Transcription of adenovirus type 2 genes in a cell-free system: apparent heterogeneity of initiation at some promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;1(7):635–651. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.7.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao H. H., Rabinowitz J. C. Clostridial apoferredoxin messenger ribonucleic acid. Assay and partial purification. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 29;608(2):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky R. H., Hylemon P. B. Characterization of a NADH:flavin oxidoreductase induced by cholic acid in a 7 alpha-dehydroxylating intestinal Eubacterium species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 11;612(2):328–336. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90115-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. G. Use of sodium trichloroacetate and mung bean nuclease to increase sensitivity and precision during transcript mapping. Anal Biochem. 1986 Oct;158(1):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90605-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narisawa T., Magadia N. E., Weisburger J. H., Wynder E. L. Promoting effect of bile acids on colon carcinogenesis after intrarectal instillation of N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine in rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Oct;53(4):1093–1097. doi: 10.1093/jnci/53.4.1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newbury S. F., Smith N. H., Robinson E. C., Hiles I. D., Higgins C. F. Stabilization of translationally active mRNA by prokaryotic REP sequences. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):297–310. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90433-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. W., Bilton R. F. The degradation of cholic acid by Pseudomonas sp. N.C.I.B. 10590 under anaerobic conditions. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 15;216(3):641–654. doi: 10.1042/bj2160641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paone D. A., Hylemon P. B. HPLC purification and preparation of antibodies to cholic acid-inducible polypeptides from Eubacterium sp. V.P.I. 12708. J Lipid Res. 1984 Dec 1;25(12):1343–1349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skrede S., Björkhem I. Biosynthesis of cholestanol from intestinal 7 alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8363–8367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. J., Ames G. F., Smith N. H., Robinson E. C., Higgins C. F. Repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences: a major component of the bacterial genome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1015–1026. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90436-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thatcher D. R. The complete amino acid sequence of three alcohol dehydrogenase alleloenzymes (AdhN-11, AdhS and AdhUF) from the fruitfly Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 1;187(3):875–883. doi: 10.1042/bj1870875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Suggs S. V., Miyoshi K., Bhatt R., Itakura K. A set of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide primers for DNA sequencing in the plasmid vector pBR322. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Cacciapuoti A. F., Fricke R. J., Whitehead T. R., Mosbach E. H., Hylemon P. B. Cofactor requiremets for 7 alpha-dehydroxylation of cholic and chenodeoxycholic acid in cell extracts of the intestinal anaerobic bacterium, Eubacterium species V.P.I. 13708. J Lipid Res. 1981 Aug;22(6):891–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Lipsky R. L., Fricke R. J., Hylemon P. B. Bile acid induction specificity of 7 alpha-dehydroxylase activity in an intestinal Eubacterium species. Steroids. 1980 Jan;35(1):103–109. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(80)90115-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Paone D. A., Cacciapuoti A. F., Fricke R. J., Mosbach E. H., Hylemon P. B. Regulation of bile acid 7-dehydroxylase activity by NAD+ and NADH in cell extracts of Eubacterium species V.P.I. 12708. J Lipid Res. 1983 Jan;24(1):20–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Gutell R., Gupta R., Noller H. F. Detailed analysis of the higher-order structure of 16S-like ribosomal ribonucleic acids. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):621–669. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.621-669.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Stackebrandt E., Macke T. J., Fox G. E. A phylogenetic definition of the major eubacterial taxa. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1985;6:143–151. doi: 10.1016/s0723-2020(85)80047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong H. C., Chang S. Identification of a positive retroregulator that stabilizes mRNAs in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3233–3237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]