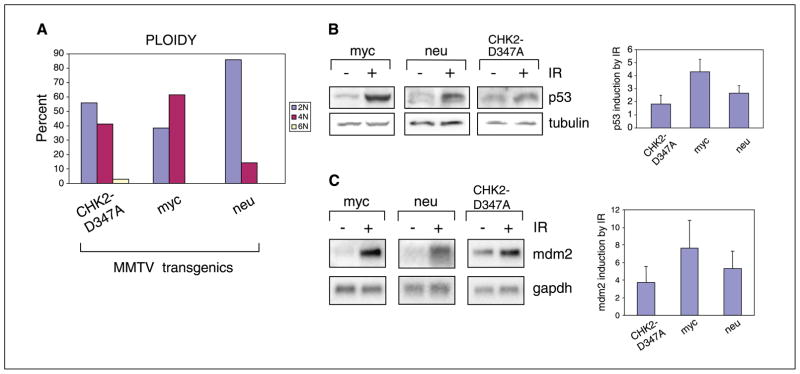
Figure 3.
Functional abnormalities in MMTV-CHK2-D347A–derived tumor cells. A, ploidy of mitoses from seven independent CHK2-D347A tumor–derived cell lines (56% of mitoses were 2N, 41% were 4N, 3% were 6N), two c-myc cell lines (38% of mitoses were 2N, 62% were 4N), and two c-neu cell lines (86% of mitoses were 2N, 14% were 4N). Cells were karyotyped at passages 2 to 5. Virtually all CHK2-D347A cells with 2N ploidy exhibited gains or losses of individual chromosomes. B, quantitation of p53 protein levels following ionizing radiation. Immunoblot analysis of lysates from c-myc, c-neu, and CHK2-D347A mammary tumor-derived cells following 10-Gy ionizing radiation. Equal quantities of protein lysates (tubulin control) were analyzed 1 hour after ionizing radiation and representative samples are shown. Densitometric analysis of multiple immunoblots showing p53 expression following ionizing radiation for three cell lines derived from CHK2-D347A, c-myc, and c-neu tumors. Columns, mean fold induction (standardized to baseline); bars, SD. C, Northern blot analysis of mdm2 expression in c-myc, c-neu, and CHK2-D347A mammary tumor cells 2 hours after ionizing radiation (10 Gy). Representative samples are shown with glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (gapdh) control. Densitometric quantitation of multiple experiments showing mdm2 induction by ionizing radiation for CHK2-D347A tumors (nine cell lines), c-myc tumors (five cell lines), and c-neu tumors (three cell lines). Columns, mean fold induction (standardized to baseline); bars, SD.