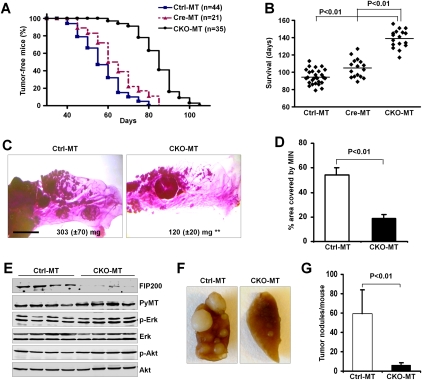
Figure 1.
Conditional deletion of FIP200 in MaEC suppresses breast cancer initiation, progression, and metastasis. (A) Kaplan-Meier analysis of mammary tumor development in the Ctrl-MT (n = 44), Cre-MT (n = 21), and CKO-MT (n = 35) mice. CKO-MT versus Ctrl-MT or Cre-MT: P < 0.01 by the log-rank test. (B) Scatter plots showing days of survival for indicated mouse strains before they succumb to their tumor burden. Horizontal line represents the mean. (C) Representative mammary gland whole mounts from 10-wk-old Ctrl-MT (left) and CKO-MT mice (right). The average mass of inguinal mammary glands from Ctrl-MT (left, n = 6) and CKO-MT (right, n = 7) mice are also shown. Bar, 5 mm. (**) P < 0.01. (D) Quantification of the area occupied by hyperplastic lesions expressed as a percentage of the total mammary gland surface. (E) Lysates were prepared from four tumors in four different Ctrl-MT (left four lanes) and CKO-MT (right four lanes) mice and analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies against various proteins as indicated. (F,G) Lungs were harvested from Ctrl-MT (n = 17) and CKO-MT (n = 12) mice at 7 wk after initial detection of palpable primary tumors. (F) Representative images from these mice. (G) The mean ± SD of the number of metastatic nodules on the surfaces of lungs per mouse.