Abstract
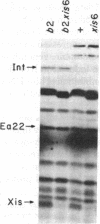
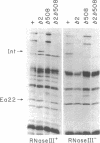
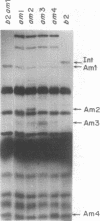
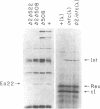
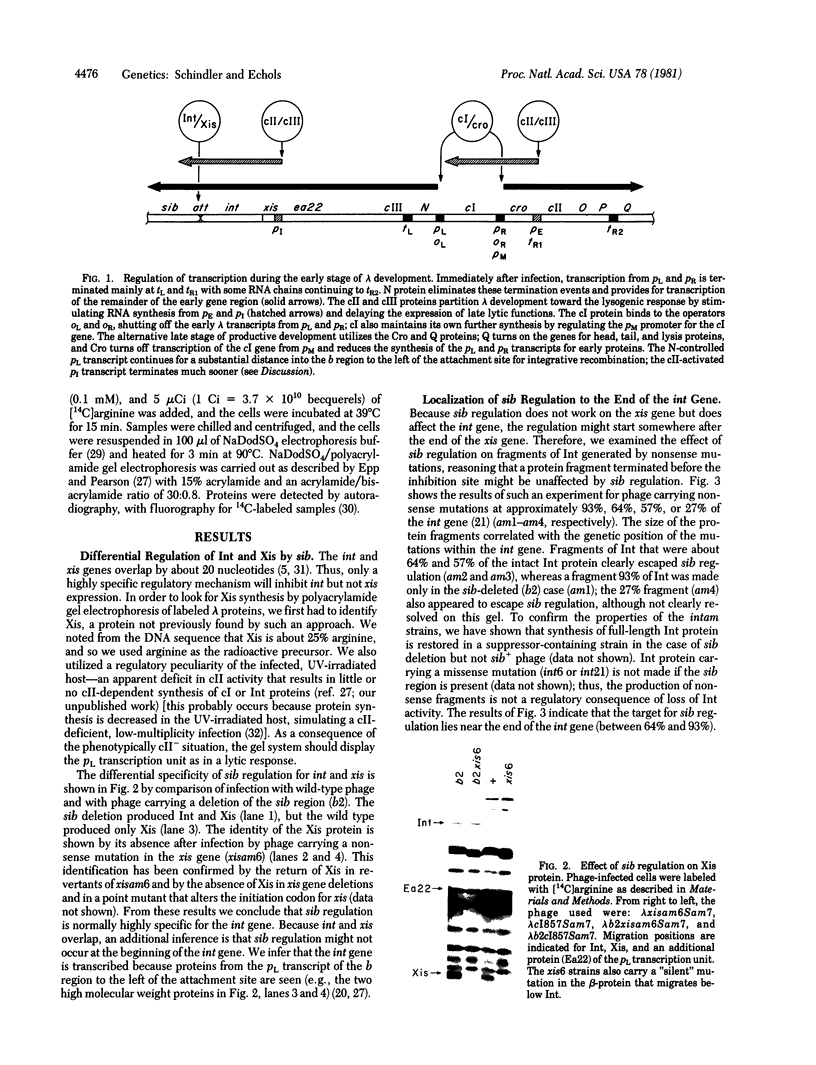
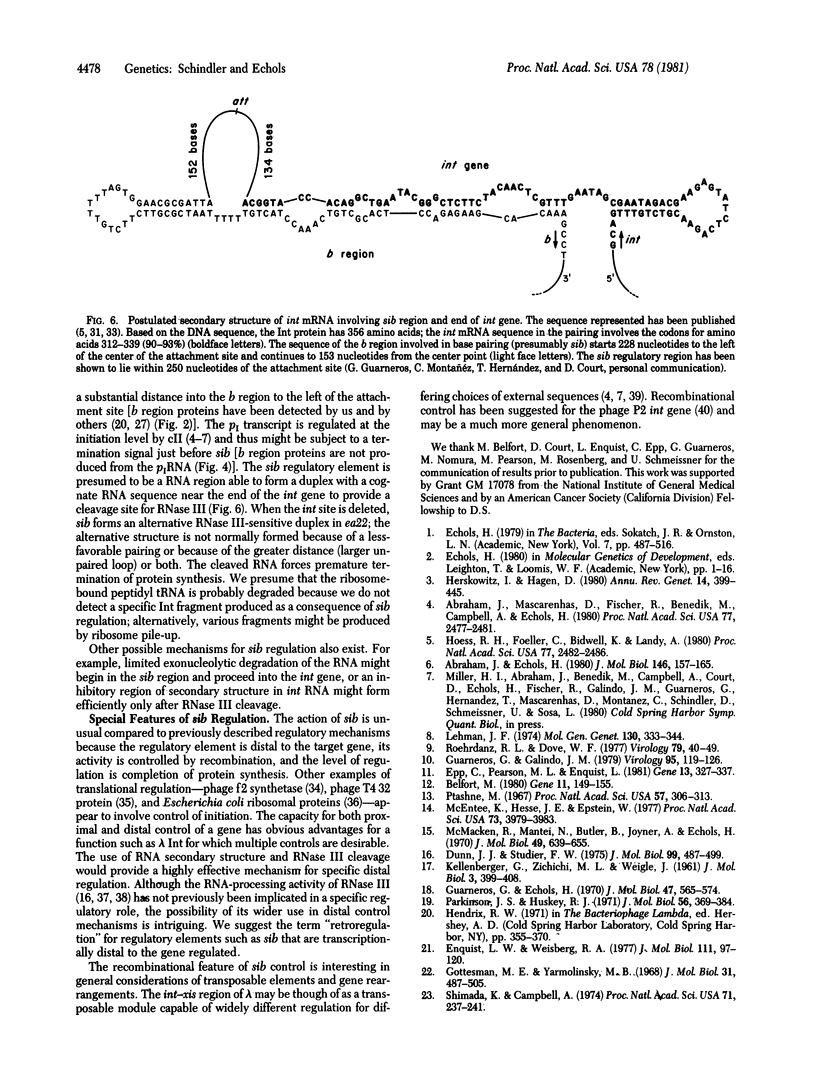
Bacteriophage lambda regulates the integration--excision reaction as a crucial aspect of the choice of pathway during lysogenic or lytic viral development. This control involves differential expression of the tightly linked, partially overlapping int and xis genes from two promoter sites: pI, positively regulated by cII/cIII proteins, and pL, positively regulated by N protein. After lambda infection, Int is synthesized from the pI transcript under cII regulation; however, very little Int is produced from the pL RNA because of the existence of a cis-acting regulatory element, sib, on the opposite side of the int gene from the pL promoter. Presumably sib serves to prevent unwanted synthesis of Int protein during the lytic response; the Int protein necessary for excisive recombination from a prophage can be supplied by pL transcription because sib is separated from int by prophage insertion. We have studied the effect of sib on nearby lambda genes by means of gel electrophoresis of labeled proteins from infected cells. Deletion of the sib region greatly enhances production of Int protein without substantial effect on Xis production; thus, sib regulation normally is highly specific for Int. When the sib region is moved past int and xis by deletion, regulation of the adjacent gene for the protein Ea22 occurs, suggesting that sib regulation can work on other genes. Although synthesis of wild-type Int is severely inhibited by sib, shorter Int protein fragments generated by nonsense mutations escape sib regulation, indicating that the regulation is translational and occurs near the completion stage of protein synthesis. Regulation by sib thus exhibits novel regulatory features: distal location, recombinational control, and regulation of the completion of protein synthesis. Because Int and Ea22 control is lost in a RNase III- host, we suggest that sib regulation might involve RNase III cleavage of a RNA duplex region that includes sib and the regulatory _target (normally the int gene). We note such a potential site within int.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J., Echols H. Regulation of int gene transcription by bacteriophage lambda. Location of the RNA start generated by an int constitutive mutation. J Mol Biol. 1981 Feb 15;146(1):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90371-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham J., Mascarenhas D., Fischer R., Benedik M., Campbell A., Echols H. DNA sequence of regulatory region for integration gene of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2477–2481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry G., Squires C., Squires C. L. Attenuation and processing of RNA from the rplJL--rpoBC transcription unit of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3331–3335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfort M. The cII-independent expression of the phage lambda int gene in RNase III-defective E. coli. Gene. 1980 Oct;11(1-2):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90094-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertani L. E. Split-operon control of a prophage gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Feb;65(2):331–336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.2.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Young R. A., Steitz J. A. The ribonuclease III site flanking 23S sequences in the 30S ribosomal precursor RNA of E. coli. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90513-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Court D., Green L., Echols H. Positive and negative regulation by the cII and cIII gene products of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1975 Feb;63(2):484–491. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90321-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. W. DNA sequence of the int-xis-Pi region of the bacteriophage lambda; overlap of the int and xis genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 25;8(8):1765–1782. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.8.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Effect of RNAase III, cleavage on translation of bacteriophage T7 messenger RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 15;99(3):487–499. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epp C., Pearson M. L., Enquist L. Downstream regulation of int gene expression by the b2 region in phage lambda. Gene. 1981 May;13(4):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. R., Howe M. New mutations in the S cistron of bacteriophage lambda affecting host cell lysis. Virology. 1969 May;38(1):200–202. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. E., Yarmolinsky M. B. Integration-negative mutants of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):487–505. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90423-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarneros G., Echols H. New mutants of bacteriophage lambda with a specific defect in excision from the host chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 14;47(3):565–574. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90323-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarneros G., Galindo J. M. The regulation of integrative recombination by the b2 region and the cII gene of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1979 May;95(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I., Hagen D. The lysis-lysogeny decision of phage lambda: explicit programming and responsiveness. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:399–445. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.002151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoess R. H., Foeller C., Bidwell K., Landy A. Site-specific recombination functions of bacteriophage lambda: DNA sequence of regulatory regions and overlapping structural genes for Int and Xis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2482–2486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu P. L., Ross W., Landy A. The lambda phage att site: functional limits and interaction with Int protein. Nature. 1980 May 8;285(5760):85–91. doi: 10.1038/285085a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., CAMPBELL A. Sur le système de répression assurant l'immunité chez les bactéries lysogenes. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1959 Jun 1;248(22):3219–3221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER G., ZICHICHI M. L., WEIGLE J. A mutation affecting the DNA content of bacteriophage lambda and its lysogenizing properties. J Mol Biol. 1961 Aug;3:399–408. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman J. F. Lambda site-specific recombination: local transcription and an inhibitor specified by the b2 region. Mol Gen Genet. 1974 Jun 27;130(4):333–344. doi: 10.1007/BF00333873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire G., Gold L., Yarus M. Autogenous translational repression of bacteriophage T4 gene 32 expression in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1978 Nov 25;126(1):73–90. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90280-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEntee K., Hesse J. E., Epstein W. Identification and radiochemical purification of the recA protein of Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3979–3983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMacken R., Mantei N., Butler B., Joyner A., Echols H. Effect of mutations in the c2 and c3 genes of bacteriophage lambda on macromolecular synthesis in infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 14;49(3):639–655. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90288-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Yates J. L., Dean D., Post L. E. Feedback regulation of ribosomal protein gene expression in Escherichia coli: structural homology of ribosomal RNA and ribosomal protein MRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7084–7088. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Huskey R. J. Deletion mutants of bacteriophage lambda. I. Isolation and initial characterization. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 14;56(2):369–384. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90471-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. ISOLATION OF THE lambda PHAGE REPRESSOR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):306–313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietra P. J., Molenaar J. L., Hamers M. N., Tager J. M., Borst P. Investigation of the alpha-galactosidase deficiency in Fabry's disease using antibodies against the purified enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):89–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehrdanz R. L., Dove W. F. A factor in the b2 region affecting site-specific recombinations in lambda. Virology. 1977 Jun 1;79(1):40–49. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90332-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada K., Campbell A. Int-constitutive mutants of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):237–241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]