Abstract
Aging is characterized by a progressive loss of physiological integrity, leading to impaired function and increased vulnerability to death. This deterioration is the primary risk factor for major human pathologies including cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases. Aging research has experienced an unprecedented advance over recent years, particularly with the discovery that the rate of aging is controlled, at least to some extent, by genetic pathways and biochemical processes conserved in evolution. This review enumerates nine tentative hallmarks that represent common denominators of aging in different organisms, with special emphasis on mammalian aging. These hallmarks are: genomic instability, telomere attrition, epigenetic alterations, loss of proteostasis, deregulated nutrient-sensing, mitochondrial dysfunction, cellular senescence, stem cell exhaustion, and altered intercellular communication. A major challenge is to dissect the interconnectedness between the candidate hallmarks and their relative contribution to aging, with the final goal of identifying pharmaceutical _targets to improve human health during aging with minimal side-effects.
Keywords: aging, cancer, DNA damage, epigenetic, healthspan, lifespan, longevity, metabolism, mitochondria, nutrient-signaling pathways, senescence, stem cells, telomeres
Introduction
Aging, which we broadly define as the time-dependent functional decline that affects most living organisms, has attracted curiosity and excited imagination throughout the history of humankind. However, it is only 30 years since a new era in aging research was inaugurated after the isolation of the first long-lived strains in Caenorhabditis elegans (Klass, 1983). Nowadays, aging is subjected to scientific scrutiny based on the ever-expanding knowledge of the molecular and cellular bases of life and disease. The current situation of aging research exhibits many parallels with that of cancer research in previous decades. The cancer field gained major momentum in 2000 with the publication of a landmark paper that enumerated six hallmarks of cancer (Hanahan and Weinberg, 2000), and that has been recently expanded to ten hallmarks (Hanahan and Weinberg, 2011). This categorization has helped to conceptualize the essence of cancer and its underlying mechanisms.
At first sight, cancer and aging may seem opposite processes: cancer is the consequence of an aberrant gain of cellular fitness, while aging is characterized by a loss of fitness. At a deeper level, however, cancer and aging may share common origins. The time-dependent accumulation of cellular damage is widely considered the general cause of aging (Gems and Partridge, 2013; Kirkwood, 2005; Vijg and Campisi, 2008). Concomitantly, cellular damage may occasionally provide aberrant advantages to certain cells, which can eventually produce cancer. Therefore, cancer and aging can be regarded as two different manifestations of the same underlying process, namely, the accumulation of cellular damage. In addition, several of the pathologies associated with aging, such as atherosclerosis and inflammation, involve uncontrolled cellular overgrowth or hyperactivity (Blagosklonny, 2008). Based on this conceptual framework, a series of critical questions have arisen in the field of aging regarding the physiological sources of aging-causing damage, the compensatory responses that try to re-establish homeostasis, the interconnection between the different types of damage and compensatory responses, and the possibilities to intervene exogenously to delay aging.
Here, we have attempted to identify and categorize the cellular and molecular hallmarks of aging. We propose nine candidate hallmarks that are generally considered to contribute to the aging process and together determine the aging phenotype (Figure 1). Given the complexity of the issue, we have emphasized current understanding of mammalian aging, while recognizing pioneer insights from simpler model organisms (Gems and Partridge, 2013; Kenyon, 2010). Each ‘hallmark’ should ideally fulfil the following criteria: (i) it should manifest during normal aging; (ii) its experimental aggravation should accelerate aging; and (iii) its experimental amelioration should retard the normal aging process and, hence, increase healthy lifespan. This set of ideal requisites is met to varying degrees by the proposed hallmarks, an aspect that will be discussed in detail for each of them. The last criterion is the most difficult to achieve, even if restricted to just one aspect of aging. For this reason, not all the hallmarks are fully supported yet by interventions that succeed in ameliorating aging. This caveat is tempered by the extensive interconnectedness between the aging hallmarks, implying that experimental amelioration of one particular hallmark may impinge on others.
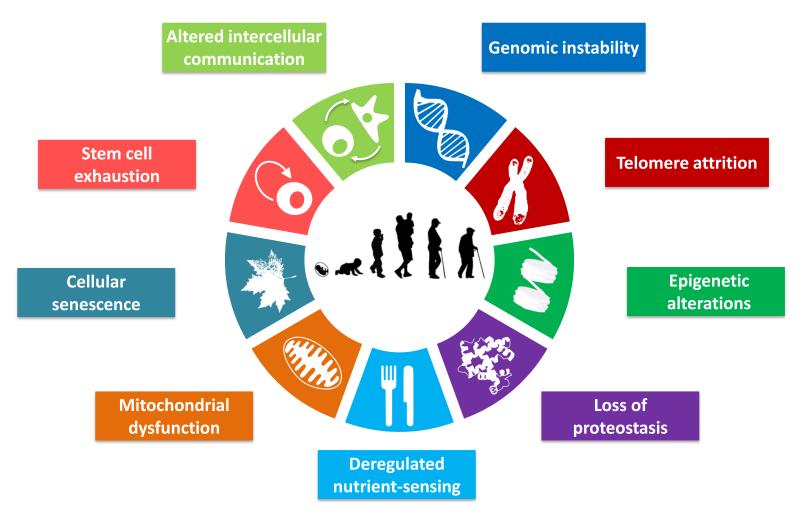
Figure 1. The Hallmarks of Aging.
The scheme enumerates the nine hallmarks described in this review: genomic instability, telomere attrition, epigenetic alterations, loss of proteostasis, deregulated nutrient-sensing, mitochondrial dysfunction, cellular senescence, stem cell exhaustion, and altered intercellular communication.
Genomic Instability
One common denominator of aging is the accumulation of genetic damage throughout life (Moskalev et al., 2012) (Figure 2A). Moreover, numerous premature aging diseases, such as Werner syndrome and Bloom syndrome, are the consequence of increased DNA damage accumulation (Burtner and Kennedy, 2010), although the relevance of these and other progeroid syndromes to normal aging remains unresolved due in part to the fact that they recapitulate only some aspects of aging. The integrity and stability of DNA is continuously challenged by exogenous physical, chemical and biological agents, as well as by endogenous threats including DNA replication errors, spontaneous hydrolytic reactions, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) (Hoeijmakers, 2009). The genetic lesions arising from extrinsic or intrinsic damage are highly diverse and include point mutations, translocations, chromosomal gains and losses, telomere shortening, and gene disruption caused by the integration of viruses or transposons. To minimize these lesions, organisms have evolved a complex network of DNA repair mechanisms that are collectively capable of dealing with most of the damage inflicted to nuclear DNA (Lord and Ashworth, 2012). The genomic stability systems also include specific mechanisms for maintaining the appropriate length and functionality of telomeres (which are the topic of a separate hallmark, see below), and for ensuring the integrity of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) (Blackburn et al., 2006; Kazak et al., 2012). In addition to these direct lesions in the DNA, defects in the nuclear architecture, known as laminopathies, can cause genome instability and result in premature aging syndromes (Worman, 2012).
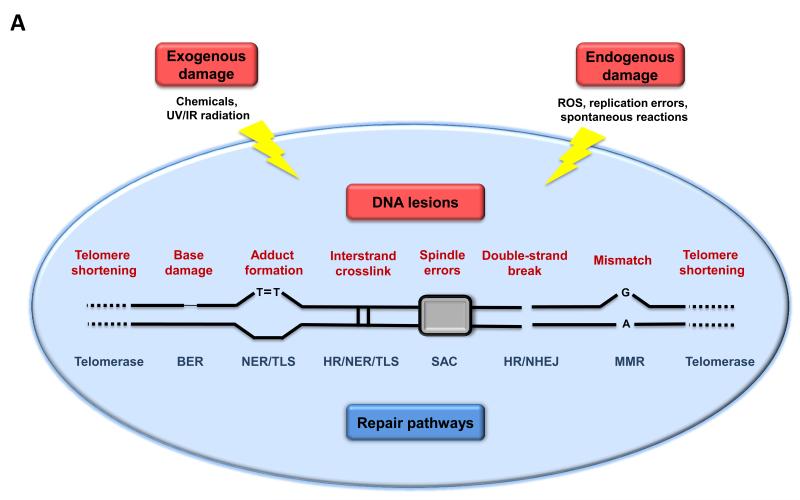
Figure 2. Genomic and Epigenomic Alterations.
A) Genomic instability and telomere attrition. Endogenous or exogenous agents can stimulate a variety of DNA lesions that are schematically represented on one single chromosome. Such lesions can by repaired by a variety of mechanisms. Excessive DNA damage or insufficient DNA repair favors the aging process. Note that both nuclear DNA and mitochondrial DNA (not represented here) are subjected to age-associated genomic alterations. BER, base excision repair; HR, homologous recombination; NER, nucleotide excision repair; NHEJ, non-homologous end joining; MMR, mismatch repair; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TLS, translesion synthesis; SAC, spindle assembly checkpoint.
B) Epigenetic alterations. Alterations in the acetylation and methylation of DNA or histones, as well as of other chromatin-associated proteins, can induce epigenetic changes that contribute to the aging process.
Nuclear DNA
Somatic mutations accumulate within cells from aged humans and model organisms (Moskalev et al., 2012). Other forms of DNA damage, such as chromosomal aneuploidies and copy-number variations have also been found associated with aging (Faggioli et al., 2012; Forsberg et al., 2012). Increased clonal mosaicism for large chromosomal anomalies has been also reported (Jacobs et al., 2012; Laurie et al., 2012). All these forms of DNA alterations may affect essential genes and transcriptional pathways, resulting in dysfunctional cells that, if not eliminated by apoptosis or senescence, may jeopardize tissue and organismal homeostasis. This is especially relevant when DNA damage impacts on the functional competence of stem cells, thus compromising their role in tissue renewal (Jones and Rando, 2011; Rossi et al., 2008) (see also the section Stem Cell Exhaustion).
Causal evidence for the proposed links between lifelong increase in genomic damage and aging has arisen from studies in mice and humans, showing that deficiencies in DNA repair mechanisms cause accelerated aging in mice and underlie several human progeroid syndromes such as Werner syndrome, Bloom syndrome, xeroderma pigmentosum, trichothiodystrophy, Cockayne syndrome, or Seckel syndrome (Gregg et al., 2012; Hoeijmakers, 2009; Murga et al., 2009). Moreover, transgenic mice overexpressing BubR1, a mitotic checkpoint component that ensures accurate segregation of chromosomes, exhibit an increased protection against aneuploidy and cancer, and extended healthy lifespan (Baker et al., 2012). These findings provide experimental evidence that artificial reinforcement of nuclear DNA repair mechanisms may delay aging.
Mitochondrial DNA
Mutations and deletions in aged mtDNA may also contribute to aging (Park and Larsson, 2011). mtDNA has been considered a major _target for aging-associated somatic mutations due to the oxidative microenvironment of the mitochondria, the lack of protective histones in the mtDNA, and the limited efficiency of the mtDNA repair mechanisms compared to those of nuclear DNA (Linnane et al., 1989). The causal implication of mtDNA mutations in aging has been controversial because of the multiplicity of mitochondrial genomes, which allows for the co-existence of mutant and wild-type genomes within the same cell, a phenomenon that is referred to as ‘heteroplasmy’. However, single-cell analyses have revealed that, despite the low overall level of mtDNA mutations, the mutational load of individual aging cells becomes significant and may attain a state of homoplasmy in which a mutant genome dominates the normal one (Khrapko et al., 1999). Interestingly, contrary to previous expectations, most mtDNA mutations in adult or aged cells appear to be caused by replication errors early in life, rather than by oxidative damage. These mutations may undergo polyclonal expansion and cause respiratory chain dysfunction in different tissues (Ameur et al., 2011). Studies of accelerated aging in HIV-infected patients treated with anti-retroviral drugs, which interfere with mtDNA replication, have supported the concept of clonal expansion of mtDNA mutations originated early in life (Payne et al., 2011).
The first evidence that mtDNA damage might be important for aging and age-related diseases derived from the identification of human multisystem disorders caused by mtDNA mutations that partially phenocopy aging (Wallace, 2005). Further causative evidence comes from studies on mice deficient in mitochondrial DNA polymerase γ. These mutant mice exhibit aspects of premature aging and reduced lifespan in association with the accumulation of random point mutations and deletions in mtDNA (Kujoth et al., 2005; Trifunovic et al., 2004; Vermulst et al., 2008). Cells from these mice show impaired mitochondrial function but, unexpectedly, this is not accompanied by increased ROS production (Edgar et al., 2009; Hiona et al., 2010). Moreover, stem cells from these progeroid mice are particularly sensitive to the accumulation of mtDNA mutations (Ahlqvist et al., 2012) (see also the section on Stem Cell Exhaustion). Future studies are necessary to determine whether genetic manipulations that decrease the load of mtDNA mutations are able to extend lifespan.
Nuclear architecture
In addition to genomic damage affecting nuclear or mtDNA, defects in the nuclear lamina can also cause genome instability (Dechat et al., 2008). Nuclear lamins constitute the major components of the nuclear lamina, and participate in genome maintenance by providing a scaffold for tethering chromatin and protein complexes that regulate genomic stability (Gonzalez-Suarez et al., 2009; Liu et al., 2005). The nuclear lamina attracted the attention of aging researchers after the discovery that mutations in genes encoding protein components of this structure, or factors affecting their maturation and dynamics, cause accelerated aging syndromes such as the Hutchinson-Gilford and the Néstor-Guillermo progeria syndromes (HGPS and NGPS, respectively) (Cabanillas et al., 2011; De Sandre-Giovannoli et al., 2003; Eriksson et al., 2003). Alterations of the nuclear lamina and production of an aberrant prelamin A isoform called progerin have also been detected during normal human aging (Ragnauth et al., 2010; Scaffidi and Misteli, 2006). Telomere dysfunction also promotes progerin production in normal human fibroblasts upon prolonged in vitro culture, suggesting intimate links between telomere maintenance and progerin expression during normal aging (Cao et al., 2011). In addition to these age-associated changes in A-type lamins, lamin B1 levels decline during cell senescence, pointing to its utility as a biomarker of this process (Freund et al., 2012; Shimi et al., 2011).
Animal and cellular models have facilitated the identification of the stress pathways elicited by aberrations in the nuclear lamina characteristic of HGPS. These pathways include the activation of p53 (Varela et al., 2005), deregulation of the somatotrophic axis (Marino et al., 2010), and attrition of adult stem cells (Espada et al., 2008; Scaffidi and Misteli, 2008). The causal relevance of nuclear lamina abnormalities in premature aging has been supported by the observation that decreasing prelamin A or progerin levels delays the onset of progeroid features and extends lifespan in mouse models of HGPS. This can be achieved by systemic injection of antisense oligonucleotides, farnesyltransferase inhibitors or a combination of statins and aminobisphosphonates (Osorio et al., 2011; Varela et al., 2008; Yang et al., 2006). Restoration of the somatotrophic axis through hormonal treatments or inhibition of NF-κB signaling also extends lifespan in these progeroid mice (Marino et al., 2010; Osorio et al., 2012). Moreover, a homologous recombination-based strategy has been developed to correct the LMNA mutations in induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) derived from HGPS patients, opening an avenue towards future cell therapies (Liu et al., 2011b). Further studies are necessary to validate the idea that reinforcement of the nuclear architecture can delay normal aging.
Overview
There is extensive evidence that genomic damage accompanies aging and that its artificial induction can provoke aspects of accelerated aging. In the case of the machinery that ensures faithful chromosomal segregation, there is genetic evidence that its enhancement can extend longevity in mammals (Baker et al., 2012). Also, in the particular case of progerias associated with nuclear architecture defects, there is proof of principle for treatments that can delay premature aging. Similar avenues should be explored to find interventions that reinforce other aspects of nuclear and mitochondrial genome stability, such as DNA repair, and their impact on normal aging (telomeres constitute a particular case and are discussed separately).
Telomere Attrition
Accumulation of DNA damage with age appears to affect the genome near-to-randomly, but there are some chromosomal regions, such as telomeres, that are particularly susceptible to age-related deterioration (Blackburn et al., 2006) (Figure 2A). Replicative DNA polymerases lack the capacity to replicate completely the terminal ends of linear DNA molecules, a function that is proprietary of a specialized DNA polymerase known as telomerase. However, most mammalian somatic cells do not express telomerase and this leads to the progressive and cumulative loss of telomere-protective sequences from chromosome ends. Telomere exhaustion explains the limited proliferative capacity of some types of in vitro cultured cells, the so-called replicative senescence or Hayflick limit (Hayflick and Moorhead, 1961; Olovnikov, 1996). Indeed, ectopic expression of telomerase is sufficient to confer immortality to otherwise mortal cells, without causing oncogenic transformation (Bodnar et al., 1998). Importantly, telomere shortening is also observed during normal aging both in human and mice (Blasco, 2007).
Telomeres can be regarded as DNA breaks that are made invisible to the DNA repair machinery through the formation of specialized nucleoprotein complex known as shelterin (Palm and de Lange, 2008). This adds another peculiarity to telomeres, not only telomeres are progressively shortened in the absence of telomerase but, also, even in the presence of telomerase, the infliction of exogenous DNA damage to telomeres becomes invisible to the DNA repair machineries due to the presence of shelterins. Therefore, DNA damage at telomeres causes a persistent type of DNA damage that leads to deleterious cellular effects including senescence and/or apoptosis (Fumagalli et al., 2012; Hewitt et al., 2012).
Telomerase deficiency in humans is associated with premature development of diseases, such as pulmonary fibrosis, dyskeratosis congenita and aplastic anemia, which involve the loss of the regenerative capacity of different tissues (Armanios and Blackburn, 2012). Severe telomere uncapping can also result from deficiencies in shelterin components (Palm and de Lange, 2008). Shelterin mutations have been found in some cases of aplastic anemia and dyskeratosis congenita (Savage et al., 2008; Walne et al., 2008; Zhong et al., 2011). Various loss-of-function models for shelterin components are characterized by rapid decline of the regenerative capacity of tissues and accelerated aging, a phenomenon that occurs even in the presence of telomeres with a normal length (Martinez and Blasco, 2010).
Genetically-modified animal models have established causal links between telomere loss, cellular senescence and organismal aging. Thus, mice with shortened or lengthened telomeres exhibit decreased or increased lifespan, respectively (Armanios et al., 2009; Rudolph et al., 1999; Tomas-Loba et al., 2008). Recent evidence also indicates that aging can be reverted by telomerase activation. In particular, the premature aging of telomerase-deficient mice can be reverted when telomerase is genetically reactivated in these aged mice (Jaskelioff et al., 2011). Moreover, normal physiological aging can be delayed without increasing the incidence of cancer in adult wild-type mice by pharmacological activation or systemic viral transduction of telomerase (Bernardes de Jesus et al., 2012; de Jesus et al., 2011). In humans, recent meta-analyses have indicated a strong relation between short telomeres and mortality risk, particularly at younger ages (Boonekamp et al., 2013).
Overview
Normal aging is accompanied by telomere attrition in mammals. Moreover, pathological telomere dysfunction accelerates aging in mice and humans, while experimental stimulation of telomerase can delay aging in mice, thus fulfilling all of the criteria for a hallmark of aging.
Epigenetic Alterations
A variety of epigenetic alterations affects all cells and tissues throughout life (Talens et al., 2012) (Figure 2B). Epigenetic changes involve alterations in DNA methylation patterns, post-translational modification of histones, and chromatin remodeling. Increased histone H4K16 acetylation, H4K20 trimethylation or H3K4 trimethylation, as well as decreased H3K9 methylation or H3K27 trimethylation, constitute age-associated epigenetic marks (Fraga and Esteller, 2007; Han and Brunet, 2012). The multiple enzymatic systems assuring the generation and maintenance of epigenetic patterns include DNA methyltransferases, histone acetylases, deacetylases, methylases and demethylases, as well as protein complexes implicated in chromatin remodeling.
Histone modifications
Histone methylation meets the criteria for a hallmark of aging in invertebrates. Deletion of components of histone methylation complexes extends longevity in nematodes and flies (Greer et al., 2010; Siebold et al., 2010). Moreover, histone demethylases modulate lifespan by _targeting components of key longevity routes such as the insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway (Jin et al., 2011). It is not clear yet whether manipulations of histone-modifying enzymes can influence aging through purely epigenetic mechanisms, by impinging on DNA repair and genome stability, or through transcriptional alterations affecting metabolic or signaling pathways outside of the nucleus.
The sirtuin family of NAD-dependent protein deacetylases and ADP-ribosyltransferases has been studied extensively as potential anti-aging factors. Interest in this family of proteins in relation to aging stems from a series of studies in yeast, flies and worms reporting that the single sirtuin gene of these organisms, named Sir2, had a remarkable longevity activity (Guarente, 2011). Overexpression of Sir2 was first shown to extend replicative lifespan in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Kaeberlein et al., 1999), and subsequent reports indicated that enhanced expression of the worm (sir-2.1) and fly (dSir2) orthologs could extend lifespan in both invertebrate model systems (Rogina and Helfand, 2004; Tissenbaum and Guarente, 2001). These findings have recently been called into question, however, with the report that the lifespan extension originally observed in the worm and fly studies was mostly due to confounding genetic background differences and not to the overexpression of sir-2.1 or dSir2, respectively (Burnett et al., 2011). In fact, careful reassessments indicate that overexpression of sir-2.1 only results in modest lifespan extension in C. elegans (Viswanathan and Guarente, 2011).
Regarding mammals, several studies have shown that several of the seven mammalian sirtuins can delay various parameters of aging in mice (Houtkooper et al., 2012; Sebastian et al., 2012). In particular, transgenic overexpression of mammalian SIRT1, which is the closest homologue to invertebrate Sir2, improves aspects of health during aging but does not increase longevity (Herranz et al., 2010). The mechanisms involved in the beneficial effects of SIRT1 are complex and interconnected, including a wide range of cellular actions from improved genomic stability (Oberdoerffer et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2008) to enhanced metabolic efficiency (Nogueiras et al., 2012) (see also Deregulated Nutrient-sensing). More compelling evidence for a sirtuin-mediated pro-longevity role in mammals has been obtained for SIRT6, which regulates genomic stability, NF-κB signaling and glucose homeostasis through histone H3K9 deacetylation (Kanfi et al., 2010; Kawahara et al., 2009; Zhong et al., 2010). Mutant mice deficient in SIRT6 exhibit accelerated aging (Mostoslavsky et al., 2006), whereas male transgenic mice overexpressing Sirt6 have a longer lifespan than control animals, associated with reduced serum IGF-1 and other indicators of IGF-1 signaling (Kanfi et al., 2012). Interestingly, the mitochondria-located SIRT3 has been reported to mediate some of the beneficial effects of dietary restriction (DR) in longevity, although its effects are not due to histone modifications but to the deacetylation of mitochondrial proteins (Someya et al., 2010). Very recently, overexpression of SIRT3 has been reported to reverse the regenerative capacity of aged hematopoietic stem cells (Brown et al., 2013). Therefore, in mammals, at least three members of the sirtuin family, SIRT1, SIRT3 and SIRT6, contribute to healthy aging.
DNA methylation
The relationship between DNA methylation and aging is complex. Early studies described an age-associated global hypomethylation, but subsequent analyses revealed that several loci, including those corresponding to various tumor suppressor genes and Polycomb _target genes, actually become hypermethylated with age (Maegawa et al., 2010). Cells from patients and mice with progeroid syndromes exhibit DNA methylation patterns and histone modifications that largely recapitulate those found in normal aging (Osorio et al., 2010; Shumaker et al., 2006). All of these epigenetic defects or epimutations accumulated throughout life may specifically affect the behavior and functionality of stem cells (Pollina and Brunet, 2011) (see section on Stem Cell Exhaustion). Nevertheless, thus far there is no direct experimental demonstration that organismal lifespan can be extended by altering patterns of DNA methylation.
Chromatin remodeling
DNA- and histone-modifying enzymes act in concert with key chromosomal proteins, such as the heterochromatin protein 1α (HP1α), and chromatin remodeling factors, such as Polycomb group proteins or the NuRD complex, whose levels are diminished in both normally and pathologically aged cells (Pegoraro et al., 2009; Pollina and Brunet, 2011). Alterations in these epigenetic factors together with the above discussed epigenetic modifications in histones and DNA-methylation determine changes in chromatin architecture, such as global heterochromatin loss and redistribution, which constitute characteristic features of aging (Oberdoerffer and Sinclair, 2007; Tsurumi and Li, 2012). The causal relevance of these chromatin alterations in aging is supported by the finding that flies with loss-of-function mutations in HP1α have a shortened lifespan, whereas overexpression of this heterochromatin protein extends longevity in flies and delays the muscular deterioration characteristic of old age (Larson et al., 2012).
Supporting the functional relevance of epigenetically-mediated chromatin alterations in aging, there is a notable connection between heterochromatin formation at repeated DNA domains and chromosomal stability. In particular, heterochromatin assembly at pericentric regions requires trimethylation of histones H3K9 and H4K20, as well as HP1α binding, and is important for chromosomal stability (Schotta et al., 2004). Mammalian telomeric repeats are also enriched for these chromatin modifications, indicating that chromosome ends are assembled into heterochromatin domains (Gonzalo et al., 2006). Subtelomeric regions also show features of constitutive heterochromatin including H3K9 and H4K20 trimethylation, HP1α binding, and DNA hypermethylation. Thus, epigenetic alterations can directly impinge on the regulation of telomere length, one of the hallmarks of aging. Moreover, in response to DNA damage, SIRT1 and other chromatin-modifying proteins relocalize to DNA breaks to promote repair and genomic stability (Oberdoerffer et al., 2008). Beyond its role in chromatin remodeling and DNA repair, SIRT1 also modulates proteostasis, mitochondrial function, nutrient-sensing pathways and inflammation (see below), illustrating the interconnectedness between aging hallmarks.
Transcriptional alterations
Aging is associated with an increase in transcriptional noise (Bahar et al., 2006), and an aberrant production and maturation of many mRNAs (Harries et al., 2011; Nicholas et al., 2010). Microarray-based comparisons of young and old tissues from several species have identified age-related transcriptional changes in genes encoding key components of inflammatory, mitochondrial and lysosomal degradation pathways (de Magalhaes et al., 2009). These aging-associated transcriptional signatures also affect non-coding RNAs, including a class of miRNAs (gero-miRs) that is associated with the aging process and influences lifespan by _targeting components of longevity networks or by regulating stem cell behavior (Boulias and Horvitz, 2012; Toledano et al., 2012; Ugalde et al., 2011). Gain- and loss-of-function studies have confirmed the capacity of several miRNAs to modulate longevity in Drosophila melanogaster and C. elegans (Liu et al., 2012; Shen et al., 2012; Smith-Vikos and Slack, 2012).
Reversion of epigenetic changes
Unlike DNA mutations, epigenetic alterations are – at least theoretically – reversible, hence offering opportunities for the design of novel anti-aging treatments (Freije and Lopez-Otin, 2012; Rando and Chang, 2012). Restoration of physiological H4 acetylation through administration of histone deacetylase inhibitors, avoids the manifestation of age-associated memory impairment in mice (Peleg et al., 2010), indicating that reversion of epigenetic changes may have neuroprotective effects. Inhibitors of histone acetyltransferases also ameliorate the premature aging phenotype and extend longevity of progeroid mice (Krishnan et al., 2011). Moreover, the recent discovery of transgenerational epigenetic inheritance of longevity in C. elegans suggests that manipulation of specific chromatin modifications in parents can induce an epigenetic memory of longevity in their descendants (Greer et al., 2011). Conceptually similar to histone acetyltransferase inhibitors, histone deacetylase activators may conceivably promote longevity. Resveratrol has been extensively studied in relation to aging and among its multiple mechanisms of action is the upregulation of SIRT1 activity, but also other effects associated with energetic deficits (see Mitochondrial Dysfunction).
Overview
There are multiple lines of evidence suggesting that aging is accompanied by epigenetic changes, and that epigenetic perturbations can provoke progeroid syndromes in model organisms. Furthermore, SIRT6 exemplifies an epigenetically relevant enzyme whose loss-of-function reduces longevity and whose gain-of-function extends longevity in mice (Kanfi et al., 2012; Mostoslavsky et al., 2006). Collectively, these works suggest that understanding and manipulating the epigenome holds promise for improving age-related pathologies and extending healthy lifespan.
Loss of Proteostasis
Aging and some aging-related diseases are linked to impaired protein homeostasis or proteostasis (Powers et al., 2009) (Figure 3). All cells take advantage of an array of quality control mechanisms to preserve the stability and functionality of their proteomes. Proteostasis involves mechanisms for the stabilization of correctly folded proteins, most prominently the heat-shock family of proteins, and mechanisms for the degradation of proteins by the proteasome or the lysosome (Hartl et al., 2011; Koga et al., 2011; Mizushima et al., 2008). Moreover, there are regulators of age-related proteotoxicity, such as MOAG-4, that act through an alternative pathway distinct from molecular chaperones and proteases (van Ham et al., 2010). All these systems function in a coordinated fashion to restore the structure of misfolded polypeptides or to remove and degrade them completely, thus preventing the accumulation of damaged components and assuring the continuous renewal of intracellular proteins. Accordingly, many studies have demonstrated that proteostasis is altered with aging (Koga et al., 2011). Additionally, chronic expression of unfolded, misfolded or aggregated proteins contributes to the development of some age-related pathologies, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and cataracts (Powers et al., 2009).
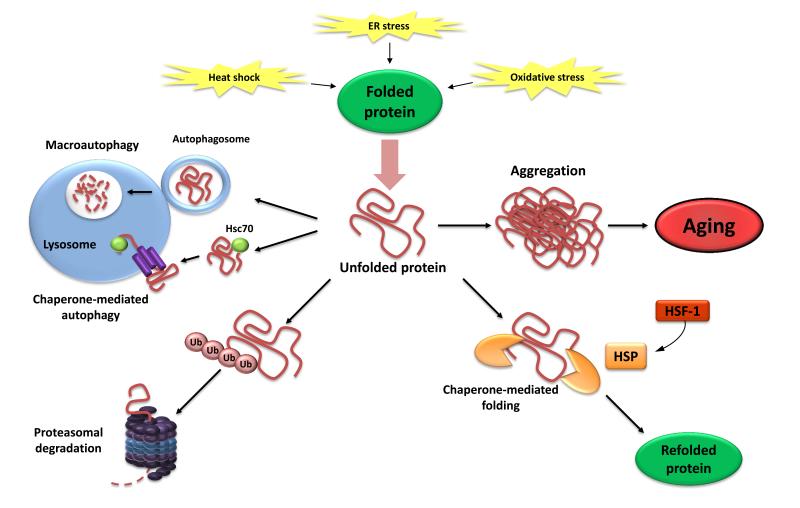
Figure 3. Loss of Proteostasis.
Endogenous and exogenous stress causes the unfolding of proteins (or impairs proper folding during protein synthesis). Unfolded proteins are usually refolded by heat-shock proteins (HSP) or _targeted to destruction by the ubiquitin-proteasome or lysosomal (autophagic) pathways. The autophagic pathways include recognition of unfolded proteins by the chaperone Hsc70 and their subsequent import into lysosomes (chaperone-mediated autophagy) or sequestration of damaged proteins and organelles in autophagosomes that later fuse with lysosomes (macroautophagy). Failure to refold or degrade unfolded proteins can lead to their accumulation and aggregation, resulting in proteotoxic effects.
Chaperone-mediated protein folding and stability
The stress-induced synthesis of cytosolic and organelle-specific chaperones is significantly impaired in aging (Calderwood et al., 2009). A number of animal models support a causative impact of chaperone decline on longevity. In particular, transgenic worms and flies overexpressing chaperones are long-lived (Morrow et al., 2004; Walker and Lithgow, 2003). Also, mutant mice deficient in a co-chaperone of the heat-shock family exhibit accelerated-aging phenotypes, whereas long-lived mouse strains show a marked up-regulation of some heat-shock proteins (Min et al., 2008; Swindell et al., 2009). Moreover, activation of the master regulator of the heat-shock response, the transcription factor HSF-1, increases longevity and thermotolerance in nematodes (Chiang et al., 2012; Hsu et al., 2003), while amyloid-binding components can maintain proteostasis during aging and extend lifespan (Alavez et al., 2011). In mammalian cells, deacetylation of HSF-1 by SIRT1 potentiates the transactivation of heat-shock genes such as Hsp70, whereas down-regulation of SIRT1 attenuates the heat-shock response (Westerheide et al., 2009).
Several approaches for maintaining or enhancing proteostasis aim at activating protein folding and stability mediated by chaperones. Pharmacological induction of the heat-shock protein Hsp72 preserves muscle function and delays progression of dystrophic pathology in mouse models of muscular dystrophy (Gehrig et al., 2012). Small molecules may be also employed as pharmacological chaperones to assure the refolding of damaged proteins and to improve age-related phenotypes in model organisms (Calamini et al., 2012).
Proteolytic systems
The activities of the two principal proteolytic systems implicated in protein quality control, namely, the autophagy-lysosomal system and the ubiquitin-proteasome system, decline with aging (Rubinsztein et al., 2011; Tomaru et al., 2012), supporting the idea that collapsing proteostasis constitutes a common feature of old age.
Regarding autophagy, transgenic mice with an extra copy of the chaperone-mediated autophagy receptor LAMP2a do not experience aging-associated decline in autophagic activity and preserve improved hepatic function with aging (Zhang and Cuervo, 2008). Interventions using chemical inducers of macroautophagy (another type of autophagy different from chaperone-mediated autophagy) have spurred extraordinary interest after the discovery that constant or intermittent administration of the mTOR inhibitor rapamycin can increase the lifespan of middle-aged mice (Blagosklonny, 2011; Harrison et al., 2009). Notably, rapamycin delays multiple aspects of aging in mice (Wilkinson et al., 2012). The lifespan-extending effect of rapamycin is strictly dependent on the induction of autophagy in yeast, nematodes and flies (Bjedov et al., 2010; Rubinsztein et al., 2011). However, similar evidence does not exist yet for the effects of rapamycin on mammalian aging, and other mechanisms such as inhibition of the ribosomal S6 protein kinase 1 (S6K1) implicated in protein synthesis (Selman et al., 2009), could contribute to explain the pro-longevity effects of rapamycin (see section on Deregulated Nutrient-sensing). Spermidine, another macroautophagy inducer that, in contrast to rapamycin, has no immunosuppressive side-effects, also promotes longevity in yeast, flies and worms via the induction of autophagy (Eisenberg et al., 2009). Similarly, nutrient supplementation with polyamine preparations containing spermidine or provision of a polyamine-producing gut flora increases longevity in mice (Matsumoto et al., 2011; Soda et al., 2009). Dietary supplementation with ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids also extends lifespan in nematodes through autophagy activation (O’Rourke et al., 2013).
In relation to the proteasome, activation of EGF-signaling extends longevity in nematodes by increasing the expression of various components of the ubiquitin-proteasome system (Liu et al., 2011a). Likewise, the enhancement of proteasome activity by deubiquitylase inhibitors or proteasome activators accelerates the clearance of toxic proteins in human cultured cells (Lee et al., 2010), and extends replicative lifespan in yeast (Kruegel et al., 2011). Moreover, increased expression of the proteasome subunit RPN-6 by the FOXO transcription factor DAF-16 confers proteotoxic stress resistance and extends lifespan in C. elegans (Vilchez et al., 2012).
Overview
There is evidence that aging is associated with perturbed proteostasis, and experimental perturbation of proteostasis can precipitate age-associated pathologies. There are also promising examples of genetic manipulations that improve proteostasis and delay aging in mammals (Zhang and Cuervo, 2008).
Deregulated Nutrient-sensing
The somatotrophic axis in mammals comprises the growth hormone (GH), produced by the anterior pituitary, and its secondary mediator, the insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1), produced in response to GH by many cell types, most notably hepatocytes. The intracellular signaling pathway of IGF-1 is the same as that elicited by insulin, which informs cells of the presence of glucose. For this reason, IGF-1 and insulin signaling are known as the ‘insulin and IGF-1 signaling’ (IIS) pathway. Remarkably, the IIS pathway is the most conserved aging-controlling pathway in evolution and among its multiple _targets are the FOXO family of transcription factors and the mTOR complexes, which are also involved in aging and conserved through evolution (Barzilai et al., 2012; Fontana et al., 2010; Kenyon, 2010). Genetic polymorphisms or mutations that reduce the functions of GH, IGF-1 receptor, insulin receptor or downstream intracellular effectors such as AKT, mTOR and FOXO, have been linked to longevity, both in humans and in model organisms, further illustrating the major impact of trophic and bioenergetic pathways on longevity (Barzilai et al., 2012; Fontana et al., 2010; Kenyon, 2010) (Figure 4A).
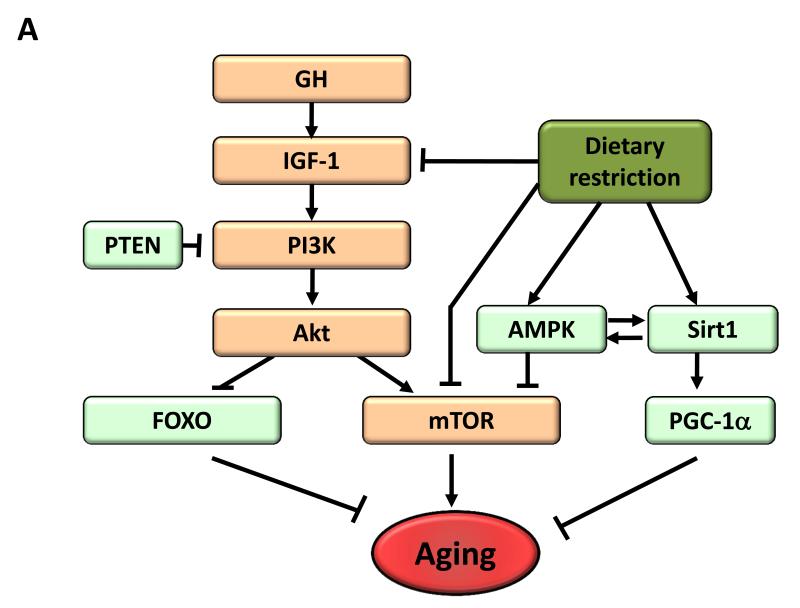
Figure 4. Metabolic Alterations.
A) Deregulated nutrient-sensing. Overview of the somatroph axis involving growth hormone (GH) and the insulin/insulin growth factor 1 (IGF-1) signaling pathway, and its relationship to dietary restriction and aging. Molecules that favor aging are shown in orange, while molecules with anti-aging properties are shown in light green.
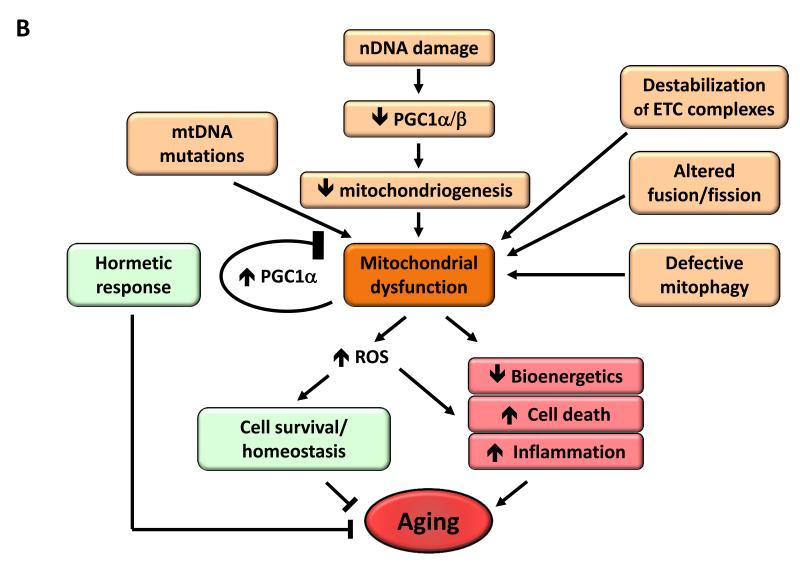
B) Mitochondrial dysfunction. Mitochondrial function becomes perturbed by aging-associated mtDNA mutations, reduced mitochondriogenesis, destabilization of the electron transport chain (ETC) complexes, altered mitochondrial dynamics or defective quality control by mitophagy. Stress signals and defective mitochondrial function generate ROS that, below a certain threshold, induce survival signals to restore cellular homeostasis, but at higher or continued levels can contribute to aging. Similarly, mild mitochondrial damage can induce a hormetic response (mitohormesis) that triggers adaptive compensatory processes.
Consistent with the relevance of deregulated nutrient-sensing as a hallmark of aging, dietary restriction (DR) increases lifespan or healthspan in all investigated eukaryote species, including unicellular and multicellular organisms of several distinct phyla, including non-human primates (Colman et al., 2009; Fontana et al., 2010; Mattison et al., 2012).
The insulin and IGF-1 signaling pathway
Multiple genetic manipulations that attenuate signaling intensity at different levels of the IIS pathway consistently extend the lifespan of worms, flies and mice (Fontana et al., 2010). Genetic analyses indicate that this pathway mediates part of the beneficial effects of DR on longevity in worms and flies (Fontana et al., 2010). Among the downstream effectors of the IIS pathway, the most relevant one for longevity in worms and flies is the transcription factor FOXO (Kenyon et al., 1993; Slack et al., 2011). In mice, there are four FOXO members, but the effect of their over-expression on longevity and their role in mediating increased healthspan through reduced IIS have not yet been determined. Mouse FOXO1 is required for the tumor suppressive effect of DR (Yamaza et al., 2010), but it is not yet known whether this factor is involved in DR-mediated lifespan extension. Mice with increased dosage of the tumor suppressor PTEN exhibit a general down-modulation of the IIS pathway and an increased energy expenditure that is associated with improved mitochondrial oxidative metabolism, as well as with an enhanced activity of the brown adipose tissue (Garcia-Cao et al., 2012; Ortega-Molina et al., 2012). In line with other mouse models with decreased IIS activity, Pten-overexpressing mice, as well as hypomorphic PI3K mice show an increased longevity (Foukas et al., 2013; Ortega-Molina et al., 2012).
Paradoxically, GH and IGF-1 levels decline during normal aging, as well as in mouse models of premature aging (Schumacher et al., 2008). Thus, a decreased IIS is a common characteristic of both physiological and accelerated aging, while a constitutively decreased IIS extends longevity. These apparently contradictory observations could be accommodated under a unifying model by which IIS down-modulation reflects a defensive response aimed at minimizing cell growth and metabolism in the context of systemic damage (Garinis et al., 2008). According to this view, organisms with a constitutively decreased IIS can survive longer because they have lower rates of cell growth and metabolism, and hence lower rates of cellular damage. Along the same lines, physiologically or pathologically aged organisms decrease IIS in an attempt to extend their lifespan. However, and this is a concept that will recur in the following sections, defensive responses against aging may have the risk of eventually becoming deleterious and aggravating aging. Thus, extremely low levels of IIS signaling are incompatible with life, as exemplified by mouse null mutations in the PI3K or AKT kinases that are embryonic lethal (Renner and Carnero, 2009). Also, there are cases of progeroid mice with very low levels of IGF-1, in which supplementation of IGF-1 can ameliorate premature aging (Marino et al., 2010).
Other nutrient-sensing systems: mTOR, AMPK and sirtuins
In addition to the IIS pathway that participates in glucose-sensing, three additional related and interconnected nutrient-sensing systems are the focus of intense investigation: mTOR, for the sensing of high amino acid concentrations; AMPK, which senses low energy states by detecting high AMP levels; and sirtuins, which sense low energy states by detecting high NAD+ levels (Houtkooper et al., 2010) (Figure 4A).
The mTOR kinase is part of two multiprotein complexes, mTORC1 and mTORC2, that regulate essentially all aspects of anabolic metabolism (Laplante and Sabatini, 2012). Genetic down-regulation of mTORC1 activity in yeast, worms and flies extends longevity and attenuates further longevity benefits from DR, suggesting that mTOR inhibition phenocopies DR (Johnson et al., 2013). In mice, treatment with rapamycin also extends longevity in what is considered the most robust chemical intervention to increase lifespan in mammals (Harrison et al., 2009). Genetically-modified mice with low levels of mTORC1 activity, but normal levels of mTORC2, have increased lifespan (Lamming et al., 2012), and mice deficient in S6K1 (a main mTORC1 substrate) are also long-lived (Selman et al., 2009), thus pointing to the downregulation of mTORC1/S6K1 as the critical mediator of longevity in relation to mTOR. Moreover, mTOR activity increases during aging in mouse hypothalamic neurons, contributing to age-related obesity, which is reversed by direct infusion of rapamycin to the hypothalamus (Yang et al., 2012). These observations, together with those involving the IIS pathway, indicate that intense trophic and anabolic activity, signaled through the IIS or the mTORC1 pathways, are major accelerators of aging. Although inhibition of TOR activity clearly has beneficial effects during aging, it also has undesirable side-effects, such as impaired wound healing, insulin resistance, cataract and testicular degeneration in mice (Wilkinson et al., 2012). It will thus be important to understand the mechanisms involved, in order to determine the extent to which beneficial and damaging effects of TOR inhibition can be separated from each other.
The other two nutrient sensors, AMPK and sirtuins, act in the opposite direction to IIS and mTOR, meaning that they signal nutrient scarcity and catabolism instead of nutrient abundance and anabolism. Accordingly, their up-regulation favors healthy aging. AMPK activation has multiple effects on metabolism and, remarkably, shuts off mTORC1 (Alers et al., 2012). There is evidence indicating that AMPK activation may mediate lifespan-extension following metformin administration to worms and mice (Anisimov et al., 2011; Mair et al., 2011; Onken and Driscoll, 2010). The role of sirtuins in lifespan regulation has been discussed above (see section on Epigenetic Alterations). In addition, SIRT1 can deacetylate and activate the PPARγ co-activator 1α (PGC-1α) (Rodgers et al., 2005). PGC-1α orchestrates a complex metabolic response that includes mitochondriogenesis, enhanced anti-oxidant defenses, and improved fatty acid oxidation (Fernandez-Marcos and Auwerx, 2011). Moreover, SIRT1 and AMPK can engage in a positive feedback loop, thus connecting both sensors of low-energy states into a unified response (Price et al., 2012).
Overview
Collectively, current available evidence strongly supports the idea that anabolic signaling accelerates aging, and decreased nutrient signaling extends longevity (Fontana et al., 2010). Even more, a pharmacological manipulation that mimics a state of limited nutrient availability, such as rapamycin, can extend longevity in mice (Harrison et al., 2009).
Mitochondrial Dysfunction
As cells and organisms age, the efficacy of the respiratory chain tends to diminish, thus increasing electron leakage and reducing ATP generation (Green et al., 2011) (Figure 4B). The relation between mitochondrial dysfunction and aging has been long suspected but dissecting its details remains as a major challenge for aging research.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS)
The mitochondrial free radical theory of aging proposes that the progressive mitochondrial dysfunction that occurs with aging results in increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which in turn causes further mitochondrial deterioration and global cellular damage (Harman, 1965). Multiple data support a role for ROS in aging, but we focus here on the developments of the last five years which have forced an intense re-evaluation of the mitochondrial free radical theory of aging (Hekimi et al., 2011). Of particular impact has been the unexpected observation that increased ROS may prolong lifespan in yeast and C. elegans (Doonan et al., 2008; Mesquita et al., 2010; Van Raamsdonk and Hekimi, 2009). In mice, genetic manipulations that increase mitochondrial ROS and oxidative damage do not accelerate aging (Van Remmen et al., 2003; Zhang et al., 2009), manipulations that increase antioxidant defenses do not extend longevity (Perez et al., 2009), and, finally, genetic manipulations that impair mitochondrial function but do not increase ROS accelerate aging (Edgar et al., 2009; Hiona et al., 2010; Kujoth et al., 2005; Trifunovic et al., 2004; Vermulst et al., 2008). These and similar data have paved the way to a reconsideration of the role of ROS in aging (Ristow and Schmeisser, 2011). Indeed, parallel and separate to the work on the damaging effects of ROS, the field of intracellular signaling has been accumulating solid evidence for the role of ROS in triggering proliferative and survival signals, in response to physiological signals and stress conditions (Sena and Chandel, 2012). The two lines of evidence can be harmonized if ROS is regarded as a stress-elicited survival signal aimed at compensating for the progressive deterioration associated with aging. As chronological age advances, the levels of ROS increase in an attempt to maintain survival until they betray their original purpose and eventually aggravate, rather than alleviate, the age-associated damage (Hekimi et al., 2011). This new conceptual framework may accommodate apparently conflicting evidence regarding the positive, negative or neutral effects of ROS on aging.
Mitochondrial integrity and biogenesis
Dysfunctional mitochondria can contribute to aging independently of ROS, as exemplified by studies with mice deficient in DNA polymerase γ (Edgar et al., 2009; Hiona et al., 2010) (see above Genomic Instability). This could happen through a number of mechanisms, for example, mitochondrial deficiencies may affect apoptotic signaling by increasing the propensity of mitochondria to permeabilize in response to stress (Kroemer et al., 2007), and trigger inflammatory reactions by favoring ROS-mediated and/or permeabilization-facilitated activation of inflammasomes (Green et al., 2011). Also, mitochondrial dysfunction may directly impact on cellular signaling and interorganellar crosstalk, by affecting mitochondrion-associated membranes that constitute an interface between the outer mitochondrial membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum (Raffaello and Rizzuto, 2011).
The reduced efficiency of mitochondrial bioenergetics with aging may result from multiple converging mechanisms including reduced biogenesis of mitochondria, for instance as a consequence of telomere attrition in telomerase-deficient mice, with subsequent p53-mediated repression of PGC-1α and PGC-1β (Sahin and Depinho, 2012). This mitochondrial decline also occurs during physiological aging in wild-type mice and can be partially reversed by telomerase activation (Bernardes de Jesus et al., 2012). SIRT1 modulates mitochondrial biogenesis through a process involving the transcriptional co-activator PGC-1α (Rodgers et al., 2005) and the removal of damaged mitochondria by autophagy (Lee et al., 2008). SIRT3, which is the main mitochondrial deacetylase (Lombard et al., 2007), _targets many enzymes involved in energy metabolism, including components of the respiratory chain, tricarboxylic acid cycle, ketogenesis and fatty acid β-oxidation pathways (Giralt and Villarroya, 2012). SIRT3 may also directly control the rate of ROS production by deacetylating manganese superoxide dismutase, a major mitochondrial antioxidant enzyme (Qiu et al., 2010; Tao et al., 2010). Collectively, these results support the idea that sirtuins may act as metabolic sensors to control mitochondrial function and play a protective role against age-associated diseases.
Other mechanisms causing defective bioenergetics include accumulation of mutations and deletions in mtDNA, oxidation of mitochondrial proteins, destabilization of the macromolecular organization of respiratory chain (super)complexes, changes in the lipid composition of mitochondrial membranes, alterations in mitochondrial dynamics resulting from imbalance of fission and fusion events, and defective quality control by mitophagy, an organelle-specific form of macroautophagy that _targets deficient mitochondria for proteolytic degradation (Wang and Klionsky, 2011). The combination of increased damage and reduced turnover in mitochondria, due to lower biogenesis and reduced clearance, may contribute to the aging process (Figure 4B).
Interestingly, endurance training and alternate-day-fasting may improve healthspan through their capacity to avoid mitochondrial degeneration (Castello et al., 2011; Safdar et al., 2011). It is tempting to speculate that these beneficial effects are mediated, at least in part, through the induction of autophagy, for which both endurance training and fasting constitute potent triggers (Rubinsztein et al., 2011). However, autophagy induction is probably not the sole mechanism through which a healthy lifestyle can retard aging since, depending on the precise DR regime, additional longevity pathways can be activated (Kenyon, 2010).
Mitohormesis
Mitochondrial dysfunctions during aging are also connected with hormesis, a concept on which a number of aging research lines have recently converged (Calabrese et al., 2011). According to this concept, mild toxic treatments trigger beneficial compensatory responses that surpass the repair of the triggering damage, and actually produce an improvement in cellular fitness when compared to the starting pre-damage conditions. Thus, although severe mitochondrial dysfunction is pathogenic, mild respiratory deficiencies may increase lifespan, perhaps due to a hormetic response (Haigis and Yankner, 2010). Such hormetic reactions may consist in the induction of a mitochondrial stress response either in the same tissue in which mitochondria are defective, or even in distant tissues, as shown in C. elegans (Durieux et al., 2011). There is compelling evidence that compounds such as metformin and resveratrol are mild mitochondrial poisons that induce a low energy state characterized by increased AMP levels and activation of AMPK (Hawley et al., 2010). Importantly, metformin extends lifespan in C. elegans through the induction of a compensatory stress response mediated by AMPK and the master anti-oxidant regulator Nrf2 (Onken and Driscoll, 2010). Recent studies have also shown that metformin retards aging in worms by impairing folate and methionine metabolism of their intestinal microbiome (Cabreiro et al., 2013). Regarding mammals, metformin can increase mouse lifespan when administered from early life (Anisimov et al., 2011). In the cases of resveratrol and the sirtuin activator SRT1720, there is convincing evidence that they protect from metabolic damage and improve mitochondrial respiration in a PGC-1α-dependent fashion (Baur et al., 2006; Feige et al., 2008; Lagouge et al., 2006; Minor et al., 2011), although resveratrol does not extend mouse lifespan under normal dietary conditions (Pearson et al., 2008; Strong et al., 2012). Further support for the role of PGC-1α in longevity comes from the observation that PGC-1α overexpression suffices to extend Drosophila lifespan in association with improved mitochondrial activity (Rera et al., 2011). Finally, mitochondrial uncoupling, either genetically through the overexpression of the uncoupling protein UCP1 or by administration of the chemical uncoupler 2-4-dinitrophenol can increase lifespan in flies and mice (Caldeira da Silva et al., 2008; Fridell et al., 2009; Gates et al., 2007; Mookerjee et al., 2010).
Overview
Mitochondrial function has a profound impact on the aging process. Mitochondrial dysfunction can accelerate aging in mammals (Kujoth et al., 2005; Trifunovic et al., 2004; Vermulst et al., 2008), but it is less clear whether improving mitochondrial function, for example through mitohormesis, can extend lifespan in mammals, although suggestive evidence in this sense already exists.
Cellular Senescence
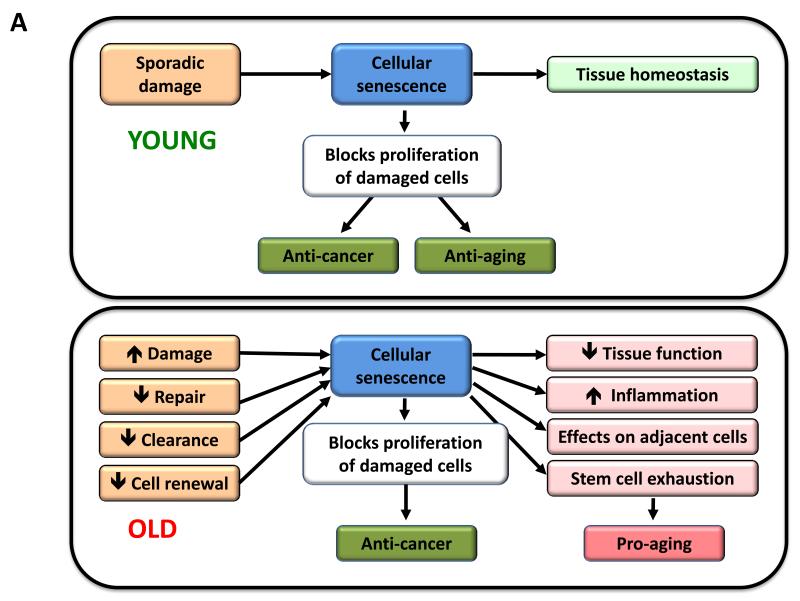
Cellular senescence can be defined as a stable arrest of the cell cycle coupled to stereotyped phenotypic changes (Campisi and d’Adda di Fagagna, 2007; Collado et al., 2007; Kuilman et al., 2010) (Figure 5A). This phenomenon was originally described by Hayflick in human fibroblasts serially passaged in culture (Hayflick and Moorhead, 1961). Today, we know that the senescence observed by Hayflick is caused by telomere shortening (Bodnar et al., 1998), but there are other aging-associated stimuli that trigger senescence independently of this telomeric process. Most notably, non-telomeric DNA damage and de-repression of the INK4/ARF locus, both of which progressively occur with chronological aging, are also capable of inducing senescence (Collado et al., 2007). The accumulation of senescent cells in aged tissues has been often inferred using surrogate markers such as DNA damage. Some studies have directly used senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SABG) to identify senescence in tissues (Dimri et al., 1995). Of note, a detailed and parallel quantification of SABG and DNA damage in liver produced comparable quantitative data, yielding a total of ~8 % senescent cells in young mice and ~17% in very old mice (Wang et al., 2009). Similar results were obtained in the skin, lung and spleen, but no changes were observed in heart, skeletal muscle and kidney (Wang et al., 2009). Based on these data, it is clear that cellular senescence is not a generalized property of all tissues in aged organisms. In the case of senescent tumor cells, there is good evidence that they are subjected to strict immune surveillance and are efficiently removed by phagocytosis (Hoenicke and Zender, 2012; Kang et al., 2011; Xue et al., 2007). Conceivably, the accumulation of senescent cells with aging can reflect an increase in the rate of generation of senescent cells and/or a decrease in their rate of clearance, for example, as a consequence of an attenuated immune response.
Figure 5. Cellular Senescence, Stem Cell Exhaustion and Altered Intercellular Communication.
A) Cellular senescence. In young organisms, cellular senescence prevents the proliferation of damaged cells, thus protecting from cancer and contributing to tissue homeostasis. In old organisms, the pervasive damage and the deficient clearance and replenishment of senescent cells results in their accumulation, and this has a number of deleterious effects on tissue homeostasis that contribute to aging.
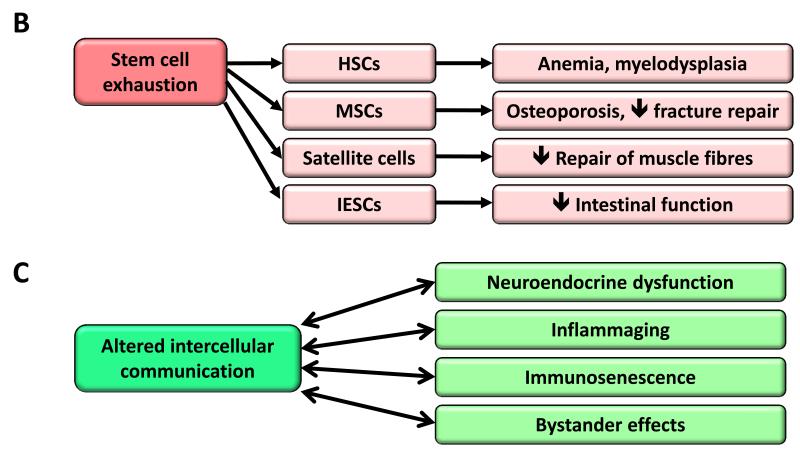
B) Stem cell exhaustion. Consequences of the exhaustion of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), satellite cells and intestinal epithelial stem cells (IESCs) are exemplified.
C) Altered intercellular communication. Examples of altered intercellular communication associated with aging.
Since the amount of senescent cells increases with aging, it has been widely assumed that senescence contributes to aging. However, this view undervalues what conceivably is the primary purpose of senescence, which is to prevent the propagation of damaged cells and to trigger their demise by the immune system. Therefore, it is possible that senescence is a beneficial compensatory response that contributes to rid tissues from damaged and potentially oncogenic cells. This cellular checkpoint, however, requires an efficient cell replacement system that involves clearance of senescent cells and mobilization of progenitors to re-establish cell numbers. In aged organisms, this turnover system may become inefficient or may exhaust the regenerative capacity of progenitor cells, eventually resulting in the accumulation of senescent cells that may aggravate the damage and contribute to aging (Figure 5A).
In recent years, it has been appreciated that senescent cells manifest dramatic alterations in their secretome, which is particularly enriched in pro-inflammatory cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases, and is referred to as the ‘senescence-associated secretory phenotype’ (Kuilman et al., 2010; Rodier and Campisi, 2011). This pro-inflammatory secretome may contribute to aging (see section on Intercellular Communication).
The INK4a/ARF locus and p53
In addition to DNA damage, excessive mitogenic signaling is the other stress most robustly associated to senescence. A recent account listed more than 50 oncogenic or mitogenic alterations that are able to induce senescence (Gorgoulis and Halazonetis, 2010). The number of mechanisms that implement senescence in response to this variety of oncogenic insults has also grown, but, still, the originally reported p16INK4a/Rb and p19ARF/p53 pathways remain, in general, the most important ones (Serrano et al., 1997). The relevance of these pathways for aging becomes even more striking when considering that the levels of p16INK4a (and to a lower extent also p19ARF) correlate with the chronological age of essentially all tissues analyzed, both in mice and humans (Krishnamurthy et al., 2004; Ressler et al., 2006). We are not aware of any other gene or protein whose expression is so robustly correlated with chronological aging, across tissues, across species, and with a range of variation that, on average, is one order of magnitude between young and old tissues. Both p16INK4a and p19ARF are encoded by the same genetic locus, the INK4a/ARF locus. A recent meta-analysis of more than 300 genome wide association studies (GWAS) identified the INK4a/ARF locus as the genomic locus that is genetically linked to the highest number of age-associated pathologies, including several types of cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, glaucoma, and Alzheimer’s disease (Jeck et al., 2012).
The critical role of p16INK4a and p53 in the induction of cell senescence has favored the hypothesis that p16INK4a-induced and p53-induced senescence contribute to physiological aging. According to this view, the pro-aging activity of p16INK4a and p53 would be a tolerable toll compared to their benefits in tumor suppression. In support of this, mutant mice with premature aging due to extensive and persistent damage, present dramatic levels of senescence and their progeroid phenotypes are ameliorated by elimination of p16Ink4a or p53. This is the case of mice deficient in BRCA1 (Cao et al., 2003), of a mouse model of HGPS (Varela et al., 2005), and of mice with defective chromosomal stability due to a hypomorphic mutation of BubR1 (Baker et al., 2011). However, other evidence suggests a more complicated picture. In contrast to their anticipated pro-aging role, mice with a mild and systemic increase in p16Ink4a, p19Arf or p53 tumor suppressors exhibit extended longevity, which cannot be accounted for by their lower cancer incidence (Matheu et al., 2009; Matheu et al., 2007). Also, elimination of p53 aggravates the phenotypes of some progeroid mutant mice (Begus-Nahrmann et al., 2009; Murga et al., 2009; Ruzankina et al., 2009). Again, as discussed above for senescence, the activation of p53 and INK4a/ARF can be regarded as a beneficial compensatory response aimed at avoiding the propagation of damaged cells and its consequences on aging and cancer. However, when damage is pervasive, the regenerative capacity of tissues can be exhausted or saturated and, under these extreme conditions, the p53 and INK4a/ARF responses can become deleterious and accelerate aging.
Overview
We propose that cellular senescence is a beneficial compensatory response to damage that becomes deleterious and accelerates aging when tissues exhaust their regenerative capacity. Given these complexities, it is not possible to give a simple answer to the question of whether cell senescence fulfills the third ideal criteria for the definition of a hallmark. A moderate enhancement of the senescence-inducing tumor suppressor pathways may extend longevity (Matheu et al., 2009; Matheu et al., 2007), and, at the same time, elimination of senescent cells in an experimental progeria model delays age-related pathologies (Baker et al., 2011). Therefore, two interventions that are conceptually opposite are able to extend healthspan.
Stem Cell Exhaustion
The decline in the regenerative potential of tissues is one of the most obvious characteristics of aging (Figure 5B). For example, hematopoiesis declines with age, resulting in a diminished production of adaptive immune cells, a process termed immunosenescence, and in an increased incidence of anemia and myeloid malignancies (Shaw et al., 2010). A similar functional attrition of stem cells has been found in essentially all adult stem cell compartments, including the mouse forebrain (Molofsky et al., 2006), the bone (Gruber et al., 2006), or the muscle fibers (Conboy and Rando, 2012). Studies on aged mice have revealed an overall decrease in cell cycle activity of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), with old HSCs undergoing fewer cell divisions than young HSCs (Rossi et al., 2007). This correlates with the accumulation of DNA damage (Rossi et al., 2007), and with the overexpression of cell cycle-inhibitory proteins such as p16INK4a (Janzen et al., 2006). In fact, old INK4a−/− HSCs exhibit better engraftment capacity and increased cell cycle activity compared with old wild-type HSCs (Janzen et al., 2006). Telomere shortening is also an important cause of stem cell decline with aging in multiple tissues (Flores and Blasco, 2010; Sharpless and DePinho, 2007). These are just examples of a much larger picture where stem cell decline emerges as the integrative consequence of multiple types of damage.
Although deficient proliferation of stem and progenitor cells is obviously detrimental for the long-term maintenance of the organism, an excessive proliferation of stem and progenitor cells can also be deleterious by accelerating the exhaustion of stem cell niches. The importance of stem cell quiescence for the long-term functionality of stem cells has been compellingly demonstrated in the case of Drosophila intestinal stem cells, where excessive proliferation leads to exhaustion and premature aging (Rera et al., 2011). A similar situation is encountered in p21-null mice, which present premature exhaustion of HSCs and neural stem cells (Cheng et al., 2000; Kippin et al., 2005). In this regard, the induction of INK4a during aging (see section on Cellular Senescence) and the decrease of serum IGF-1 (see section on Deregulated Nutrient-sensing), may both reflect an attempt of the organism to preserve the quiescence of stem cells. Also, recent studies have shown that an increase in FGF2 signaling in the aged muscle stem cell niche results in the loss of quiescence, and eventually in stem cell depletion and diminished regenerative capacity, while suppression of this signaling pathway rescues these defects (Chakkalakal et al., 2012). This opens the possibility of designing strategies aimed at inhibiting FGF2 signaling to reduce stem cell exhaustion during aging.
An important debate regarding the decline in stem-cell function is the relative role of cell-intrinsic pathways compared to cell-extrinsic ones (Conboy and Rando, 2012). Recent work has provided strong support for the latter. In particular, DR increases intestinal and muscle stem functions through cell-extrinsic mechanisms (Cerletti et al., 2012; Yilmaz et al., 2012). Likewise, transplantation of muscle-derived stem cells from young mice to progeroid mice extends lifespan and improves degenerative changes of these animals even in tissues where donor cells are not detected, suggesting that their therapeutic benefit may derive from systemic effects caused by secreted factors (Lavasani et al., 2012). Furthermore, parabiosis experiments have demonstrated that the decline in neural and muscle stem cell function in old mice can be reversed by systemic factors from young mice (Conboy et al., 2005; Villeda et al., 2011).
Pharmacological interventions are also being explored to improve stem cell function. In particular, mTORC1 inhibition with rapamycin, which can postpone aging by improving proteostasis (see section on Loss of Proteostasis) and by affecting energy sensing (see section on Deregulated Nutrient-sensing), may also improve stem cell function in the epidermis, in the hematopoietic system, and in the intestine (Castilho et al., 2009; Chen et al., 2009; Yilmaz et al., 2012). This illustrates the difficulty of disentangling the mechanistic basis for the anti-aging activity of rapamycin, and underscores the interconnectedness between the different hallmarks of aging discussed here. It is also worth mentioning that it is possible to rejuvenate human senescent cells by pharmacological inhibition of the GTPase CDC42, whose activity is increased in aged HSCs (Florian et al., 2012).
Overview
Stem cell exhaustion unfolds as the integrative consequence of multiple types of aging-associated damages and likely constitutes one of the ultimate culprits of tissue and organismal aging. Recent promising studies suggest that stem cell rejuvenation may reverse the aging phenotype at the organismal level (Rando and Chang, 2012).
Altered Intercellular Communication
Beyond cell-autonomous alterations, aging also involves changes at the level of intercellular communication, be it endocrine, neuroendocrine or neuronal (Laplante and Sabatini, 2012; Rando and Chang, 2012; Russell and Kahn, 2007; Zhang et al., 2013) (Figure 5C). Thus, neurohormonal signaling (eg, renin-angiotensin, adrenergic, insulin-IGF1 signaling) tends to be deregulated in aging as inflammatory reactions increase, immunosurveillance against pathogens and premalignant cells declines, and the composition of the peri- and extracellular environment changes, thereby affecting the mechanical and functional properties of all tissues.
Inflammation
A prominent aging-associated alteration in intercellular communication is ‘inflammaging’, i.e. a smoldering pro-inflammatory phenotype that accompanies aging in mammals (Salminen et al., 2012). Inflammaging may result from multiple causes such as the accumulation of pro-inflammatory tissue damage, the failure of an ever more dysfunctional immune system to effectively clear pathogens and dysfunctional host cells, the propensity of senescent cells to secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines (see section on Cellular Senescence), the enhanced activation of the NF-κB transcription factor, or the occurrence of a defective autophagy response (Salminen et al., 2012). These alterations result in an enhanced activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and other pro-inflammatory pathways, finally leading to increased production of IL-1ß, tumor necrosis factor and interferons (Green et al., 2011; Salminen et al., 2012). Inflammation is also involved in the pathogenesis of obesity and type 2 diabetes, two conditions that contribute to, and correlate with aging in the human population (Barzilai et al., 2012). Likewise, defective inflammatory responses play a critical role in atherosclerosis (Tabas, 2010). The recent finding that age-associated inflammation inhibits epidermal stem cell function (Doles et al., 2012), further supports the intricate concatenation of different hallmarks that reinforces the aging process. Paralleling inflammaging, the function of the adaptive immune system declines (Deeks, 2011). This immunosenescence may aggravate the aging phenotype at the systemic level, due to the failure of the immune system to clear infectious agents, infected cells, and cells on the verge of malignant transformation. Moreover, one of the functions of the immune system is to recognize and eliminate senescent cells (see section on Stem Cell Exhaustion), as well as hyperploid cells that accumulate in aging tissues and premalignant lesions (Davoli and de Lange, 2011; Senovilla et al., 2012).
Global studies on the transcriptional landscape of aged tissues have also emphasized the relevance of inflammatory pathways in aging (de Magalhaes et al., 2009; Lee et al., 2012). Over-activation of the NF-κB pathway is one of these transcriptional signatures of aging and conditional expression of an NF-κB inhibitor in the aged skin of transgenic mice causes the phenotypic rejuvenation of this tissue, as well as the restoration of the transcriptional signature corresponding to young age (Adler et al., 2007). Likewise, genetic and pharmacological inhibition of NF-κB signaling prevents age-associated features in different mouse models of accelerated aging (Osorio et al., 2012; Tilstra et al., 2012). A novel link between inflammation and aging derives from the recent finding that inflammatory and stress responses activate NF-κB in the hypothalamus and induce a signaling pathway that results in reduced production of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) by neurons (Zhang et al., 2013). This GnRH decline can contribute to numerous aging-related changes such as bone fragility, muscle weakness, skin atrophy and reduced neurogenesis. Consistently, GnRH treatment prevents aging-impaired neurogenesis and decelerates aging development in mice (Zhang et al., 2013). These findings suggest that the hypothalamus may modulate systemic aging by integrating NF-kB-driven inflammatory responses with GnRH-mediated neuroendocrine effects.
Further in vivo evidence linking inflammation and aging derives from work on the mRNA decay factor AUF1, which is implicated in the cessation of the inflammatory response by mediating cytokine mRNA degradation (Pont et al., 2012). AUF1-deficient mice exhibit a marked cellular senescence and premature aging phenotype that can be rescued by re-expression of this RNA-binding factor. Interestingly, and in addition to directing inflammatory cytokine mRNA decay, AUF1 contributes to maintaining telomere length by activating the expression of the telomerase catalytic subunit TERT (Pont et al., 2012), again demonstrating that one single factor may have a strong impact on different aging hallmarks.
A similar situation occurs with sirtuins, which may also have an impact on inflammatory responses associated with aging. Several studies have revealed that, by deacetylating histones and components of inflammatory signaling pathways such as NF-κB, SIRT1 can down-regulate inflammation-related genes (Xie et al., 2012). Consistent with these findings, reduction of SIRT1 levels correlates with the development and progression of many inflammatory diseases, while pharmacologic activation of SIRT1 may prevent inflammatory responses in mice (Gillum et al., 2011; Yao et al., 2012; Zhang et al., 2010). SIRT2 and SIRT6 may also down-regulate the inflammatory response through deacetylation of NF-kB subunits and transcriptional repression of their _target genes (Kawahara et al., 2009; Rothgiesser et al., 2010).
Other types of intercellular communication
Beyond inflammation, accumulating evidence indicates that aging-related changes in one tissue can lead to aging-specific deterioration of other tissues, explaining the inter-organ coordination of the aging phenotype. In addition to inflammatory cytokines, there are other examples of ‘contagious aging’ or bystander effects in which senescent cells induce senescence in neighboring cells via gap junction-mediated cell-cell contacts and processes involving ROS (Nelson et al., 2012). The microenvironment contributes to the age-related functional defects of CD4 T cells, as assessed by using an adoptive transfer model in mice (Lefebvre et al., 2012). Likewise, impaired kidney function can increase the risk of heart disease in humans (Sarnak et al., 2003). Conversely, lifespan-extending manipulations _targeting one single tissue can retard the aging process in other tissues (Durieux et al., 2011; Lavasani et al., 2012; Tomas-Loba et al., 2008).
Restoring defective intercellular communication
There are several possibilities for restoring defective intercellular communication underlying aging processes, including genetic, nutritional or pharmacological interventions that may improve the cell-cell communication properties that are lost with aging (Freije and Lopez-Otin, 2012; Rando and Chang, 2012). Of special interest in this regard are the DR approaches to extend healthy lifespan (Piper et al., 2011; Sanchez-Roman et al., 2012), and the rejuvenation strategies based on the use of blood-borne systemic factors identified in parabiosis experiments (Conboy et al., 2005; Loffredo et al., 2013; Villeda et al., 2011). Moreover, the long-term administration of anti-inflammatory agents such as aspirin may increase longevity in mice and healthy aging in humans (Rothwell et al., 2011; Strong et al., 2008). Additionally, given that the gut microbiome shapes the function of the host immune system and exerts systemic metabolic effects, it appears possible to extend lifespan by manipulating the composition and functionality of the complex and dynamic intestinal bacterial ecosystem of the human body (Claesson et al., 2012; Ottaviani et al., 2011).
Overview
There is compelling evidence that aging is not an exclusively cell biological phenomenon and that it is coupled to a general alteration in intercellular communication, offering opportunities to modulate aging at this level. Excitingly, proof of principle exists for rejuvenation through blood-borne systemic factors (Conboy et al., 2005; Loffredo et al., 2013; Villeda et al., 2011).
Conclusions and Perspectives
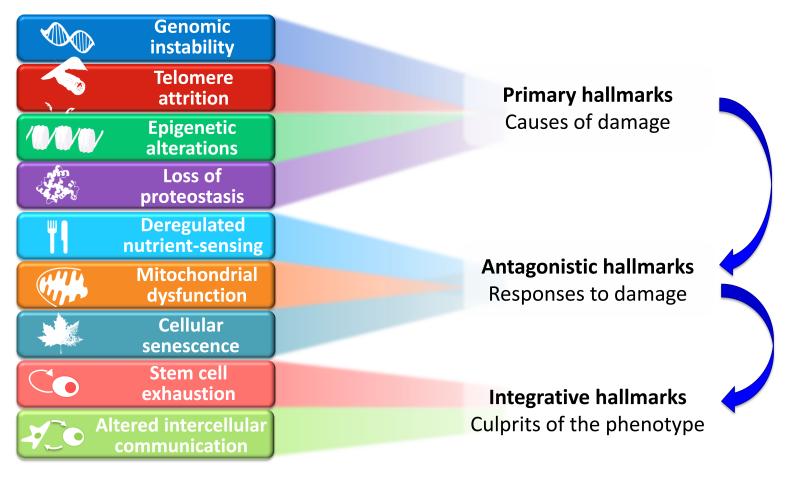
A global view at the nine candidate hallmarks of aging enumerated in this review allows grouping them into three categories: primary hallmarks, antagonistic hallmarks, and integrative hallmarks (Figure 6). The common characteristic of the primary hallmarks is the fact that they are all unequivocally negative. This is the case of DNA damage, including chromosomal aneuploidies, mitochondrial DNA mutations and telomere loss, epigenetic drift, and defective proteostasis. In contrast to the primary hallmarks, antagonistic hallmarks have opposite effects depending on their intensity. At low levels, they mediate beneficial effects, but at high levels, they become deleterious. This is the case for senescence, which protects the organism from cancer, but in excess can promote aging; similarly, reactive oxygen species (ROS) mediate cell signaling and survival, but at chronic high levels can produce cellular damage; likewise, an optimal nutrient-sensing and anabolism is obviously important for survival but in excess and during time can become pathological. These hallmarks can be viewed as designed for protecting the organism from damage or from nutrient scarcity, but when exacerbated or chronic, subvert their purpose and generate further damage. A third category comprises the integrative hallmarks, stem cell exhaustion and altered intercellular communication, which directly affect tissue homeostasis and function. Notwithstanding the interconnectedness between all hallmarks, we propose some degree of hierarchical relation between them (Figure 6). The primary hallmarks could be the initiating triggers whose damaging events progressively accumulate with time. The antagonistic hallmarks, being in principle beneficial, become progressively negative in a process that is partly promoted or accelerated by the primary hallmarks. Finally, the integrative hallmarks arise when the accumulated damage caused by the primary and antagonistic hallmarks cannot be compensated by tissue homeostatic mechanisms. Because the hallmarks co-occur during aging and are interconnected, understanding their exact causal network is an exciting challenge for future work.
Figure 6. Functional Interconnections between the Hallmarks of Aging.
The proposed nine hallmarks of aging are grouped into three categories. In the top, those hallmarks considered to be the primary causes of cellular damage. In the middle, those considered to be part of compensatory or antagonistic responses to the damage. These responses initially mitigate the damage, but eventually, if chronic or exacerbated, they become deleterious themselves. In the bottom, there are integrative hallmarks that are the end result of the previous two groups of hallmarks and are ultimately responsible for the functional decline associated with aging.
The definition of hallmarks of aging may contribute to build a framework for future studies on the molecular mechanisms of aging as well as for designing interventions to improve human healthspan (Figure 7). However, there are still numerous challenges ahead in relation to understanding this complex biological process (Martin, 2011; Miller, 2012). The rapid development of next-generation sequencing technologies may have a special impact on aging research by facilitating the evaluation of the genetic and epigenetic changes specifically accumulated by individual cells in an aging organism (de Magalhaes et al., 2010; Gundry and Vijg, 2012). These techniques are already being used to determine the whole-genome sequence of individuals with exceptional longevity, to perform comparative genomic studies between short-lived and long-lived animal species and strains, and to analyze age-associated epigenetic changes at maximum resolution (Heyn et al., 2012; Kim et al., 2011; Sebastiani et al., 2011). Parallel in vivo studies with gain- or loss-of-function animal models will be necessary for moving beyond correlative analyses and providing causal evidence in favor of the implication of these proposed hallmarks in the aging process. Besides the characterization of individual hallmarks, systems biology approaches will be required to understand the mechanistic links among the processes that accompany and lead to aging (Gems and Partridge, 2013; Kirkwood, 2008). Additionally, molecular analysis of the genome-environment interactions that modulate aging will help to identify drug _targets for longevity promotion (de Magalhaes et al., 2012). We surmise that ever more sophisticated approaches for disentangling the complexities of normal, accelerated and delayed aging will eventually resolve many of the pending issues. Hopefully, these combined approaches will allow a detailed understanding of the mechanisms underlying the hallmarks of aging and will facilitate future interventions for improving human healthspan and longevity.
Figure 7. Interventions that Might Extend Human Healthspan.
The nine hallmarks of aging are shown together with those therapeutic strategies for which there are proof of principle in mice.
Acknowledgements
We thank all members of our labs for their helpful comments on the manuscript and apologize for omission of relevant works due to space constraints. C.L-O. is supported by grants from Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (MINECO) and Instituto de Salud Carlos III (RTICC), and is an Investigator of the Botín Foundation. M.S. is funded by grants from the MINECO, European Union (ERC Advanced Grant), Regional Government of Madrid, Botín Foundation, Ramón Areces Foundation, and AXA Foundation. L.P. is supported by the Max Planck Society, the ERC and the Wellcome Trust (UK). M.A.B. is funded by ERC Project TEL STEM CELL, FP7 Projects MARK-AGE and EuroBATS, MINECO, Regional Government of Madrid, AXA Research Fund, Botín Foundation and Fundación Lilly (Spain). G.K. is supported by the Ligue Nationale contre le Cancer (Equipes labellisée), Agence Nationale pour la Recherche, AXA Foundation Chair for Longevity Research, European Commission (ERC Advanced Grant, ArtForce, ChemoRes), Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (FRM), Institut National du Cancer (INCa), Fondation de France, Cancéropôle Ile-de-France, Fondation Bettencourt-Schueller, the LabEx Immuno-Oncology, and the Paris Alliance of Cancer Research Institutes.
References
- Adler AS, Sinha S, Kawahara TL, Zhang JY, Segal E, Chang HY. Motif module map reveals enforcement of aging by continual NF-kappaB activity. Genes Dev. 2007;21:3244–3257. doi: 10.1101/gad.1588507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahlqvist KJ, Hamalainen RH, Yatsuga S, Uutela M, Terzioglu M, Gotz A, Forsstrom S, Salven P, Angers-Loustau A, Kopra OH, et al. Somatic progenitor cell vulnerability to mitochondrial DNA mutagenesis underlies progeroid phenotypes in Polg mutator mice. Cell Metab. 2012;15:100–109. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.11.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alavez S, Vantipalli MC, Zucker DJ, Klang IM, Lithgow GJ. Amyloid-binding compounds maintain protein homeostasis during ageing and extend lifespan. Nature. 2011;472:226–229. doi: 10.1038/nature09873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alers S, Loffler AS, Wesselborg S, Stork B. Role of AMPK-mTOR Ulk1/2 in the regulation of autophagy: cross talk, shortcuts, and feedbacks. Mol Cell Biol. 2012;32:2–11. doi: 10.1128/MCB.06159-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ameur A, Stewart JB, Freyer C, Hagstrom E, Ingman M, Larsson NG, Gyllensten U. Ultra-deep sequencing of mouse mitochondrial DNA: mutational patterns and their origins. PLoS Genet. 2011;7:e1002028. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anisimov VN, Berstein LM, Popovich IG, Zabezhinski MA, Egormin PA, Piskunova TS, Semenchenko AV, Tyndyk ML, Yurova MN, Kovalenko IG, et al. If started early in life, metformin treatment increases life span and postpones tumors in female SHR mice. Aging. 2011;3:148–157. doi: 10.18632/aging.100273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armanios M, Alder JK, Parry EM, Karim B, Strong MA, Greider CW. Short telomeres are sufficient to cause the degenerative defects associated with aging. Am J Hum Genet. 2009;85:823–832. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.10.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armanios M, Blackburn EH. The telomere syndromes. Nat Rev Genet. 2012;13:693–704. doi: 10.1038/nrg3246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahar R, Hartmann CH, Rodriguez KA, Denny AD, Busuttil RA, Dolle ME, Calder RB, Chisholm GB, Pollock BH, Klein CA, et al. Increased cell-to-cell variation in gene expression in ageing mouse heart. Nature. 2006;441:1011–1014. doi: 10.1038/nature04844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker DJ, Dawlaty MM, Wijshake T, Jeganathan KB, Malureanu L, van Ree JH, Crespo-Diaz R, Reyes S, Seaburg L, Shapiro V, et al. Increased expression of BubR1 protects against aneuploidy and cancer and extends healthy lifespan. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;15:96–102. doi: 10.1038/ncb2643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker DJ, Wijshake T, Tchkonia T, LeBrasseur NK, Childs BG, van de Sluis B, Kirkland JL, van Deursen JM. Clearance of p16Ink4a-positive senescent cells delays ageing-associated disorders. Nature. 2011;479:232–236. doi: 10.1038/nature10600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barzilai N, Huffman DM, Muzumdar RH, Bartke A. The critical role of metabolic pathways in aging. Diabetes. 2012;61:1315–1322. doi: 10.2337/db11-1300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baur JA, Pearson KJ, Price NL, Jamieson HA, Lerin C, Kalra A, Prabhu VV, Allard JS, Lopez-Lluch G, Lewis K, et al. Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high-calorie diet. Nature. 2006;444:337–342. doi: 10.1038/nature05354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begus-Nahrmann Y, Lechel A, Obenauf AC, Nalapareddy K, Peit E, Hoffmann E, Schlaudraff F, Liss B, Schirmacher P, Kestler H, et al. p53 deletion impairs clearance of chromosomal-instable stem cells in aging telomere-dysfunctional mice. Nat Genet. 2009;41:1138–1143. doi: 10.1038/ng.426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardes de Jesus B, Vera E, Schneeberger K, Tejera AM, Ayuso E, Bosch F, Blasco MA. Telomerase gene therapy in adult and old mice delays aging and increases longevity without increasing cancer. EMBO Mol Med. 2012;4:691–704. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201200245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjedov I, Toivonen JM, Kerr F, Slack C, Jacobson J, Foley A, Partridge L. Mechanisms of life span extension by rapamycin in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. Cell Metab. 2010;11:35–46. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2009.11.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn EH, Greider CW, Szostak JW. Telomeres and telomerase: the path from maize, Tetrahymena and yeast to human cancer and aging. Nat Med. 2006;12:1133–1138. doi: 10.1038/nm1006-1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blagosklonny MV. Aging: ROS or TOR. Cell Cycle. 2008;7:3344–3354. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.21.6965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blagosklonny MV. Rapamycin-induced glucose intolerance: hunger or starvation diabetes. Cell Cycle. 2011;10:4217–4224. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.24.18595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasco MA. Telomere length, stem cells and aging. Nat Chem Biol. 2007;3:640–649. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2007.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodnar AG, Ouellette M, Frolkis M, Holt SE, Chiu CP, Morin GB, Harley CB, Shay JW, Lichtsteiner S, Wright WE. Extension of life-span by introduction of telomerase into normal human cells. Science. 1998;279:349–352. doi: 10.1126/science.279.5349.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boonekamp JJ, Simons MJ, Hemerik L, Verhulst S. Telomere length behaves as biomarker of somatic redundancy rather than biological age. Aging Cell. 2013;12:330–332. doi: 10.1111/acel.12050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulias K, Horvitz HR. The C. elegans microRNA mir-71 acts in neurons to promote germline-mediated longevity through regulation of DAF-16/FOXO. Cell Metab. 2012;15:439–450. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.02.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K, Xie S, Qiu X, Mohrin M, Shin J, Liu Y, Zhang D, Scadden DT, Chen D. SIRT3 reverses aging-associated degeneration. Cell Rep. 2013;3:319–327. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.01.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett C, Valentini S, Cabreiro F, Goss M, Somogyvari M, Piper MD, Hoddinott M, Sutphin GL, Leko V, McElwee JJ, et al. Absence of effects of Sir2 overexpression on lifespan in C. elegans and Drosophila. Nature. 2011;477:482–485. doi: 10.1038/nature10296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtner CR, Kennedy BK. Progeria syndromes and ageing: what is the connection? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:567–578. doi: 10.1038/nrm2944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabanillas R, Cadinanos J, Villameytide JA, Perez M, Longo J, Richard JM, Alvarez R, Duran NS, Illan R, Gonzalez DJ, et al. Nestor-Guillermo progeria syndrome: a novel premature aging condition with early onset and chronic development caused by BANF1 mutations. Am J Med Genet A. 2011;155A:2617–2625. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.34249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabreiro F, Au C, Leung KY, Vergara-Irigaray N, Cocheme HM, Noori T, Weinkove D, Schuster E, Greene ND, Gems D. Metformin retards aging in C. elegans by altering microbial folate and methionine metabolism. Cell. 2013;153:228–239. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.02.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese V, Cornelius C, Cuzzocrea S, Iavicoli I, Rizzarelli E, Calabrese EJ. Hormesis, cellular stress response and vitagenes as critical determinants in aging and longevity. Mol Aspects Med. 2011;32:279–304. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2011.10.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calamini B, Silva MC, Madoux F, Hutt DM, Khanna S, Chalfant MA, Saldanha SA, Hodder P, Tait BD, Garza D, et al. Small-molecule proteostasis regulators for protein conformational diseases. Nat Chem Biol. 2012;8:185–196. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldeira da Silva CC, Cerqueira FM, Barbosa LF, Medeiros MH, Kowaltowski AJ. Mild mitochondrial uncoupling in mice affects energy metabolism, redox balance and longevity. Aging Cell. 2008;7:552–560. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2008.00407.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderwood SK, Murshid A, Prince T. The shock of aging: molecular chaperones and the heat shock response in longevity and aging--a mini-review. Gerontology. 2009;55:550–558. doi: 10.1159/000225957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J, d’Adda di Fagagna F. Cellular senescence: when bad things happen to good cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:729–740. doi: 10.1038/nrm2233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao K, Blair CD, Faddah DA, Kieckhaefer JE, Olive M, Erdos MR, Nabel EG, Collins FS. Progerin and telomere dysfunction collaborate to trigger cellular senescence in normal human fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:2833–2844. doi: 10.1172/JCI43578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao L, Li W, Kim S, Brodie SG, Deng CX. Senescence, aging, and malignant transformation mediated by p53 in mice lacking the Brca1 full-length isoform. Genes Dev. 2003;17:201–213. doi: 10.1101/gad.1050003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castello L, Maina M, Testa G, Cavallini G, Biasi F, Donati A, Leonarduzzi G, Bergamini E, Poli G, Chiarpotto E. Alternate-day fasting reverses the age-associated hypertrophy phenotype in rat heart by influencing the ERK and PI3K signaling pathways. Mech Ageing Dev. 2011;132:305–314. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2011.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castilho RM, Squarize CH, Chodosh LA, Williams BO, Gutkind JS. mTOR mediates Wnt-induced epidermal stem cell exhaustion and aging. Cell Stem Cell. 2009;5:279–289. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2009.06.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerletti M, Jang YC, Finley LW, Haigis MC, Wagers AJ. Short-term calorie restriction enhances skeletal muscle stem cell function. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10:515–519. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2012.04.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesson MJ, Jeffery IB, Conde S, Power SE, O’Connor EM, Cusack S, Harris HM, Coakley M, Lakshminarayanan B, O’Sullivan O, et al. Gut microbiota composition correlates with diet and health in the elderly. Nature. 2012;488:178–184. doi: 10.1038/nature11319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman RJ, Anderson RM, Johnson SC, Kastman EK, Kosmatka KJ, Beasley TM, Allison DB, Cruzen C, Simmons HA, Kemnitz JW, et al. Caloric restriction delays disease onset and mortality in rhesus monkeys. Science. 2009;325:201–204. doi: 10.1126/science.1173635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collado M, Blasco MA, Serrano M. Cellular senescence in cancer and aging. Cell. 2007;130:223–233. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conboy IM, Conboy MJ, Wagers AJ, Girma ER, Weissman IL, Rando TA. Rejuvenation of aged progenitor cells by exposure to a young systemic environment. Nature. 2005;433:760–764. doi: 10.1038/nature03260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conboy IM, Rando TA. Heterochronic parabiosis for the study of the effects of aging on stem cells and their niches. Cell Cycle. 2012;11:2260–2267. doi: 10.4161/cc.20437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakkalakal JV, Jones KM, Basson MA, Brack AS. The aged niche disrupts muscle stem cell quiescence. Nature. 2012;490:355–360. doi: 10.1038/nature11438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C, Liu Y, Zheng P. mTOR regulation and therapeutic rejuvenation of aging hematopoietic stem cells. Sci Signal. 2009;2:ra75. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2000559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng T, Rodrigues N, Shen H, Yang Y, Dombkowski D, Sykes M, Scadden DT. Hematopoietic stem cell quiescence maintained by p21cip1/waf1. Science. 2000;287:1804–1808. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5459.1804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang WC, Ching TT, Lee HC, Mousigian C, Hsu AL. HSF-1 regulators DDL-1/2 link insulin-like signaling to heat-shock responses and modulation of longevity. Cell. 2012;148:322–334. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.12.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davoli T, de Lange T. The causes and consequences of polyploidy in normal development and cancer. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2011;27:585–610. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-092910-154234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jesus BB, Schneeberger K, Vera E, Tejera A, Harley CB, Blasco MA. The telomerase activator TA-65 elongates short telomeres and increases health span of adult/old mice without increasing cancer incidence. Aging Cell. 2011;10:604–621. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2011.00700.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Magalhaes JP, Curado J, Church GM. Meta-analysis of age-related gene expression profiles identifies common signatures of aging. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:875–881. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Magalhaes JP, Finch CE, Janssens G. Next-generation sequencing in aging research: emerging applications, problems, pitfalls and possible solutions. Ageing Res Rev. 2010;9:315–323. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2009.10.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Magalhaes JP, Wuttke D, Wood SH, Plank M, Vora C. Genome-environment interactions that modulate aging: powerful _targets for drug discovery. Pharmacol Rev. 2012;64:88–101. doi: 10.1124/pr.110.004499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Sandre-Giovannoli A, Bernard R, Cau P, Navarro C, Amiel J, Boccaccio I, Lyonnet S, Stewart CL, Munnich A, Le Merrer M, et al. Lamin a truncation in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria. Science. 2003;300:2055. doi: 10.1126/science.1084125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dechat T, Pfleghaar K, Sengupta K, Shimi T, Shumaker DK, Solimando L, Goldman RD. Nuclear lamins: major factors in the structural organization and function of the nucleus and chromatin. Genes Dev. 2008;22:832–853. doi: 10.1101/gad.1652708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeks SG. HIV infection, inflammation, immunosenescence, and aging. Annu Rev Med. 2011;62:141–155. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-042909-093756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimri GP, Lee X, Basile G, Acosta M, Scott G, Roskelley C, Medrano EE, Linskens M, Rubelj I, Pereira-Smith O, et al. A biomarker that identifies senescent human cells in culture and in aging skin in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92:9363–9367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doles J, Storer M, Cozzuto L, Roma G, Keyes WM. Age-associated inflammation inhibits epidermal stem cell function. Genes Dev. 2012;26:2144–2153. doi: 10.1101/gad.192294.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doonan R, McElwee JJ, Matthijssens F, Walker GA, Houthoofd K, Back P, Matscheski A, Vanfleteren JR, Gems D. Against the oxidative damage theory of aging: superoxide dismutases protect against oxidative stress but have little or no effect on life span in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genes Dev. 2008;22:3236–3241. doi: 10.1101/gad.504808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durieux J, Wolff S, Dillin A. The cell-non-autonomous nature of electron transport chain-mediated longevity. Cell. 2011;144:79–91. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.12.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar D, Shabalina I, Camara Y, Wredenberg A, Calvaruso MA, Nijtmans L, Nedergaard J, Cannon B, Larsson NG, Trifunovic A. Random point mutations with major effects on protein-coding genes are the driving force behind premature aging in mtDNA mutator mice. Cell Metab. 2009;10:131–138. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2009.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg T, Knauer H, Schauer A, Buttner S, Ruckenstuhl C, Carmona-Gutierrez D, Ring J, Schroeder S, Magnes C, Antonacci L, et al. Induction of autophagy by spermidine promotes longevity. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11:1305–1314. doi: 10.1038/ncb1975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson M, Brown WT, Gordon LB, Glynn MW, Singer J, Scott L, Erdos MR, Robbins CM, Moses TY, Berglund P, et al. Recurrent de novo point mutations in lamin A cause Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. Nature. 2003;423:293–298. doi: 10.1038/nature01629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espada J, Varela I, Flores I, Ugalde AP, Cadinanos J, Pendas AM, Stewart CL, Tryggvason K, Blasco MA, Freije JM, et al. Nuclear envelope defects cause stem cell dysfunction in premature-aging mice. J Cell Biol. 2008;181:27–35. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200801096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faggioli F, Wang T, Vijg J, Montagna C. Chromosome-specific accumulation of aneuploidy in the aging mouse brain. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21:5246–5253. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feige JN, Lagouge M, Canto C, Strehle A, Houten SM, Milne JC, Lambert PD, Mataki C, Elliott PJ, Auwerx J. Specific SIRT1 activation mimics low energy levels and protects against diet-induced metabolic disorders by enhancing fat oxidation. Cell Metab. 2008;8:347–358. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2008.08.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Marcos PJ, Auwerx J. Regulation of PGC-1alpha, a nodal regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;93:884S–890. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.110.001917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores I, Blasco MA. The role of telomeres and telomerase in stem cell aging. FEBS Lett. 2010;584:3826–3830. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.07.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florian MC, Dorr K, Niebel A, Daria D, Schrezenmeier H, Rojewski M, Filippi MD, Hasenberg A, Gunzer M, Scharffetter-Kochanek K, et al. Cdc42 activity regulates hematopoietic stem cell aging and rejuvenation. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10:520–530. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2012.04.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana L, Partridge L, Longo VD. Extending healthy life span--from yeast to humans. Science. 2010;328:321–326. doi: 10.1126/science.1172539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg LA, Rasi C, Razzaghian HR, Pakalapati G, Waite L, Thilbeault KS, Ronowicz A, Wineinger NE, Tiwari HK, Boomsma D, et al. Age-related somatic structural changes in the nuclear genome of human blood cells. Am J Hum Genet. 2012;90:217–228. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.12.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foukas LC, Bilanges B, Bettedi L, Pearce W, Ali K, Sancho S, Withers DJ, Vanhaesebroeck B. Long-term p110alpha PI3K inactivation exerts a beneficial effect on metabolism. EMBO Mol Med. 2013;5:563–571. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201201953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraga MF, Esteller M. Epigenetics and aging: the _targets and the marks. Trends Genet. 2007;23:413–418. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2007.05.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freije JM, Lopez-Otin C. Reprogramming aging and progeria. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012 doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2012.08.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund A, Laberge RM, Demaria M, Campisi J. Lamin B1 loss is a senescence-associated biomarker. Mol Biol Cell. 2012;23:2066–2075. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-10-0884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridell YW, Hoh M, Kreneisz O, Hosier S, Chang C, Scantling D, Mulkey DK, Helfand SL. Increased uncoupling protein (UCP) activity in Drosophila insulin-producing neurons attenuates insulin signaling and extends lifespan. Aging. 2009;1:699–713. doi: 10.18632/aging.100067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fumagalli M, Rossiello F, Clerici M, Barozzi S, Cittaro D, Kaplunov JM, Bucci G, Dobreva M, Matti V, Beausejour CM, et al. Telomeric DNA damage is irreparable and causes persistent DNA-damage-response activation. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14:355–365. doi: 10.1038/ncb2466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Cao I, Song MS, Hobbs RM, Laurent G, Giorgi C, de Boer VC, Anastasiou D, Ito K, Sasaki AT, Rameh L, et al. Systemic elevation of PTEN induces a tumor-suppressive metabolic state. Cell. 2012;149:49–62. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garinis GA, van der Horst GT, Vijg J, Hoeijmakers JH. DNA damage and ageing: new-age ideas for an age-old problem. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:1241–1247. doi: 10.1038/ncb1108-1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gates AC, Bernal-Mizrachi C, Chinault SL, Feng C, Schneider JG, Coleman T, Malone JP, Townsend RR, Chakravarthy MV, Semenkovich CF. Respiratory uncoupling in skeletal muscle delays death and diminishes age-related disease. Cell Metab. 2007;6:497–505. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2007.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehrig SM, van der Poel C, Sayer TA, Schertzer JD, Henstridge DC, Church JE, Lamon S, Russell AP, Davies KE, Febbraio MA, et al. Hsp72 preserves muscle function and slows progression of severe muscular dystrophy. Nature. 2012;484:394–398. doi: 10.1038/nature10980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gems D, Partridge L. Genetics of longevity in model organisms: debates and paradigm shifts. Annu Rev Physiol. 2013;75:621–644. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-030212-183712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillum MP, Kotas ME, Erion DM, Kursawe R, Chatterjee P, Nead KT, Muise ES, Hsiao JJ, Frederick DW, Yonemitsu S, et al. SirT1 regulates adipose tissue inflammation. Diabetes. 2011;60:3235–3245. doi: 10.2337/db11-0616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giralt A, Villarroya F. SIRT3, a pivotal actor in mitochondrial functions: metabolism, cell death and aging. Biochem J. 2012;444:1–10. doi: 10.1042/BJ20120030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Suarez I, Redwood AB, Perkins SM, Vermolen B, Lichtensztejin D, Grotsky DA, Morgado-Palacin L, Gapud EJ, Sleckman BP, Sullivan T, et al. Novel roles for A-type lamins in telomere biology and the DNA damage response pathway. EMBO J. 2009;28:2414–2427. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalo S, Jaco I, Fraga MF, Chen T, Li E, Esteller M, Blasco MA. DNA methyltransferases control telomere length and telomere recombination in mammalian cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:416–424. doi: 10.1038/ncb1386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorgoulis VG, Halazonetis TD. Oncogene-induced senescence: the bright and dark side of the response. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010;22:816–827. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2010.07.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green DR, Galluzzi L, Kroemer G. Mitochondria and the autophagy-inflammation-cell death axis in organismal aging. Science. 2011;333:1109–1112. doi: 10.1126/science.1201940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer EL, Maures TJ, Hauswirth AG, Green EM, Leeman DS, Maro GS, Han S, Banko MR, Gozani O, Brunet A. Members of the H3K4 trimethylation complex regulate lifespan in a germline-dependent manner in C. elegans. Nature. 2010;466:383–387. doi: 10.1038/nature09195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer EL, Maures TJ, Ucar D, Hauswirth AG, Mancini E, Lim JP, Benayoun BA, Shi Y, Brunet A. Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance of longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2011;479:365–371. doi: 10.1038/nature10572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg SQ, Gutierrez V, Robinson AR, Woodell T, Nakao A, Ross MA, Michalopoulos GK, Rigatti L, Rothermel CE, Kamileri I, et al. A mouse model of accelerated liver aging caused by a defect in DNA repair. Hepatology. 2012;55:609–621. doi: 10.1002/hep.24713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber R, Koch H, Doll BA, Tegtmeier F, Einhorn TA, Hollinger JO. Fracture healing in the elderly patient. Exp Gerontol. 2006;41:1080–1093. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2006.09.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Sirtuins, aging, and metabolism. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2011;76:81–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2011.76.010629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundry M, Vijg J. Direct mutation analysis by high-throughput sequencing: from germline to low-abundant, somatic variants. Mutat Res. 2012;729:1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2011.10.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigis MC, Yankner BA. The aging stress response. Mol Cell. 2010;40:333–344. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.10.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han S, Brunet A. Histone methylation makes its mark on longevity. Trends Cell Biol. 2012;22:42–49. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2011.11.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81683-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harman D. The free radical theory of aging: effect of age on serum copper levels. J Gerontol. 1965;20:151–153. doi: 10.1093/geronj/20.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harries LW, Hernandez D, Henley W, Wood AR, Holly AC, Bradley-Smith RM, Yaghootkar H, Dutta A, Murray A, Frayling TM, et al. Human aging is characterized by focused changes in gene expression and deregulation of alternative splicing. Aging Cell. 2011;10:868–878. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2011.00726.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison DE, Strong R, Sharp ZD, Nelson JF, Astle CM, Flurkey K, Nadon NL, Wilkinson JE, Frenkel K, Carter CS, et al. Rapamycin fed late in life extends lifespan in genetically heterogeneous mice. Nature. 2009;460:392–395. doi: 10.1038/nature08221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl FU, Bracher A, Hayer-Hartl M. Molecular chaperones in protein folding and proteostasis. Nature. 2011;475:324–332. doi: 10.1038/nature10317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley SA, Ross FA, Chevtzoff C, Green KA, Evans A, Fogarty S, Towler MC, Brown LJ, Ogunbayo OA, Evans AM, et al. Use of cells expressing gamma subunit variants to identify diverse mechanisms of AMPK activation. Cell Metab. 2010;11:554–565. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2010.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick L, Moorhead PS. The serial cultivation of human diploid cell strains. Exp Cell Res. 1961;25:585–621. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekimi S, Lapointe J, Wen Y. Taking a “good” look at free radicals in the aging process. Trends Cell Biol. 2011;21:569–576. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2011.06.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herranz D, Munoz-Martin M, Canamero M, Mulero F, Martinez-Pastor B, Fernandez-Capetillo O, Serrano M. Sirt1 improves healthy ageing and protects from metabolic syndrome-associated cancer. Nat Commun. 2010;1:3. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt G, Jurk D, Marques FD, Correia-Melo C, Hardy T, Gackowska A, Anderson R, Taschuk M, Mann J, Passos JF. Telomeres are favoured _targets of a persistent DNA damage response in ageing and stress-induced senescence. Nat Commun. 2012;3:708. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyn H, Li N, Ferreira HJ, Moran S, Pisano DG, Gomez A, Diez J, Sanchez-Mut JV, Setien F, Carmona FJ, et al. Distinct DNA methylomes of newborns and centenarians. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:10522–10527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1120658109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiona A, Sanz A, Kujoth GC, Pamplona R, Seo AY, Hofer T, Someya S, Miyakawa T, Nakayama C, Samhan-Arias AK, et al. Mitochondrial DNA mutations induce mitochondrial dysfunction, apoptosis and sarcopenia in skeletal muscle of mitochondrial DNA mutator mice. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e11468. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeijmakers JH. DNA damage, aging, and cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1475–1485. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0804615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoenicke L, Zender L. Immune surveillance of senescent cells--biological significance in cancer- and non-cancer pathologies. Carcinogenesis. 2012;33:1123–1126. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgs124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houtkooper RH, Pirinen E, Auwerx J. Sirtuins as regulators of metabolism and healthspan. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13:225–238. doi: 10.1038/nrm3293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houtkooper RH, Williams RW, Auwerx J. Metabolic networks of longevity. Cell. 2010;142:9–14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.06.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu AL, Murphy CT, Kenyon C. Regulation of aging and age-related disease by DAF-16 and heat-shock factor. Science. 2003;300:1142–1145. doi: 10.1126/science.1083701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs KB, Yeager M, Zhou W, Wacholder S, Wang Z, Rodriguez-Santiago B, Hutchinson A, Deng X, Liu C, Horner MJ, et al. Detectable clonal mosaicism and its relationship to aging and cancer. Nat Genet. 2012;44:651–658. doi: 10.1038/ng.2270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janzen V, Forkert R, Fleming HE, Saito Y, Waring MT, Dombkowski DM, Cheng T, DePinho RA, Sharpless NE, Scadden DT. Stem-cell ageing modified by the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16INK4a. Nature. 2006;443:421–426. doi: 10.1038/nature05159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaskelioff M, Muller FL, Paik JH, Thomas E, Jiang S, Adams AC, Sahin E, Kost-Alimova M, Protopopov A, Cadinanos J, et al. Telomerase reactivation reverses tissue degeneration in aged telomerase-deficient mice. Nature. 2011;469:102–106. doi: 10.1038/nature09603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeck WR, Siebold AP, Sharpless NE. Review: a meta-analysis of GWAS and age-associated diseases. Aging Cell. 2012;11:727–731. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2012.00871.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin C, Li J, Green CD, Yu X, Tang X, Han D, Xian B, Wang D, Huang X, Cao X, et al. Histone demethylase UTX-1 regulates C. elegans life span by _targeting the insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway. Cell Metab. 2011;14:161–172. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson SC, Rabinovitch PS, Kaeberlein M. mTOR is a key modulator of ageing and age-related disease. Nature. 2013;493:338–345. doi: 10.1038/nature11861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones DL, Rando TA. Emerging models and paradigms for stem cell ageing. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13:506–512. doi: 10.1038/ncb0511-506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaeberlein M, McVey M, Guarente L. The SIR2/3/4 complex and SIR2 alone promote longevity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by two different mechanisms. Genes Dev. 1999;13:2570–2580. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.19.2570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanfi Y, Naiman S, Amir G, Peshti V, Zinman G, Nahum L, Bar-Joseph Z, Cohen HY. The sirtuin SIRT6 regulates lifespan in male mice. Nature. 2012;483:218–221. doi: 10.1038/nature10815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanfi Y, Peshti V, Gil R, Naiman S, Nahum L, Levin E, Kronfeld-Schor N, Cohen HY. SIRT6 protects against pathological damage caused by diet-induced obesity. Aging Cell. 2010;9:162–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2009.00544.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang TW, Yevsa T, Woller N, Hoenicke L, Wuestefeld T, Dauch D, Hohmeyer A, Gereke M, Rudalska R, Potapova A, et al. Senescence surveillance of pre-malignant hepatocytes limits liver cancer development. Nature. 2011;479:547–551. doi: 10.1038/nature10599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara TL, Michishita E, Adler AS, Damian M, Berber E, Lin M, McCord RA, Ongaigui KC, Boxer LD, Chang HY, et al. SIRT6 links histone H3 lysine 9 deacetylation to NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression and organismal life span. Cell. 2009;136:62–74. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.10.052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazak L, Reyes A, Holt IJ. Minimizing the damage: repair pathways keep mitochondrial DNA intact. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13:659–671. doi: 10.1038/nrm3439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon C, Chang J, Gensch E, Rudner A, Tabtiang R. A C. elegans mutant that lives twice as long as wild type. Nature. 1993;366:461–464. doi: 10.1038/366461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon CJ. The genetics of ageing. Nature. 2010;464:504–512. doi: 10.1038/nature08980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khrapko K, Bodyak N, Thilly WG, van Orsouw NJ, Zhang X, Coller HA, Perls TT, Upton M, Vijg J, Wei JY. Cell-by-cell scanning of whole mitochondrial genomes in aged human heart reveals a significant fraction of myocytes with clonally expanded deletions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999;27:2434–2441. doi: 10.1093/nar/27.11.2434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim EB, Fang X, Fushan AA, Huang Z, Lobanov AV, Han L, Marino SM, Sun X, Turanov AA, Yang P, et al. Genome sequencing reveals insights into physiology and longevity of the naked mole rat. Nature. 2011;479:223–227. doi: 10.1038/nature10533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kippin TE, Martens DJ, van der Kooy D. p21 loss compromises the relative quiescence of forebrain stem cell proliferation leading to exhaustion of their proliferation capacity. Genes Dev. 2005;19:756–767. doi: 10.1101/gad.1272305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood TB. Understanding the odd science of aging. Cell. 2005;120:437–447. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood TB. A systematic look at an old problem. Nature. 2008;451:644–647. doi: 10.1038/451644a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klass MR. A method for the isolation of longevity mutants in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans and initial results. Mech Ageing Dev. 1983;22:279–286. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(83)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga H, Kaushik S, Cuervo AM. Protein homeostasis and aging: The importance of exquisite quality control. Ageing Res Rev. 2011;10:205–215. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2010.02.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthy J, Torrice C, Ramsey MR, Kovalev GI, Al-Regaiey K, Su L, Sharpless NE. Ink4a/Arf expression is a biomarker of aging. J Clin Invest. 2004;114:1299–1307. doi: 10.1172/JCI22475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan V, Chow MZ, Wang Z, Zhang L, Liu B, Liu X, Zhou Z. Histone H4 lysine 16 hypoacetylation is associated with defective DNA repair and premature senescence in Zmpste24-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:12325–12330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102789108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Brenner C. Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev. 2007;87:99–163. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00013.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruegel U, Robison B, Dange T, Kahlert G, Delaney JR, Kotireddy S, Tsuchiya M, Tsuchiyama S, Murakami CJ, Schleit J, et al. Elevated proteasome capacity extends replicative lifespan in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS Genet. 2011;7:e1002253. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuilman T, Michaloglou C, Mooi WJ, Peeper DS. The essence of senescence. Genes Dev. 2010;24:2463–2479. doi: 10.1101/gad.1971610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kujoth GC, Hiona A, Pugh TD, Someya S, Panzer K, Wohlgemuth SE, Hofer T, Seo AY, Sullivan R, Jobling WA, et al. Mitochondrial DNA mutations, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in mammalian aging. Science. 2005;309:481–484. doi: 10.1126/science.1112125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagouge M, Argmann C, Gerhart-Hines Z, Meziane H, Lerin C, Daussin F, Messadeq N, Milne J, Lambert P, Elliott P, et al. Resveratrol improves mitochondrial function and protects against metabolic disease by activating SIRT1 and PGC-1alpha. Cell. 2006;127:1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.11.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamming DW, Ye L, Katajisto P, Goncalves MD, Saitoh M, Stevens DM, Davis JG, Salmon AB, Richardson A, Ahima RS, et al. Rapamycin-induced insulin resistance is mediated by mTORC2 loss and uncoupled from longevity. Science. 2012;335:1638–1643. doi: 10.1126/science.1215135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laplante M, Sabatini DM. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell. 2012;149:274–293. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson K, Yan SJ, Tsurumi A, Liu J, Zhou J, Gaur K, Guo D, Eickbush TH, Li WX. Heterochromatin formation promotes longevity and represses ribosomal RNA synthesis. PLoS Genet. 2012;8:e1002473. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie CC, Laurie CA, Rice K, Doheny KF, Zelnick LR, McHugh CP, Ling H, Hetrick KN, Pugh EW, Amos C, et al. Detectable clonal mosaicism from birth to old age and its relationship to cancer. Nat Genet. 2012;44:642–650. doi: 10.1038/ng.2271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavasani M, Robinson AR, Lu A, Song M, Feduska JM, Ahani B, Tilstra JS, Feldman CH, Robbins PD, Niedernhofer LJ, et al. Muscle-derived stem/progenitor cell dysfunction limits healthspan and lifespan in a murine progeria model. Nat Commun. 2012;3:608. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee BH, Lee MJ, Park S, Oh DC, Elsasser S, Chen PC, Gartner C, Dimova N, Hanna J, Gygi SP, et al. Enhancement of proteasome activity by a small-molecule inhibitor of USP14. Nature. 2010;467:179–184. doi: 10.1038/nature09299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee IH, Cao L, Mostoslavsky R, Lombard DB, Liu J, Bruns NE, Tsokos M, Alt FW, Finkel T. A role for the NAD-dependent deacetylase Sirt1 in the regulation of autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:3374–3379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0712145105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee JS, Ward WO, Ren H, Vallanat B, Darlington GJ, Han ES, Laguna JC, DeFord JH, Papaconstantinou J, Selman C, et al. Meta-analysis of gene expression in the mouse liver reveals biomarkers associated with inflammation increased early during aging. Mech Ageing Dev. 2012;133:467–478. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2012.05.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre JS, Maue AC, Eaton SM, Lanthier PA, Tighe M, Haynes L. The aged microenvironment contributes to the age-related functional defects of CD4 T cells in mice. Aging Cell. 2012;11:732–740. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2012.00836.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnane AW, Marzuki S, Ozawa T, Tanaka M. Mitochondrial DNA mutations as an important contributor to ageing and degenerative diseases. Lancet. 1989;1:642–645. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92145-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu B, Wang J, Chan KM, Tjia WM, Deng W, Guan X, Huang JD, Li KM, Chau PY, Chen DJ, et al. Genomic instability in laminopathy-based premature aging. Nat Med. 2005;11:780–785. doi: 10.1038/nm1266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu G, Rogers J, Murphy CT, Rongo C. EGF signalling activates the ubiquitin proteasome system to modulate C. elegans lifespan. EMBO J. 2011a;30:2990–3003. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu GH, Suzuki K, Qu J, Sancho-Martinez I, Yi F, Li M, Kumar S, Nivet E, Kim J, Soligalla RD, et al. _targeted gene correction of laminopathy-associated LMNA mutations in patient-specific iPSCs. Cell Stem Cell. 2011b;8:688–694. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2011.04.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu N, Landreh M, Cao K, Abe M, Hendriks GJ, Kennerdell JR, Zhu Y, Wang LS, Bonini NM. The microRNA miR-34 modulates ageing and neurodegeneration in Drosophila. Nature. 2012;482:519–523. doi: 10.1038/nature10810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loffredo FS, Steinhauser ML, Jay SM, Gannon J, Pancoast JR, Yalamanchi P, Sinha M, Dall’Osso C, Khong D, Shadrach JL, et al. Growth differentiation factor 11 is a circulating factor that reverses age-related cardiac hypertrophy. Cell. 2013;153:828–839. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.04.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombard DB, Alt FW, Cheng HL, Bunkenborg J, Streeper RS, Mostoslavsky R, Kim J, Yancopoulos G, Valenzuela D, Murphy A, et al. Mammalian Sir2 homolog SIRT3 regulates global mitochondrial lysine acetylation. Mol Cell Biol. 2007;27:8807–8814. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01636-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord CJ, Ashworth A. The DNA damage response and cancer therapy. Nature. 2012;481:287–294. doi: 10.1038/nature10760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maegawa S, Hinkal G, Kim HS, Shen L, Zhang L, Zhang J, Zhang N, Liang S, Donehower LA, Issa JP. Widespread and tissue specific age-related DNA methylation changes in mice. Genome Res. 2010;20:332–340. doi: 10.1101/gr.096826.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mair W, Morantte I, Rodrigues AP, Manning G, Montminy M, Shaw RJ, Dillin A. Lifespan extension induced by AMPK and calcineurin is mediated by CRTC-1 and CREB. Nature. 2011;470:404–408. doi: 10.1038/nature09706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marino G, Ugalde AP, Fernandez AF, Osorio FG, Fueyo A, Freije JM, Lopez-Otin C. Insulin-like growth factor 1 treatment extends longevity in a mouse model of human premature aging by restoring somatotroph axis function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:16268–16273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1002696107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin GM. The biology of aging: 1985-2010 and beyond. FASEB J. 2011;25:3756–3762. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-1102.ufm. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez P, Blasco MA. Role of shelterin in cancer and aging. Aging Cell. 2010;9:653–666. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2010.00596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matheu A, Maraver A, Collado M, Garcia-Cao I, Canamero M, Borras C, Flores JM, Klatt P, Vina J, Serrano M. Anti-aging activity of the Ink4/Arf locus. Aging Cell. 2009;8:152–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2009.00458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matheu A, Maraver A, Klatt P, Flores I, Garcia-Cao I, Borras C, Flores JM, Vina J, Blasco MA, Serrano M. Delayed ageing through damage protection by the Arf/p53 pathway. Nature. 2007;448:375–379. doi: 10.1038/nature05949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto M, Kurihara S, Kibe R, Ashida H, Benno Y. Longevity in mice is promoted by probiotic-induced suppression of colonic senescence dependent on upregulation of gut bacterial polyamine production. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e23652. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattison JA, Roth GS, Beasley TM, Tilmont EM, Handy AM, Herbert RL, Longo DL, Allison DB, Young JE, Bryant M, et al. Impact of caloric restriction on health and survival in rhesus monkeys from the NIA study. Nature. 2012;489:318–321. doi: 10.1038/nature11432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesquita A, Weinberger M, Silva A, Sampaio-Marques B, Almeida B, Leao C, Costa V, Rodrigues F, Burhans WC, Ludovico P. Caloric restriction or catalase inactivation extends yeast chronological lifespan by inducing H2O2 and superoxide dismutase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:15123–15128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1004432107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller RA. Genes against aging. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2012;67:495–502. doi: 10.1093/gerona/gls082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min JN, Whaley RA, Sharpless NE, Lockyer P, Portbury AL, Patterson C. CHIP deficiency decreases longevity, with accelerated aging phenotypes accompanied by altered protein quality control. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28:4018–4025. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00296-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor RK, Baur JA, Gomes AP, Ward TM, Csiszar A, Mercken EM, Abdelmohsen K, Shin YK, Canto C, Scheibye-Knudsen M, et al. SRT1720 improves survival and healthspan of obese mice. Sci Rep. 2011;1:70. doi: 10.1038/srep00070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM, Klionsky DJ. Autophagy fights disease through cellular self-digestion. Nature. 2008;451:1069–1075. doi: 10.1038/nature06639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molofsky AV, Slutsky SG, Joseph NM, He S, Pardal R, Krishnamurthy J, Sharpless NE, Morrison SJ. Increasing p16INK4a expression decreases forebrain progenitors and neurogenesis during ageing. Nature. 2006;443:448–452. doi: 10.1038/nature05091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mookerjee SA, Divakaruni AS, Jastroch M, Brand MD. Mitochondrial uncoupling and lifespan. Mech Ageing Dev. 2010;131:463–472. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2010.03.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow G, Samson M, Michaud S, Tanguay RM. Overexpression of the small mitochondrial Hsp22 extends Drosophila life span and increases resistance to oxidative stress. FASEB J. 2004;18:598–599. doi: 10.1096/fj.03-0860fje. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskalev AA, Shaposhnikov MV, Plyusnina EN, Zhavoronkov A, Budovsky A, Yanai H, Fraifeld VE. The role of DNA damage and repair in aging through the prism of Koch-like criteria. Ageing Res Rev. 2012 doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2012.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mostoslavsky R, Chua KF, Lombard DB, Pang WW, Fischer MR, Gellon L, Liu P, Mostoslavsky G, Franco S, Murphy MM, et al. Genomic instability and aging-like phenotype in the absence of mammalian SIRT6. Cell. 2006;124:315–329. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.11.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murga M, Bunting S, Montana MF, Soria R, Mulero F, Canamero M, Lee Y, McKinnon PJ, Nussenzweig A, Fernandez-Capetillo O. A mouse model of ATR-Seckel shows embryonic replicative stress and accelerated aging. Nat Genet. 2009;41:891–898. doi: 10.1038/ng.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson G, Wordsworth J, Wang C, Jurk D, Lawless C, Martin-Ruiz C, von Zglinicki T. A senescent cell bystander effect: senescence-induced senescence. Aging Cell. 2012;11:345–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2012.00795.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas A, de Magalhaes JP, Kraytsberg Y, Richfield EK, Levanon EY, Khrapko K. Age-related gene-specific changes of A-to-I mRNA editing in the human brain. Mech Ageing Dev. 2010;131:445–447. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2010.06.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueiras R, Habegger KM, Chaudhary N, Finan B, Banks AS, Dietrich MO, Horvath TL, Sinclair DA, Pfluger PT, Tschop MH. Sirtuin 1 and sirtuin 3: physiological modulators of metabolism. Physiol Rev. 2012;92:1479–1514. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00022.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O’Rourke EJ, Kuballa P, Xavier R, Ruvkun G. omega-6 Polyunsaturated fatty acids extend life span through the activation of autophagy. Genes Dev. 2013;27:429–440. doi: 10.1101/gad.205294.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberdoerffer P, Michan S, McVay M, Mostoslavsky R, Vann J, Park SK, Hartlerode A, Stegmuller J, Hafner A, Loerch P, et al. SIRT1 redistribution on chromatin promotes genomic stability but alters gene expression during aging. Cell. 2008;135:907–918. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.10.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberdoerffer P, Sinclair DA. The role of nuclear architecture in genomic instability and ageing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:692–702. doi: 10.1038/nrm2238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olovnikov AM. Telomeres, telomerase, and aging: origin of the theory. Exp Gerontol. 1996;31:443–448. doi: 10.1016/0531-5565(96)00005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onken B, Driscoll M. Metformin induces a dietary restriction-like state and the oxidative stress response to extend C. elegans Healthspan via AMPK, LKB1, and SKN-1. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e8758. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortega-Molina A, Efeyan A, Lopez-Guadamillas E, Munoz-Martin M, Gomez-Lopez G, Canamero M, Mulero F, Pastor J, Martinez S, Romanos E, et al. Pten positively regulates brown adipose function, energy expenditure, and longevity. Cell Metab. 2012;15:382–394. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osorio FG, Barcena C, Soria-Valles C, Ramsay AJ, de Carlos F, Cobo J, Fueyo A, Freije JM, Lopez-Otin C. Nuclear lamina defects cause ATM-dependent NF-kappaB activation and link accelerated aging to a systemic inflammatory response. Genes Dev. 2012;26:2311–2324. doi: 10.1101/gad.197954.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osorio FG, Navarro CL, Cadinanos J, Lopez-Mejia IC, Quiros PM, Bartoli C, Rivera J, Tazi J, Guzman G, Varela I, et al. Splicing-directed therapy in a new mouse model of human accelerated aging. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3:106ra107. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osorio FG, Varela I, Lara E, Puente XS, Espada J, Santoro R, Freije JM, Fraga MF, Lopez-Otin C. Nuclear envelope alterations generate an aging-like epigenetic pattern in mice deficient in Zmpste24 metalloprotease. Aging Cell. 2010;9:947–957. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2010.00621.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottaviani E, Ventura N, Mandrioli M, Candela M, Franchini A, Franceschi C. Gut microbiota as a candidate for lifespan extension: an ecological/evolutionary perspective _targeted on living organisms as metaorganisms. Biogerontology. 2011;12:599–609. doi: 10.1007/s10522-011-9352-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palm W, de Lange T. How shelterin protects mammalian telomeres. Annu Rev Genet. 2008;42:301–334. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.41.110306.130350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park CB, Larsson NG. Mitochondrial DNA mutations in disease and aging. J Cell Biol. 2011;193:809–818. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201010024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne BA, Wilson IJ, Hateley CA, Horvath R, Santibanez-Koref M, Samuels DC, Price DA, Chinnery PF. Mitochondrial aging is accelerated by anti-retroviral therapy through the clonal expansion of mtDNA mutations. Nat Genet. 2011;43:806–810. doi: 10.1038/ng.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson KJ, Baur JA, Lewis KN, Peshkin L, Price NL, Labinskyy N, Swindell WR, Kamara D, Minor RK, Perez E, et al. Resveratrol delays age-related deterioration and mimics transcriptional aspects of dietary restriction without extending life span. Cell Metab. 2008;8:157–168. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2008.06.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegoraro G, Kubben N, Wickert U, Gohler H, Hoffmann K, Misteli T. Ageing-related chromatin defects through loss of the NURD complex. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11:1261–1267. doi: 10.1038/ncb1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peleg S, Sananbenesi F, Zovoilis A, Burkhardt S, Bahari-Javan S, Agis-Balboa RC, Cota P, Wittnam JL, Gogol-Doering A, Opitz L, et al. Altered histone acetylation is associated with age-dependent memory impairment in mice. Science. 2010;328:753–756. doi: 10.1126/science.1186088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez VI, Van Remmen H, Bokov A, Epstein CJ, Vijg J, Richardson A. The overexpression of major antioxidant enzymes does not extend the lifespan of mice. Aging Cell. 2009;8:73–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2008.00449.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper MD, Partridge L, Raubenheimer D, Simpson SJ. Dietary restriction and aging: a unifying perspective. Cell Metab. 2011;14:154–160. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.06.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollina EA, Brunet A. Epigenetic regulation of aging stem cells. Oncogene. 2011;30:3105–3126. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pont AR, Sadri N, Hsiao SJ, Smith S, Schneider RJ. mRNA decay factor AUF1 maintains normal aging, telomere maintenance, and suppression of senescence by activation of telomerase transcription. Mol Cell. 2012;47:5–15. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.04.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers ET, Morimoto RI, Dillin A, Kelly JW, Balch WE. Biological and chemical approaches to diseases of proteostasis deficiency. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:959–991. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.052308.114844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price NL, Gomes AP, Ling AJ, Duarte FV, Martin-Montalvo A, North BJ, Agarwal B, Ye L, Ramadori G, Teodoro JS, et al. SIRT1 is required for AMPK activation and the beneficial effects of resveratrol on mitochondrial function. Cell Metab. 2012;15:675–690. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu X, Brown K, Hirschey MD, Verdin E, Chen D. Calorie restriction reduces oxidative stress by SIRT3-mediated SOD2 activation. Cell Metab. 2010;12:662–667. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2010.11.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raffaello A, Rizzuto R. Mitochondrial longevity pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1813:260–268. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.10.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragnauth CD, Warren DT, Liu Y, McNair R, Tajsic T, Figg N, Shroff R, Skepper J, Shanahan CM. Prelamin A acts to accelerate smooth muscle cell senescence and is a novel biomarker of human vascular aging. Circulation. 2010;121:2200–2210. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.902056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando TA, Chang HY. Aging, rejuvenation, and epigenetic reprogramming: resetting the aging clock. Cell. 2012;148:46–57. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renner O, Carnero A. Mouse models to decipher the PI3K signaling network in human cancer. Curr Mol Med. 2009;9:612–625. doi: 10.2174/156652409788488766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rera M, Bahadorani S, Cho J, Koehler CL, Ulgherait M, Hur JH, Ansari WS, Lo T, Jr., Jones DL, Walker DW. Modulation of longevity and tissue homeostasis by the Drosophila PGC-1 homolog. Cell Metab. 2011;14:623–634. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.09.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ressler S, Bartkova J, Niederegger H, Bartek J, Scharffetter-Kochanek K, Jansen-Durr P, Wlaschek M. p16INK4A is a robust in vivo biomarker of cellular aging in human skin. Aging Cell. 2006;5:379–389. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2006.00231.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristow M, Schmeisser S. Extending life span by increasing oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011;51:327–336. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers JT, Lerin C, Haas W, Gygi SP, Spiegelman BM, Puigserver P. Nutrient control of glucose homeostasis through a complex of PGC-1alpha and SIRT1. Nature. 2005;434:113–118. doi: 10.1038/nature03354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodier F, Campisi J. Four faces of cellular senescence. J Cell Biol. 2011;192:547–556. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201009094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogina B, Helfand SL. Sir2 mediates longevity in the fly through a pathway related to calorie restriction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:15998–16003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0404184101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi DJ, Bryder D, Seita J, Nussenzweig A, Hoeijmakers J, Weissman IL. Deficiencies in DNA damage repair limit the function of haematopoietic stem cells with age. Nature. 2007;447:725–729. doi: 10.1038/nature05862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi DJ, Jamieson CH, Weissman IL. Stems cells and the pathways to aging and cancer. Cell. 2008;132:681–696. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.01.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothgiesser KM, Erener S, Waibel S, Luscher B, Hottiger MO. SIRT2 regulates NF-kappaB dependent gene expression through deacetylation of p65 Lys310. J Cell Sci. 2010;123:4251–4258. doi: 10.1242/jcs.073783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell PM, Fowkes FG, Belch JF, Ogawa H, Warlow CP, Meade TW. Effect of daily aspirin on long-term risk of death due to cancer: analysis of individual patient data from randomised trials. Lancet. 2011;377:31–41. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62110-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinsztein DC, Marino G, Kroemer G. Autophagy and aging. Cell. 2011;146:682–695. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph KL, Chang S, Lee HW, Blasco M, Gottlieb GJ, Greider C, DePinho RA. Longevity, stress response, and cancer in aging telomerase-deficient mice. Cell. 1999;96:701–712. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80580-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell SJ, Kahn CR. Endocrine regulation of ageing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:681–691. doi: 10.1038/nrm2234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruzankina Y, Schoppy DW, Asare A, Clark CE, Vonderheide RH, Brown EJ. Tissue regenerative delays and synthetic lethality in adult mice after combined deletion of Atr and Trp53. Nat Genet. 2009;41:1144–1149. doi: 10.1038/ng.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safdar A, Bourgeois JM, Ogborn DI, Little JP, Hettinga BP, Akhtar M, Thompson JE, Melov S, Mocellin NJ, Kujoth GC, et al. Endurance exercise rescues progeroid aging and induces systemic mitochondrial rejuvenation in mtDNA mutator mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:4135–4140. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1019581108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahin E, Depinho RA. Axis of ageing: telomeres, p53 and mitochondria. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13:397–404. doi: 10.1038/nrm3352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salminen A, Kaarniranta K, Kauppinen A. Inflammaging: disturbed interplay between autophagy and inflammasomes. Aging. 2012;4:166–175. doi: 10.18632/aging.100444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Roman I, Gomez A, Perez I, Sanchez C, Suarez H, Naudi A, Jove M, Lopez-Torres M, Pamplona R, Barja G. Effects of aging and methionine restriction applied at old age on ROS generation and oxidative damage in rat liver mitochondria. Biogerontology. 2012;13:399–411. doi: 10.1007/s10522-012-9384-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnak MJ, Levey AS, Schoolwerth AC, Coresh J, Culleton B, Hamm LL, McCullough PA, Kasiske BL, Kelepouris E, Klag MJ, et al. Kidney disease as a risk factor for development of cardiovascular disease: a statement from the American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention. Circulation. 2003;108:2154–2169. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000095676.90936.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage SA, Giri N, Baerlocher GM, Orr N, Lansdorp PM, Alter BP. TINF2, a component of the shelterin telomere protection complex, is mutated in dyskeratosis congenita. Am J Hum Genet. 2008;82:501–509. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.10.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaffidi P, Misteli T. Lamin A-dependent nuclear defects in human aging. Science. 2006;312:1059–1063. doi: 10.1126/science.1127168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaffidi P, Misteli T. Lamin A-dependent misregulation of adult stem cells associated with accelerated ageing. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:452–459. doi: 10.1038/ncb1708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schotta G, Lachner M, Sarma K, Ebert A, Sengupta R, Reuter G, Reinberg D, Jenuwein T. A silencing pathway to induce H3-K9 and H4-K20 trimethylation at constitutive heterochromatin. Genes Dev. 2004;18:1251–1262. doi: 10.1101/gad.300704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher B, van der Pluijm I, Moorhouse MJ, Kosteas T, Robinson AR, Suh Y, Breit TM, van Steeg H, Niedernhofer LJ, van Ijcken W, et al. Delayed and accelerated aging share common longevity assurance mechanisms. PLoS Genet. 2008;4:e1000161. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebastian C, Satterstrom FK, Haigis MC, Mostoslavsky R. From sirtuin biology to human diseases: an update. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:42444–42452. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R112.402768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebastiani P, Riva A, Montano M, Pham P, Torkamani A, Scherba E, Benson G, Milton JN, Baldwin CT, Andersen S, et al. Whole genome sequences of a male and female supercentenarian, ages greater than 114 years. Front Genet. 2011;2:90. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2011.00090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selman C, Tullet JM, Wieser D, Irvine E, Lingard SJ, Choudhury AI, Claret M, Al-Qassab H, Carmignac D, Ramadani F, et al. Ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 signaling regulates mammalian life span. Science. 2009;326:140–144. doi: 10.1126/science.1177221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sena LA, Chandel NS. Physiological roles of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Mol Cell. 2012;48:158–167. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.09.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senovilla L, Vitale I, Martins I, Tailler M, Pailleret C, Michaud M, Galluzzi L, Adjemian S, Kepp O, Niso-Santano M, et al. An immunosurveillance mechanism controls cancer cell ploidy. Science. 2012;337:1678–1684. doi: 10.1126/science.1224922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano M, Lin AW, McCurrach ME, Beach D, Lowe SW. Oncogenic ras provokes premature cell senescence associated with accumulation of p53 and p16INK4a. Cell. 1997;88:593–602. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81902-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpless NE, DePinho RA. How stem cells age and why this makes us grow old. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:703–713. doi: 10.1038/nrm2241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw AC, Joshi S, Greenwood H, Panda A, Lord JM. Aging of the innate immune system. Curr Opin Immunol. 2010;22:507–513. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2010.05.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen Y, Wollam J, Magner D, Karalay O, Antebi A. A steroid receptor-microRNA switch regulates life span in response to signals from the gonad. Science. 2012;338:1472–1476. doi: 10.1126/science.1228967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimi T, Butin-Israeli V, Adam SA, Hamanaka RB, Goldman AE, Lucas CA, Shumaker DK, Kosak ST, Chandel NS, Goldman RD. The role of nuclear lamin B1 in cell proliferation and senescence. Genes Dev. 2011;25:2579–2593. doi: 10.1101/gad.179515.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shumaker DK, Dechat T, Kohlmaier A, Adam SA, Bozovsky MR, Erdos MR, Eriksson M, Goldman AE, Khuon S, Collins FS, et al. Mutant nuclear lamin A leads to progressive alterations of epigenetic control in premature aging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:8703–8708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0602569103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebold AP, Banerjee R, Tie F, Kiss DL, Moskowitz J, Harte PJ. Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 and Trithorax modulate Drosophila longevity and stress resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:169–174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0907739107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack C, Giannakou ME, Foley A, Goss M, Partridge L. dFOXO-independent effects of reduced insulin-like signaling in Drosophila. Aging Cell. 2011;10:735–748. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2011.00707.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith-Vikos T, Slack FJ. MicroRNAs and their roles in aging. J Cell Sci. 2012;125:7–17. doi: 10.1242/jcs.099200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soda K, Dobashi Y, Kano Y, Tsujinaka S, Konishi F. Polyamine-rich food decreases age-associated pathology and mortality in aged mice. Exp Gerontol. 2009;44:727–732. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2009.08.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Someya S, Yu W, Hallows WC, Xu J, Vann JM, Leeuwenburgh C, Tanokura M, Denu JM, Prolla TA. Sirt3 mediates reduction of oxidative damage and prevention of age-related hearing loss under caloric restriction. Cell. 2010;143:802–812. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.10.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong R, Miller RA, Astle CM, Baur JA, de Cabo R, Fernandez E, Guo W, Javors M, Kirkland JL, Nelson JF, et al. Evaluation of resveratrol, green tea extract, curcumin, oxaloacetic Acid, and medium-chain triglyceride oil on life span of genetically heterogeneous mice. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2012;68:6–16. doi: 10.1093/gerona/gls070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong R, Miller RA, Astle CM, Floyd RA, Flurkey K, Hensley KL, Javors MA, Leeuwenburgh C, Nelson JF, Ongini E, et al. Nordihydroguaiaretic acid and aspirin increase lifespan of genetically heterogeneous male mice. Aging Cell. 2008;7:641–650. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2008.00414.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swindell WR, Masternak MM, Kopchick JJ, Conover CA, Bartke A, Miller RA. Endocrine regulation of heat shock protein mRNA levels in long-lived dwarf mice. Mech Ageing Dev. 2009;130:393–400. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2009.03.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabas I. Macrophage death and defective inflammation resolution in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:36–46. doi: 10.1038/nri2675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talens RP, Christensen K, Putter H, Willemsen G, Christiansen L, Kremer D, Suchiman HE, Slagboom PE, Boomsma DI, Heijmans BT. Epigenetic variation during the adult lifespan: cross-sectional and longitudinal data on monozygotic twin pairs. Aging Cell. 2012;11:694–703. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2012.00835.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao R, Coleman MC, Pennington JD, Ozden O, Park SH, Jiang H, Kim HS, Flynn CR, Hill S, Hayes McDonald W, et al. Sirt3-mediated deacetylation of evolutionarily conserved lysine 122 regulates MnSOD activity in response to stress. Mol Cell. 2010;40:893–904. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.12.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilstra JS, Robinson AR, Wang J, Gregg SQ, Clauson CL, Reay DP, Nasto LA, St Croix CM, Usas A, Vo N, et al. NF-kappaB inhibition delays DNA damage-induced senescence and aging in mice. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:2601–2612. doi: 10.1172/JCI45785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tissenbaum HA, Guarente L. Increased dosage of a sir-2 gene extends lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2001;410:227–230. doi: 10.1038/35065638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toledano H, D’Alterio C, Czech B, Levine E, Jones DL. The let-7-Imp axis regulates ageing of the Drosophila testis stem-cell niche. Nature. 2012;485:605–610. doi: 10.1038/nature11061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomaru U, Takahashi S, Ishizu A, Miyatake Y, Gohda A, Suzuki S, Ono A, Ohara J, Baba T, Murata S, et al. Decreased proteasomal activity causes age-related phenotypes and promotes the development of metabolic abnormalities. Am J Pathol. 2012;180:963–972. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.11.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomas-Loba A, Flores I, Fernandez-Marcos PJ, Cayuela ML, Maraver A, Tejera A, Borras C, Matheu A, Klatt P, Flores JM, et al. Telomerase reverse transcriptase delays aging in cancer-resistant mice. Cell. 2008;135:609–622. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.09.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifunovic A, Wredenberg A, Falkenberg M, Spelbrink JN, Rovio AT, Bruder CE, Bohlooly YM, Gidlof S, Oldfors A, Wibom R, et al. Premature ageing in mice expressing defective mitochondrial DNA polymerase. Nature. 2004;429:417–423. doi: 10.1038/nature02517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurumi A, Li WX. Global heterochromatin loss: a unifying theory of aging? Epigenetics. 2012;7:680–688. doi: 10.4161/epi.20540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugalde AP, Espanol Y, Lopez-Otin C. Micromanaging aging with miRNAs: new messages from the nuclear envelope. Nucleus. 2011;2:549–555. doi: 10.4161/nucl.2.6.17986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ham TJ, Holmberg MA, van der Goot AT, Teuling E, Garcia-Arencibia M, Kim HE, Du D, Thijssen KL, Wiersma M, Burggraaff R, et al. Identification of MOAG-4/SERF as a regulator of age-related proteotoxicity. Cell. 2010;142:601–612. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.07.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Raamsdonk JM, Hekimi S. Deletion of the mitochondrial superoxide dismutase sod-2 extends lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Genet. 2009;5:e1000361. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Remmen H, Ikeno Y, Hamilton M, Pahlavani M, Wolf N, Thorpe SR, Alderson NL, Baynes JW, Epstein CJ, Huang TT, et al. Life-long reduction in MnSOD activity results in increased DNA damage and higher incidence of cancer but does not accelerate aging. Physiol Genomics. 2003;16:29–37. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00122.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varela I, Cadinanos J, Pendas AM, Gutierrez-Fernandez A, Folgueras AR, Sanchez LM, Zhou Z, Rodriguez FJ, Stewart CL, Vega JA, et al. Accelerated ageing in mice deficient in Zmpste24 protease is linked to p53 signalling activation. Nature. 2005;437:564–568. doi: 10.1038/nature04019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varela I, Pereira S, Ugalde AP, Navarro CL, Suarez MF, Cau P, Cadinanos J, Osorio FG, Foray N, Cobo J, et al. Combined treatment with statins and aminobisphosphonates extends longevity in a mouse model of human premature aging. Nat Med. 2008;14:767–772. doi: 10.1038/nm1786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermulst M, Wanagat J, Kujoth GC, Bielas JH, Rabinovitch PS, Prolla TA, Loeb LA. DNA deletions and clonal mutations drive premature aging in mitochondrial mutator mice. Nat Genet. 2008;40:392–394. doi: 10.1038/ng.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijg J, Campisi J. Puzzles, promises and a cure for ageing. Nature. 2008;454:1065–1071. doi: 10.1038/nature07216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilchez D, Morantte I, Liu Z, Douglas PM, Merkwirth C, Rodrigues AP, Manning G, Dillin A. RPN-6 determines C. elegans longevity under proteotoxic stress conditions. Nature. 2012;489:263–268. doi: 10.1038/nature11315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeda SA, Luo J, Mosher KI, Zou B, Britschgi M, Bieri G, Stan TM, Fainberg N, Ding Z, Eggel A, et al. The ageing systemic milieu negatively regulates neurogenesis and cognitive function. Nature. 2011;477:90–94. doi: 10.1038/nature10357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viswanathan M, Guarente L. Regulation of Caenorhabditis elegans lifespan by sir-2.1 transgenes. Nature. 2011;477:E1–2. doi: 10.1038/nature10440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker GA, Lithgow GJ. Lifespan extension in C. elegans by a molecular chaperone dependent upon insulin-like signals. Aging Cell. 2003;2:131–139. doi: 10.1046/j.1474-9728.2003.00045.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walne AJ, Vulliamy T, Beswick R, Kirwan M, Dokal I. TINF2 mutations result in very short telomeres: analysis of a large cohort of patients with dyskeratosis congenita and related bone marrow failure syndromes. Blood. 2008;112:3594–3600. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-05-153445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace DC. A mitochondrial paradigm of metabolic and degenerative diseases, aging, and cancer: a dawn for evolutionary medicine. Annu Rev Genet. 2005;39:359–407. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.39.110304.095751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C, Jurk D, Maddick M, Nelson G, Martin-Ruiz C, von Zglinicki T. DNA damage response and cellular senescence in tissues of aging mice. Aging Cell. 2009;8:311–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2009.00481.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K, Klionsky DJ. Mitochondria removal by autophagy. Autophagy. 2011;7:297–300. doi: 10.4161/auto.7.3.14502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang RH, Sengupta K, Li C, Kim HS, Cao L, Xiao C, Kim S, Xu X, Zheng Y, Chilton B, et al. Impaired DNA damage response, genome instability, and tumorigenesis in SIRT1 mutant mice. Cancer Cell. 2008;14:312–323. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.09.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerheide SD, Anckar J, Stevens SM, Jr., Sistonen L, Morimoto RI. Stress-inducible regulation of heat shock factor 1 by the deacetylase SIRT1. Science. 2009;323:1063–1066. doi: 10.1126/science.1165946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson JE, Burmeister L, Brooks SV, Chan CC, Friedline S, Harrison DE, Hejtmancik JF, Nadon N, Strong R, Wood LK, et al. Rapamycin slows aging in mice. Aging Cell. 2012;11:675–682. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2012.00832.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worman HJ. Nuclear lamins and laminopathies. J Pathol. 2012;226:316–325. doi: 10.1002/path.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie J, Zhang X, Zhang L. Negative regulation of inflammation by SIRT1. Pharmacol Res. 2012;67:60–67. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2012.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xue W, Zender L, Miething C, Dickins RA, Hernando E, Krizhanovsky V, Cordon-Cardo C, Lowe SW. Senescence and tumour clearance is triggered by p53 restoration in murine liver carcinomas. Nature. 2007;445:656–660. doi: 10.1038/nature05529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaza H, Komatsu T, Wakita S, Kijogi C, Park S, Hayashi H, Chiba T, Mori R, Furuyama T, Mori N, et al. FoxO1 is involved in the antineoplastic effect of calorie restriction. Aging Cell. 2010;9:372–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2010.00563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang SB, Tien AC, Boddupalli G, Xu AW, Jan YN, Jan LY. Rapamycin ameliorates age-dependent obesity associated with increased mTOR signaling in hypothalamic POMC neurons. Neuron. 2012;75:425–436. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.03.043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang SH, Meta M, Qiao X, Frost D, Bauch J, Coffinier C, Majumdar S, Bergo MO, Young SG, Fong LG. A farnesyltransferase inhibitor improves disease phenotypes in mice with a Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome mutation. J Clin Invest. 2006;116:2115–2121. doi: 10.1172/JCI28968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao H, Chung S, Hwang JW, Rajendrasozhan S, Sundar IK, Dean DA, McBurney MW, Guarente L, Gu W, Ronty M, et al. SIRT1 protects against emphysema via FOXO3-mediated reduction of premature senescence in mice. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:2032–2045. doi: 10.1172/JCI60132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz OH, Katajisto P, Lamming DW, Gultekin Y, Bauer-Rowe KE, Sengupta S, Birsoy K, Dursun A, Yilmaz VO, Selig M, et al. mTORC1 in the Paneth cell niche couples intestinal stem-cell function to calorie intake. Nature. 2012;486:490–495. doi: 10.1038/nature11163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang C, Cuervo AM. Restoration of chaperone-mediated autophagy in aging liver improves cellular maintenance and hepatic function. Nat Med. 2008;14:959–965. doi: 10.1038/nm.1851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang G, Li J, Purkayastha S, Tang Y, Zhang H, Yin Y, Li B, Liu G, Cai D. Hypothalamic programming of systemic ageing involving IKK-beta, NF-kappaB and GnRH. Nature. 2013;497:211–216. doi: 10.1038/nature12143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y, Ikeno Y, Qi W, Chaudhuri A, Li Y, Bokov A, Thorpe SR, Baynes JW, Epstein C, Richardson A, et al. Mice deficient in both Mn superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase-1 have increased oxidative damage and a greater incidence of pathology but no reduction in longevity. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2009;64:1212–1220. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glp132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z, Lowry SF, Guarente L, Haimovich B. Roles of SIRT1 in the acute and restorative phases following induction of inflammation. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:41391–41401. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.174482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong F, Savage SA, Shkreli M, Giri N, Jessop L, Myers T, Chen R, Alter BP, Artandi SE. Disruption of telomerase trafficking by TCAB1 mutation causes dyskeratosis congenita. Genes Dev. 2011;25:11–16. doi: 10.1101/gad.2006411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong L, D’Urso A, Toiber D, Sebastian C, Henry RE, Vadysirisack DD, Guimaraes A, Marinelli B, Wikstrom JD, Nir T, et al. The histone deacetylase Sirt6 regulates glucose homeostasis via Hif1alpha. Cell. 2010;140:280–293. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.12.041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]