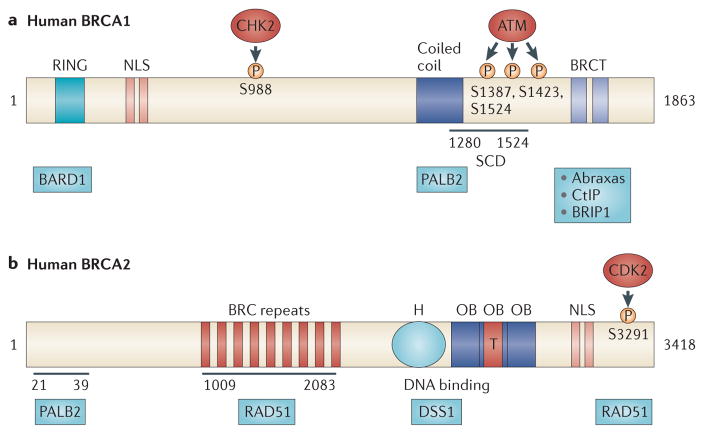
Figure 2. BRCA1 and BRCA2 functional domains.
a | The BRCA1 amino terminus contains a RING domain that associates with BRCA1-associated RING domain protein 1 (BARD1) and a nuclear localization sequence (NLS). The central region of BRCA1 contains a CHK2 phosphorylation site on S988 (REF. 25). The carboxyl terminus of BRCA1 contains: a coiled-coil domain that associates with partner and localizer of BRCA2 (PALB2); a SQ/TQ cluster domain (SCD) that contains approximately ten potential ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM) phosphorylation sites and spans amino acid residues 1280–1524; and a BRCT domain that binds ATM-phosphorylated abraxas, CtBP-interacting protein (CtIP) and BRCA1-interacting protein C-terminal helicase 1 (BRIP1). The BRCA1–abraxas complex is associated with BRCA1 recruitment to sites of DNA damage19,20,108,109. The BRCA1–BRIP1 complex, which also contains DNA topoisomerase 2-binding protein 1 (TOPBP1), is associated with DNA repair during replication110. The BRCA1–CtIP complex promotes ataxia-telangiectasia and Rad3-related (ATR) activation and homologous recombination (HR) by associating with the MRN complex (which is comprised of MRE11, RAD50 and Nijmegen breakage syndrome protein 1 (NBS1)) and facilitating DNA double-strand break resection22. The central region of BRCA1, which contains the SCD, is phosphorylated by ATM. This phosphorylation is important for BRCA1-mediated G2/M and S-phase checkpoint activation, as expression of a BRCA1 mutant that lacks three of the phosphorylation sites (S1387, S1423 and S1524) fails to rescue defective checkpoint activation and ionizing radiation hypersensitivity in a BRCA1-deficient cell line111,112. b | The N terminus of BRCA2 binds PALB2 at amino acids 21–39 (REF. 68). BRCA2 contains eight BRC repeats between amino acid residues 1009 and 2083 that bind RAD51. The BRCA2 DNA-binding domain contains a helical domain (H), three oligonucleotide binding (OB) folds and a tower domain (T), which may facilitate BRCA2 binding to both single-stranded DNA and double-stranded DNA46. This region also associates with deleted in split-hand/split-foot syndrome (DSS1)42,44,45. The C terminus of BRCA2 contains an NLS and a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) phosphorylation site at S3291 that also binds RAD51 (REF. 53).