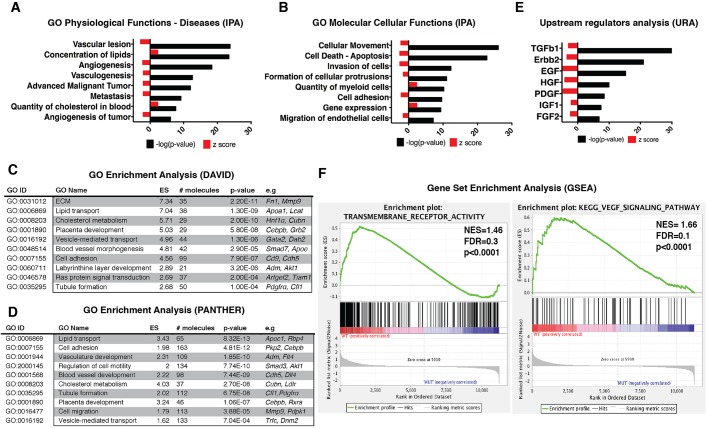
Fig. 4.
Genome-wide analysis of Usp22 mutant placentas reveals defects in vascularization, cellular movement and multiple signaling transduction pathways. (A) GO analysis of significantly affected physiological functions and diseases predicted by IPA. (B) GO analysis of significantly affected molecular and cellular functions predicted by IPA. (C,D) DAVID and PANTHER analysis software were used to find and verify the GO terms that were significantly enriched in differentially regulated gene sets produced by the RNA-seq analysis. (E) Upstream regulators analysis by IPA predicted the TGFβ1 pathway to be the most significantly inhibited (z-score: −2.900, P=4.9E-37). Several RTK pathways were predicted to be inhibited in the Usp22 mutants, including those responsive to Erbb2 (z-score: −3.369, P=1.9E-21), EGF (z-score: −4.616, P=5.2E-16), HGF (z-score: −2.051, P=1.23E-10) and PDGF (z-score: −4.560, P=3.9E-09). (F) Representative plots of gene set enrichment GSEA analysis for transmembrane receptor activity and VEGF signaling pathway. FDR, false discovery rate; NES, normalized enrichment score.