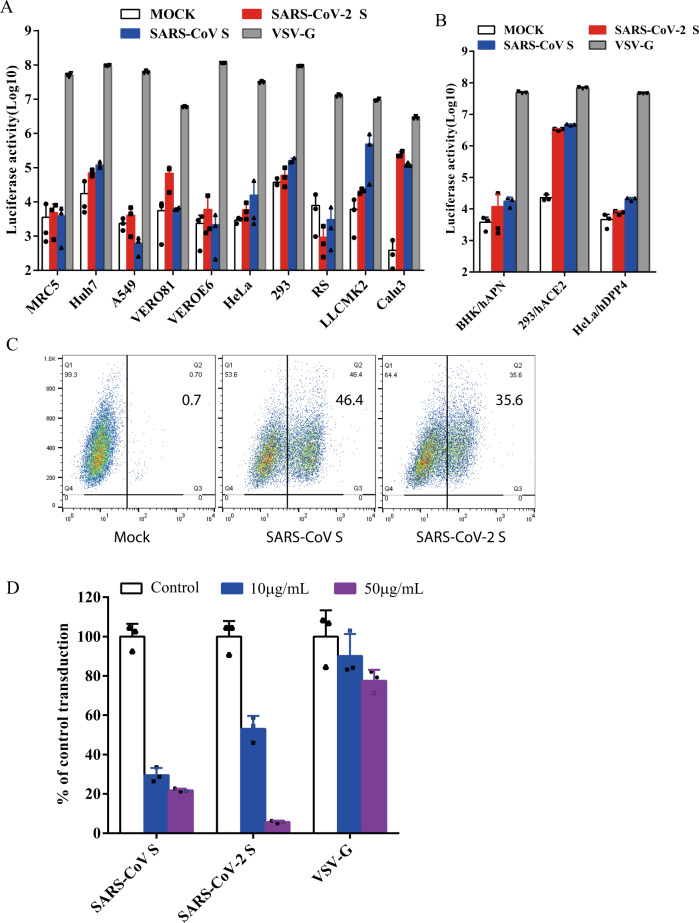
Fig. 2. Entry and receptor of SARS-CoV-2 S pseudovirons.
a, b Entry of SARS-CoV-2 S pseudovirions on indicated cell lines. Cells from human and animal origin were inoculated with SARS-CoV-2 S (red), SARS-CoV S (blue), or VSV-G (gray) pseudovirions. At 48 h post inoculation, transduction efficiency was measured according to luciferase activities. RS, Rhinolophus sinicus bat embryonic fibroblast; BHK/hAPN, BHK cells stably expressing hAPN, the hCoV-229E receptor; 293/hACE2, 293 cells stably expressing hACE2, the SARS-CoV receptor; HeLa/hDPP4, HeLa cells stably expressing hDPP4, the MERS-CoV receptor. Experiments were done in triplicates and repeated at least three times. One representative is shown with error bars indicating SEM. c Binding of SARS-CoV S and SARS-CoV-2 S proteins to soluble hACE2. HEK293T cells transiently expressing SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 S proteins were incubated with the soluble hACE2 on ice, followed by polyclonal goat anti-hACE2 antibody. Cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. The experiments were repeated at least three times. d Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 S pseudovirion entry by soluble hACE2. SARS-CoV S, SARS-CoV-2 S, or VSV-G pseudovirions were pre-incubated with soluble hACE2, then mixture were added to 293/hACE2 cells. Cells were lysed 40 h later and pseudoviral transduction was measured. Experiments were done twice and one representative is shown. Error bars indicate SEM of technical triplicates. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.