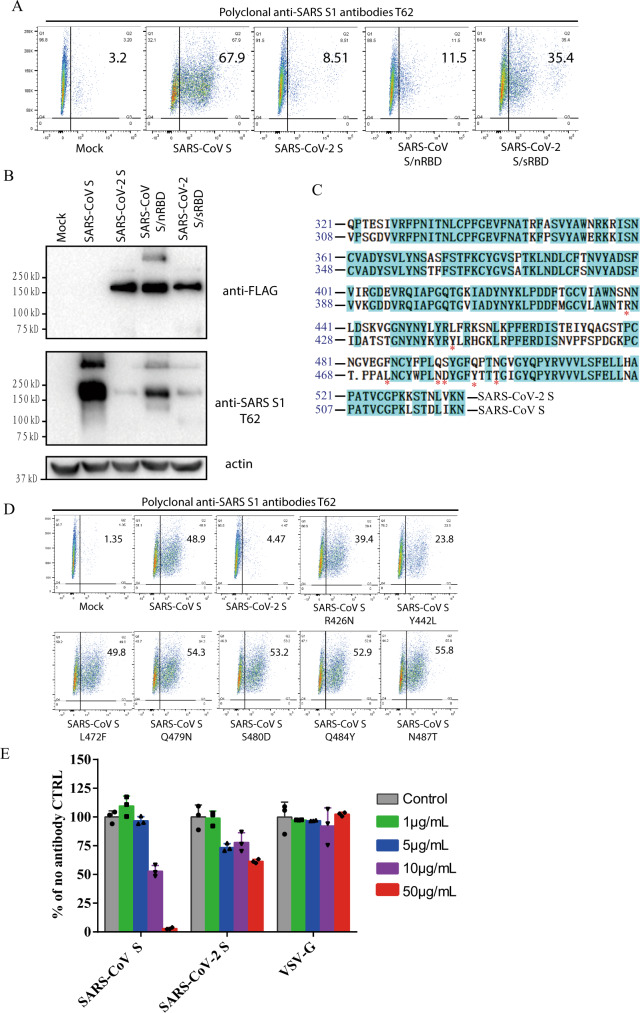
Fig. 5. Characterization of polyclonal rabbit anti-SARS S1 antibodies T62.
a Binding of polyclonal rabbit anti-SARS S1 antibodies T62 to SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV S, and chimeric S proteins. HEK293T cells transiently expressing either SARS-CoV-2 S, SARS-CoV S, SARS-CoV S/nRBD, or SARS-CoV-2 S/sRBD proteins were incubated with polyclonal rabbit anti-SARS-CoV S1 antibody T62 for 1 h on ice, followed by a FITC-conjugated secondary antibody, then cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. Experiments were done three times and one representative is shown. b Expression of SARS-CoV-2 S, SARS-CoV S, or chimeric S proteins on 293T cells. Cells from panel A were lyzed and blotted with anti-FLAG M2 antibody and polyclonal anti-SARS S1 antibody T62. c Amino acid sequence alignment of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 S RBDs. Stars (*) indicate the seven critical residues different between SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV RBDs. d Binding of polyclonal rabbit anti-SARS S1 antibodies T62 to mutant SARS-CoV S proteins. e Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 S and SARS-CoV S pseudovirions by polyclonal rabbit anti-SARS S1 antibody T62. Pseudovirons were pre-incubated with serially diluted polyclonal rabbit anti-SARS S1 antibodies T62 on ice, then virus-antibody mixture was added on 293/hACE2 cells. Pseudoviral transduction was measured 40 h later. Experiments were done in triplicates and repeated twice, and one representative is shown. Error bars indicate SEM of technical triplicates. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.