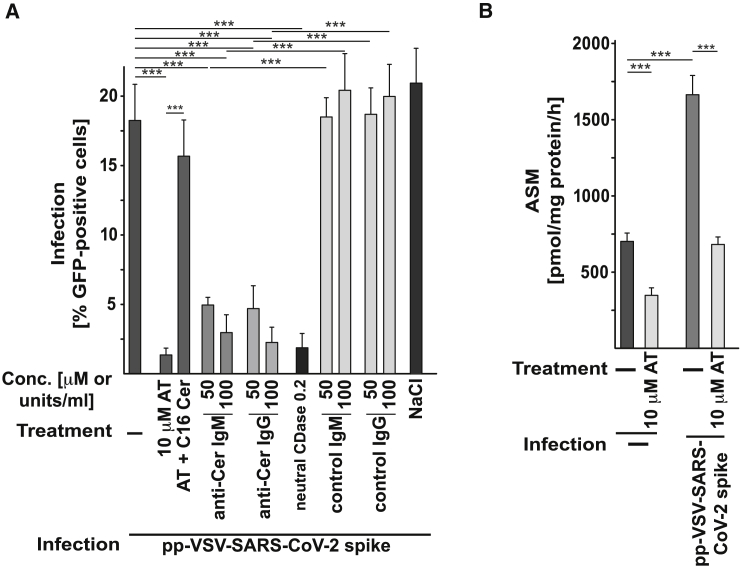
Figure 6.
Infection of Freshly Isolated Human Nasal Epithelial Cells Is Prevented by Ex Vivo Treatment with AT, Anti-Cer Antibodies, or neut. CDase
(A) Freshly isolated human nasal epithelial cells were infected with pp-VSV-SARS-CoV-2 spike for 60 min. Anti-Cer antibodies (IgM or IgG) or neut. CDase were co-applied with the virus. AT (10 μM) was applied for 60 min before the infection and was also present during the infection. All of these treatments blocked the infection of freshly isolated human nasal epithelial cells with pp-VSV-SARS-CoV-2 spike. Control IgM, IgG, or 0.9% NaCl (solvent for AT) exerted no effect. Ceramide was reconstituted in AT-treated nasal epithelial cells with 10 μM C16-Cer; this reconstitution restored the infection of the cells with pp-VSV-SARS-CoV-2 spike.
(B) AT reduced ASM activity in nasal epithelial cells upon infection.
Shown are the means ± SD of 6 (A) or 5 (B) independent experiments. ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ANOVA, followed by post hoc Student’s t tests.