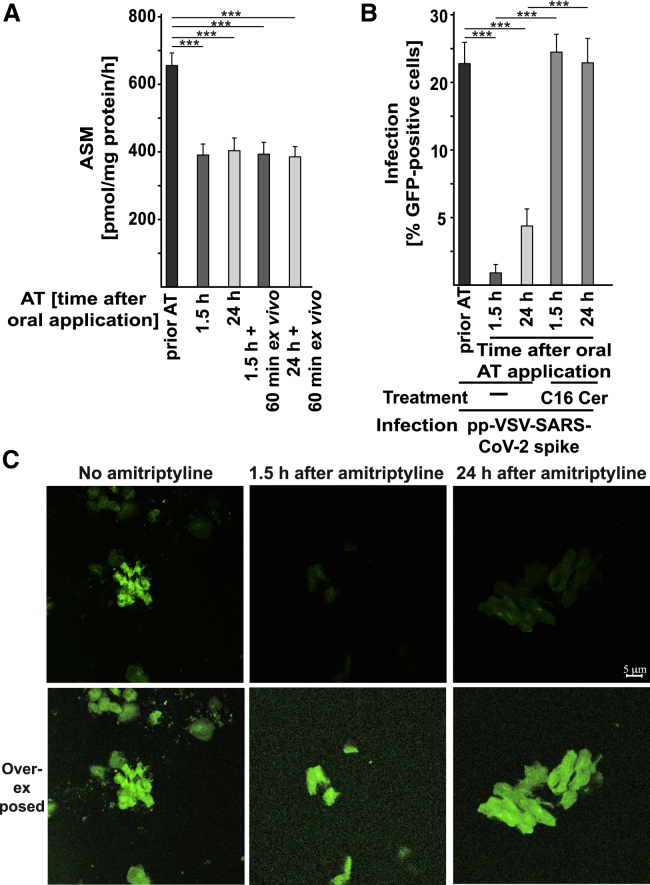
Figure 7.
In Vivo Administration of AT Prevents Infection of Nasal Epithelial Cells with pp-VSV-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Ex Vivo
Volunteers were orally treated with 0.5 mg/kg AT. Nasal epithelial cells were isolated from volunteers before and 1.5 h and 24 h after administration of AT.
(A) Activity of ASM was determined by measurement of the consumption of [14C]sphingomyelin in aliquots of freshly isolated nasal epithelial cells or after an additional 1-h culture ex vivo.
(B) After isolation, nasal epithelial cells were infected for 1 h, with pp-VSV-SARS-CoV-2 spike and washed. The expression of EGFP was determined after 24 h in at least 500 epithelial cells per sample in randomly chosen microscopic fields. Ceramide in nasal epithelial cells isolated from volunteers who had taken AT was reconstituted with 10 μM C16-Cer. This reconstitution restored the infection of the cells with pp-VSV-SARS-CoV-2 spike. The percentage of infected nasal epithelial cells is displayed.
(C) Shown is a typical result from 6 independent infection studies with nasal epithelial cells from volunteers before and after oral administration of AT. The bottom panel shows an over-exposed microphotograph to visualize all cells.
Shown are the means ± SD from 6 volunteers. ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ANOVA, followed by post hoc Student’s t tests.