c-Kit triggers dual phosphorylations, which couple activation and degradation of the essential melanocyte factor Mi
- PMID: 10673502
- PMCID: PMC316361
c-Kit triggers dual phosphorylations, which couple activation and degradation of the essential melanocyte factor Mi
Abstract
Microphthalmia (Mi) is a bHLHZip transcription factor that is essential for melanocyte development and postnatal function. It is thought to regulate both differentiated features of melanocytes such as pigmentation as well as proliferation/survival, based on phenotypes of mutant mouse alleles. Mi activity is controlled by at least two signaling pathways. Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) promotes transcription of the Mi gene through cAMP elevation, resulting in sustained Mi up-regulation over many hours. c-Kit signaling up-regulates Mi function through MAP kinase phosphorylation of Mi, thereby recruiting the p300 transcriptional coactivator. The current study reveals that c-Kit signaling triggers two phosphorylation events on Mi, which up-regulate transactivation potential yet simultaneously _target Mi for ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis. The specific activation/degradation signals derive from MAPK/ERK _targeting of serine 73, whereas serine 409 serves as a substrate for p90 Rsk-1. An unphosphorylatable double mutant at these two residues is at once profoundly stable and transcriptionally inert. These c-Kit-induced phosphorylations couple transactivation to proteasome-mediated degradation. c-Kit signaling thus triggers short-lived Mi activation and net Mi degradation, in contrast to the profoundly increased Mi expression after MSH signaling, potentially explaining the functional diversity of this transcription factor in regulating proliferation, survival, and differentiation in melanocytes.
Figures



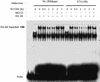
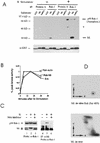


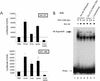
Similar articles
-
Lineage-specific signaling in melanocytes. C-kit stimulation recruits p300/CBP to microphthalmia.J Biol Chem. 1998 Jul 17;273(29):17983-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.29.17983. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9660747
-
Stimulation of melanoblast pigmentation by 8-methoxypsoralen:the involvement of microphthalmia-associated transcription factor, the protein kinase a signal pathway, and proteasome-mediated degradation.J Invest Dermatol. 2002 Dec;119(6):1341-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2002.19607.x. J Invest Dermatol. 2002. PMID: 12485437
-
MAP kinase links the transcription factor Microphthalmia to c-Kit signalling in melanocytes.Nature. 1998 Jan 15;391(6664):298-301. doi: 10.1038/34681. Nature. 1998. PMID: 9440696
-
Signaling Cascades Activated by UVB in Human Melanocytes Lead to the Increased Expression of Melanocyte Receptors, Endothelin B Receptor and c-KIT.Photochem Photobiol. 2018 May;94(3):421-431. doi: 10.1111/php.12848. Epub 2018 Mar 8. Photochem Photobiol. 2018. PMID: 28977677 Review.
-
Identifying the niche controlling melanocyte differentiation.Genes Dev. 2017 Apr 15;31(8):721-723. doi: 10.1101/gad.300665.117. Genes Dev. 2017. PMID: 28512235 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Induction of melanogenesis by 4'-O-methylated flavonoids in B16F10 melanoma cells.J Nat Med. 2013 Oct;67(4):705-10. doi: 10.1007/s11418-012-0727-y. Epub 2012 Dec 4. J Nat Med. 2013. PMID: 23208771
-
In vivo role of alternative splicing and serine phosphorylation of the microphthalmia-associated transcription factor.Genetics. 2012 May;191(1):133-44. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.135996. Epub 2012 Feb 23. Genetics. 2012. PMID: 22367038 Free PMC article.
-
ERK signalling: a master regulator of cell behaviour, life and fate.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Oct;21(10):607-632. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-0255-7. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32576977 Review.
-
Roles of cell-extrinsic growth factors in vertebrate eye pattern formation and retinogenesis.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004 Feb;15(1):91-103. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2003.09.004. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15036212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dehydroglyasperin D Suppresses Melanin Synthesis through MITF Degradation in Melanocytes.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Aug 28;32(8):982-988. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2207.07043. Epub 2022 Aug 1. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35909194 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrews RG, Briddell RA, Appelbaum FR, McNiece IK. Stimulation of hematopoiesis in vivo by stem cell factor. Curr Opin Hematol. 1994;1:187–196. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong JA, Emerson BM. Transcription of chromatin: These are complex times. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1998;8:165–172. - PubMed
-
- Berk AJ. Activation of RNA polymerase II transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999;11:330–335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
