ABC of arterial and venous disease: vascular complications of diabetes
- PMID: 10764371
- PMCID: PMC1117946
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.320.7241.1062
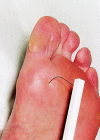
ABC of arterial and venous disease: vascular complications of diabetes
Figures



Similar articles
-
The vascular complications of diabetes mellitus.Acta Biomed Ateneo Parmense. 1995;66(3-4):119-24. Acta Biomed Ateneo Parmense. 1995. PMID: 8578928 Review. No abstract available.
-
Microvascular complications of diabetes.Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2004 Mar;33(1):215-38, xi-xii. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2003.12.003. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2004. PMID: 15053904 Review. No abstract available.
-
[Diabetes mellitus. Metabolic, vascular, neurologic and infectious complications].Soins. 1989 May;(524):8-14. Soins. 1989. PMID: 2749315 French. No abstract available.
-
[The chronic complications of diabetes].Rev Enferm. 1990 May;13(141 Suppl):14-8. Rev Enferm. 1990. PMID: 2359931 Spanish. No abstract available.
-
[Diabetic complication: definition and classification].Nihon Rinsho. 1991 Feb;49 Suppl:3-8. Nihon Rinsho. 1991. PMID: 2033818 Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus in patients with mild obesity: preliminary results of surgical treatment.Obes Surg. 2013 Feb;23(2):234-40. doi: 10.1007/s11695-012-0780-3. Obes Surg. 2013. PMID: 23054574
-
Diabetic Retinopathy and the NMDA Receptor.Drug News Perspect. 2002 May;15(4):226-232. doi: 10.1358/dnp.2002.15.4.840055. Drug News Perspect. 2002. PMID: 12677206 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation alterations in heart failure, ischaemic heart disease and diabetic cardiomyopathy.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Apr;171(8):2080-90. doi: 10.1111/bph.12475. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24147975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Different strategies for screening and prevention of type 2 diabetes in adults: cost effectiveness analysis.BMJ. 2008 May 24;336(7654):1180-5. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39545.585289.25. Epub 2008 Apr 21. BMJ. 2008. PMID: 18426840 Free PMC article.
-
High-dose thiamine therapy for patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria: a randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled pilot study.Diabetologia. 2009 Feb;52(2):208-12. doi: 10.1007/s00125-008-1224-4. Epub 2008 Dec 5. Diabetologia. 2009. PMID: 19057893 Clinical Trial.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
