The MAPK/ERK cascade _targets both Elk-1 and cAMP response element-binding protein to control long-term potentiation-dependent gene expression in the dentate gyrus in vivo
- PMID: 10844026
- PMCID: PMC6772466
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-12-04563.2000
The MAPK/ERK cascade _targets both Elk-1 and cAMP response element-binding protein to control long-term potentiation-dependent gene expression in the dentate gyrus in vivo
Abstract
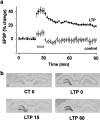
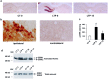
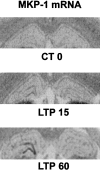
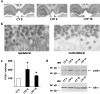
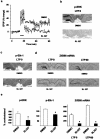
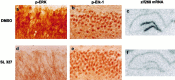
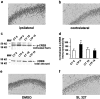
The mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MAPK/ERK) signaling cascade contributes to synaptic plasticity and to long-term memory formation, yet whether MAPK/ERK controls activity-dependent gene expression critical for long-lasting changes at the synapse and what the events underlying transduction of the signal are remain uncertain. Here we show that induction of long-term potentiation (LTP) in the dentate gyrus in vivo leads to rapid phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of MAPK/ERK. Following a similar time course, the two downstream transcriptional _targets of MAPK/ERK, cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) and the ternary complex factor Elk-1, a key transcriptional-regulator of serum response element (SRE)-driven gene expression, were hyperphosphorylated and the immediate early gene zif268 was upregulated. The mRNA encoding MAP kinase phosphatase MKP-1 was upregulated at the time point when MAPK/ERK phosphorylation had returned to basal levels, suggesting a negative feedback loop to regulate deactivation of MAPK/ERK. We also show that inhibition of the MAPK/ERK cascade by the MAPK kinase MEK inhibitor SL327 prevented CREB and Elk-1 phosphorylation, and LTP-dependent gene induction, resulting in rapidly decaying LTP. In conclusion, we suggest that Elk-1 forms an important link in the MAP kinase pathway to transduce signals from the cell surface to the nucleus to activate the genetic machinery necessary for the maintenance of synaptic plasticity in the dentate gyrus. Thus, MAPK/ERK activation is required for LTP-dependent transcriptional regulation and we suggest this is regulated by two parallel signaling pathways, the MAPK/ERK-Elk-1 pathway _targeting SRE and the MAPK/ERK-CREB pathway _targeting CRE.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) controls immediate early gene induction on corticostriatal stimulation.J Neurosci. 1998 Nov 1;18(21):8814-25. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-21-08814.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9786988 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term depression in the adult hippocampus in vivo involves activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and phosphorylation of Elk-1.J Neurosci. 2002 Mar 15;22(6):2054-62. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-06-02054.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11896145 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamate induces phosphorylation of Elk-1 and CREB, along with c-fos activation, via an extracellular signal-regulated kinase-dependent pathway in brain slices.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Jan;19(1):136-46. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.1.136. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 9858538 Free PMC article.
-
MAPK, CREB and zif268 are all required for the consolidation of recognition memory.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2003 Apr 29;358(1432):805-14. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2002.1224. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2003. PMID: 12740127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immediate early gene transcription and synaptic modulation.J Neurosci Res. 1999 Oct 1;58(1):96-106. J Neurosci Res. 1999. PMID: 10491575 Review.
Cited by
-
Dopamine D1/D5 receptor signaling regulates synaptic cooperation and competition in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons via sustained ERK1/2 activation.Hippocampus. 2016 Feb;26(2):137-50. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22497. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Hippocampus. 2016. PMID: 26194339 Free PMC article.
-
_targeting specific HATs for neurodegenerative disease treatment: translating basic biology to therapeutic possibilities.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Mar 28;7:30. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00030. eCollection 2013. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23543406 Free PMC article.
-
CXXC finger protein 4 inhibits the CDK18-ERK1/2 axis to suppress the immune escape of gastric cancer cells with involvement of ELK1/MIR100HG pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Sep;24(17):10151-10165. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15625. Epub 2020 Jul 26. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32715641 Free PMC article.
-
Histamine H3 receptor antagonists in relation to epilepsy and neurodegeneration: a systemic consideration of recent progress and perspectives.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Dec;167(7):1398-414. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02093.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22758607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mitochondrial-derived peptide humanin activates the ERK1/2, AKT, and STAT3 signaling pathways and has age-dependent signaling differences in the hippocampus.Onco_target. 2016 Jul 26;7(30):46899-46912. doi: 10.18632/onco_target.10380. Onco_target. 2016. PMID: 27384491 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atkins CM, Selcher JC, Petraitis JJ, Tzaskos JM, Sweatt JD. The MAPK cascade is required for mammalian associative learning. Nat Neurosci. 1998;1:602–609. - PubMed
-
- Barnes CA. Memory deficits associated with senescence: a neurophysiological and behavioral study in the rat. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1979;93:74–104. - PubMed
-
- Bartsch D, Ghirardi M, Skehel PA, Karl KA, Herder SP, Chen M, Bailey CH, Kandel ER. Aplysia CREB2 represses long-term facilitation: relief of repression converts transient facilitation into long-term functional and structural change. Cell. 1995;83:979–992. - PubMed
-
- Bhalla US, Iyengar R. Emergent properties of networks of biological signaling pathways. Science. 1999;283:381–387. - PubMed
-
- Bliss TVP, Collingridge GL. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993;361:31–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
