Calcium regulates the association between mitochondria and a smooth subdomain of the endoplasmic reticulum
- PMID: 10995452
- PMCID: PMC2150689
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.150.6.1489
Calcium regulates the association between mitochondria and a smooth subdomain of the endoplasmic reticulum
Abstract
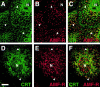
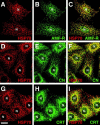
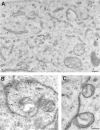
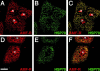
Association between the ER and mitochondria has long been observed, and the formation of close contacts between ER and mitochondria is necessary for the ER-mediated sequestration of cytosolic calcium by mitochondria. Autocrine motility factor receptor (AMF-R) is a marker for a smooth subdomain of the ER, shown here by confocal microscopy to be distinct from, yet closely associated with the calnexin- or calreticulin-labeled ER. By EM, smooth ER AMF-R tubules exhibit direct interactions with mitochondria, identifying them as a mitochondria-associated smooth ER subdomain. In digitonin-permeabilized MDCK cells, the addition of rat liver cytosol stimulates the dissociation of smooth ER and mitochondria under conditions of low calcium. Using BAPTA chelators of various affinities and CaEGTA buffers of defined free Ca(2+) concentrations and quantitative confocal microscopy, we show that free calcium concentrations <100 nM favor dissociation, whereas those >1 microM favor close association between these two organelles. Therefore, we describe a cellular mechanism that facilitates the close association of this smooth ER subdomain and mitochondria when cytosolic free calcium rises above physiological levels.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reversible interactions between smooth domains of the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria are regulated by physiological cytosolic Ca2+ levels.J Cell Sci. 2007 Oct 15;120(Pt 20):3553-64. doi: 10.1242/jcs.03486. Epub 2007 Sep 25. J Cell Sci. 2007. PMID: 17895372
-
Localization of autocrine motility factor receptor to caveolae and clathrin-independent internalization of its ligand to smooth endoplasmic reticulum.Mol Biol Cell. 1998 Jul;9(7):1773-86. doi: 10.1091/mbc.9.7.1773. Mol Biol Cell. 1998. PMID: 9658170 Free PMC article.
-
The AMF-R tubule is a smooth ilimaquinone-sensitive subdomain of the endoplasmic reticulum.J Cell Sci. 1997 Dec;110 ( Pt 24):3043-53. doi: 10.1242/jcs.110.24.3043. J Cell Sci. 1997. PMID: 9365274
-
The Gp78 ubiquitin ligase: probing endoplasmic reticulum complexity.Protoplasma. 2012 Feb;249 Suppl 1:S11-8. doi: 10.1007/s00709-011-0344-8. Epub 2011 Nov 3. Protoplasma. 2012. PMID: 22045301 Review.
-
Interaction of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria.Biochem Soc Trans. 2006 Jun;34(Pt 3):370-3. doi: 10.1042/BST0340370. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006. PMID: 16709164 Review.
Cited by
-
Switch from ER-mitochondrial to SR-mitochondrial calcium coupling during muscle differentiation.Cell Calcium. 2012 Nov;52(5):355-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2012.05.012. Epub 2012 Jul 10. Cell Calcium. 2012. PMID: 22784666 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol-related increases in degenerating bodies in the Purkinje neuron dendrites of aging rats.Brain Res. 2008 Jul 24;1221:98-107. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.05.015. Epub 2008 May 16. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18559274 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphism and structural maturation of bunyamwera virus in Golgi and post-Golgi compartments.J Virol. 2003 Jan;77(2):1368-81. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.2.1368-1381.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12502853 Free PMC article.
-
Closing the Gap: Membrane Contact Sites in the Regulation of Autophagy.Cells. 2020 May 9;9(5):1184. doi: 10.3390/cells9051184. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32397538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A tripartite organelle platform links growth factor receptor signaling to mitochondrial metabolism.Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 15;15(1):5119. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49543-z. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38879572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achleitner G., Gaigg B., Krasser A., Kainersdorfer E., Kohlwein S.D., Perktold A., Zellnig G., Daum G. Association between the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria of yeast facilitates interorganelle transport of phospholipids through membrane contact. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999;264:545–553. - PubMed
-
- Denton R.M., McCormack J.G. Ca2+ as a second messenger within mitochondria of the heart and other tissues. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1990;52:451–466. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

