Homer proteins regulate coupling of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors to N-type calcium and M-type potassium channels
- PMID: 11007880
- PMCID: PMC6772755
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-19-07238.2000
Homer proteins regulate coupling of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors to N-type calcium and M-type potassium channels
Abstract
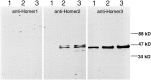
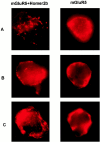
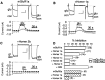
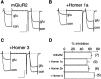
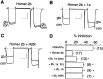
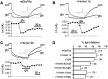
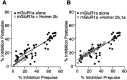
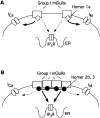
Group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR1 and 5) couple to intracellular calcium pools by a family of proteins, termed Homer, that cross-link the receptor to inositol trisphosphate receptors. mGluRs also couple to membrane ion channels via G-proteins. The role of Homer proteins in channel modulation was investigated by expressing mGluRs and various forms of Homer in rat superior cervical ganglion (SCG) sympathetic neurons by intranuclear cDNA injection. Expression of cross-linking-capable forms of Homer (Homer 1b, 1c, 2, and 3, termed long forms) occluded group I mGluR-mediated N-type calcium and M-type potassium current modulation. This effect was specific for group I mGluRs. mGluR2 (group II)-mediated inhibition of N-channels was unaltered. Long forms of Homer decreased modulation of N- and M-type currents but did not selectively block distinct G-protein pathways. Short forms of Homer, which cannot self-multimerize (Homer 1a and a Homer 2 C-terminal deletion), did not alter mGluR-ion channel coupling. When coexpressed with long forms of Homer, short forms restored the mGluR1a-mediated calcium current modulation in an apparent dose-dependent manner. Homer 2b induced cell surface clusters of mGluR5 in SCG neurons. Conversely, a uniform distribution was observed when mGluR5 was expressed alone or with Homer short forms. These studies indicate that long and short forms of Homer compete for binding to mGluRs and regulate their coupling to ion channels. In vivo, the immediate early Homer 1a is anticipated to enhance ion channel modulation and to disrupt coupling to releasable intracellular calcium pools. Thus, Homer may regulate the magnitude and predominate signaling output of group I mGluRs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Homer/Vesl proteins and their roles in CNS neurons.Mol Neurobiol. 2004 Jun;29(3):213-27. doi: 10.1385/MN:29:3:213. Mol Neurobiol. 2004. PMID: 15181235 Review.
-
Surface clustering of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 induced by long Homer proteins.BMC Neurosci. 2006 Jan 4;7:1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-7-1. BMC Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16393337 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous homer proteins regulate metabotropic glutamate receptor signaling in neurons.J Neurosci. 2008 Aug 20;28(34):8560-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1830-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18716215 Free PMC article.
-
Homer 1a uncouples metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 from postsynaptic effectors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Apr 3;104(14):6055-60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608991104. Epub 2007 Mar 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17389377 Free PMC article.
-
Complex interactions between mGluRs, intracellular Ca2+ stores and ion channels in neurons.Trends Neurosci. 2000 Feb;23(2):80-8. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(99)01492-7. Trends Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10652549 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5: molecular pharmacology, allosteric modulation and stimulus bias.Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Oct;173(20):3001-17. doi: 10.1111/bph.13281. Epub 2015 Nov 11. Br J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26276909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Homer proteins in Ca2+ signaling by excitable and non-excitable cells.Cell Calcium. 2007 Oct-Nov;42(4-5):363-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2007.05.007. Epub 2007 Jul 5. Cell Calcium. 2007. PMID: 17618683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex differences and hormonal regulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor synaptic plasticity.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2023;168:311-347. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2022.10.002. Epub 2022 Nov 11. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36868632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Homer/Vesl proteins and their roles in CNS neurons.Mol Neurobiol. 2004 Jun;29(3):213-27. doi: 10.1385/MN:29:3:213. Mol Neurobiol. 2004. PMID: 15181235 Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Memory Consolidation That Operate During Sleep.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Nov 18;14:767384. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.767384. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34867190 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bean BP. Neurotransmitter inhibition of neuronal calcium currents by changes in channel voltage dependence. Nature. 1989;340:153–156. - PubMed
-
- Beneken J, Tu JC, Xiao B, Nuriya M, Yuan JP, Worley PF, Leahy DJ. Structure of the Homer EVH1 domain-peptide complex reveals a new twist in polyproline recognition. Neuron. 2000;26:143–154. - PubMed
-
- Brakeman PR, Lanahan AA, O'Brien R, Roche K, Barnes CA, Huganir RL, Worley PF. Homer: a protein that selectively binds metabotropic glutamate receptors. Nature. 1997;386:284–288. - PubMed
-
- Brown DA, Adams PR. Muscarinic suppression of a novel voltage-sensitive K+ current in a vertebrate neurone. Nature. 1980;283:673–676. - PubMed
-
- Charpak S, Gähwiler BH, Do KQ, Knöpfel T. Potassium conductances in hippocampal neurons blocked by excitatory amino-acid transmitters. Nature. 1990;347:765–767. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
