Euplotes telomerase contains an La motif protein produced by apparent translational frameshifting
- PMID: 11080168
- PMCID: PMC305813
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.22.6230
Euplotes telomerase contains an La motif protein produced by apparent translational frameshifting
Abstract
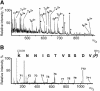
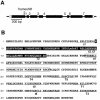
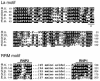
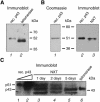
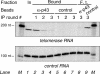
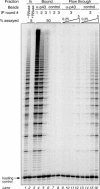
Telomerase is the ribonucleoprotein enzyme responsible for the replication of chromosome ends in most eukaryotes. In the ciliate Euplotes aediculatus, the protein p43 biochemically co-purifies with active telomerase and appears to be stoichiometric with both the RNA and the catalytic protein subunit of this telomerase complex. Here we describe cloning of the gene for p43 and present evidence that it is an authentic component of the telomerase holoenzyme. Comparison of the nucleotide sequence of the cloned gene with peptide sequences of the protein suggests that production of full-length p43 relies on a programmed ribosomal frameshift, an extremely rare translational mechanism. Anti-p43 antibodies immunodeplete telomerase RNA and telomerase activity from E.aediculatus nuclear extracts, indicating that the vast majority of mature telomerase complexes in the cell are associated with p43. The sequence of p43 reveals similarity to the La autoantigen, an RNA-binding protein involved in maturation of RNA polymerase III transcripts, and recombinant p43 binds telomerase RNA in vitro. By analogy to other La proteins, p43 may function in chaperoning the assembly and/or facilitating nuclear retention of telomerase.
Figures
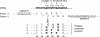

Similar articles
-
The Euplotes La motif protein p43 has properties of a telomerase-specific subunit.Biochemistry. 2003 May 20;42(19):5736-47. doi: 10.1021/bi034121y. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 12741831
-
The Euplotes telomerase subunit p43 stimulates enzymatic activity and processivity in vitro.RNA. 2004 Jul;10(7):1108-18. doi: 10.1261/rna.7400704. RNA. 2004. PMID: 15208446 Free PMC article.
-
The telomerase-associated protein p43 is involved in anchoring telomerase in the nucleus.J Cell Sci. 2003 May 1;116(Pt 9):1757-61. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00351. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 12665556
-
Telomerase and the chromosome end replication problem.Ciba Found Symp. 1997;211:20-8; discussion 28-34. doi: 10.1002/9780470515433.ch3. Ciba Found Symp. 1997. PMID: 9524749 Review.
-
Telomerase is a true reverse transcriptase. A review.Biochemistry (Mosc). 1997 Nov;62(11):1202-5. Biochemistry (Mosc). 1997. PMID: 9467843 Review.
Cited by
-
Ever shorter telomere 1 (EST1)-dependent reverse transcription by Candida telomerase in vitro: evidence in support of an activating function.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 May 13;100(10):5718-23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1036868100. Epub 2003 Apr 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12716976 Free PMC article.
-
Tetrahymena telomerase protein p65 induces conformational changes throughout telomerase RNA (TER) and rescues telomerase reverse transcriptase and TER assembly mutants.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Oct;30(20):4965-76. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00827-10. Epub 2010 Aug 16. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20713447 Free PMC article.
-
Holoenzyme proteins required for the physiological assembly and activity of telomerase.Genes Dev. 2004 May 15;18(10):1107-18. doi: 10.1101/gad.1201704. Epub 2004 May 6. Genes Dev. 2004. PMID: 15131081 Free PMC article.
-
A bulged stem tethers Est1p to telomerase RNA in budding yeast.Genes Dev. 2002 Nov 1;16(21):2800-12. doi: 10.1101/gad.1029302. Genes Dev. 2002. PMID: 12414733 Free PMC article.
-
Functional multimerization of the human telomerase reverse transcriptase.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Sep;21(18):6151-60. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.18.6151-6160.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11509658 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bandziulis R.J., Swanson,M.S. and Dreyfuss,G. (1989) RNA-binding proteins as developmental regulators. Genes Dev., 3, 431–437. - PubMed
-
- Beattie T.L., Zhou,W., Robinson,M.O. and Harrington,L. (1998) Reconstitution of human telomerase activity in vitro. Curr. Biol., 8, 177–180. - PubMed
-
- Blasco M.A, Lee,H.-W., Hande,M.P., Samper,E., Lansdorp,P.M., DePinho,R.E. and Greider,C.W. (1997) Telomere shortening and tumor formation by mouse cells lacking telomerase RNA. Cell, 91, 25–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

