Inhibitory regulation of Rac activation, membrane ruffling, and cell migration by the G protein-coupled sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor EDG5 but not EDG1 or EDG3
- PMID: 11094076
- PMCID: PMC102182
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.24.9247-9261.2000
Inhibitory regulation of Rac activation, membrane ruffling, and cell migration by the G protein-coupled sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor EDG5 but not EDG1 or EDG3
Abstract
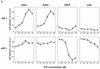
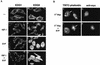
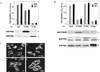
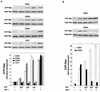
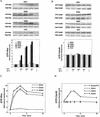
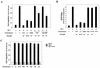
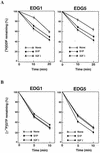
Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) is a bioactive lysophospholipid that induces a variety of biological responses in diverse cell types. Many, if not all, of these responses are mediated by members of the EDG (endothelial differentiation gene) family G protein-coupled receptors EDG1, EDG3, and EDG5 (AGR16). Among prominent activities of S1P is the regulation of cell motility; S1P stimulates or inhibits cell motility depending on cell types. In the present study, we provide evidence for EDG subtype-specific, contrasting regulation of cell motility and cellular Rac activity. In CHO cells expressing EDG1 or EDG3 (EDG1 cells or EDG3 cells, respectively) S1P as well as insulin-like growth factor I (IGF I) induced chemotaxis and membrane ruffling in phosphoinositide (PI) 3-kinase- and Rac-dependent manners. Both S1P and IGF I induced a biphasic increase in the amount of the GTP-bound active form of Rac. In CHO cells expressing EDG5 (EDG5 cells), IGF I similarly stimulated cell migration; however, in contrast to what was found for EDG1 and EDG3 cells, S1P did not stimulate migration but totally abolished IGF I-directed chemotaxis and membrane ruffling, in a manner dependent on a concentration gradient of S1P. In EDG5 cells, S1P stimulated PI 3-kinase activity as it did in EDG1 cells but inhibited the basal Rac activity and totally abolished IGF I-induced Rac activation, which involved stimulation of Rac-GTPase-activating protein activity rather than inhibition of Rac-guanine nucleotide exchange activity. S1P induced comparable increases in the amounts of GTP-RhoA in EDG3 and EDG5 cells. Neither S1P nor IGF I increased the amount of GTP-bound Cdc42. However, expression of N(17)-Cdc42, but not N(19)-RhoA, suppressed S1P- and IGF I-directed chemotaxis, suggesting a requirement for basal Cdc42 activity for chemotaxis. Taken together, the present results demonstrate that EDG5 is the first example of a hitherto-unrecognized type of receptors that negatively regulate Rac activity, thereby inhibiting cell migration and membrane ruffling.
Figures



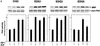
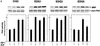

Similar articles
-
EDG3 is a functional receptor specific for sphingosine 1-phosphate and sphingosylphosphorylcholine with signaling characteristics distinct from EDG1 and AGR16.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999 Jun 24;260(1):203-8. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.0886. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999. PMID: 10381367
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced cell proliferation, survival, and related signaling events mediated by G protein-coupled receptors Edg3 and Edg5.J Biol Chem. 2000 Jan 7;275(1):288-96. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.1.288. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10617617
-
Subtype-specific differential regulation of Rho family G proteins and cell migration by the Edg family sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 May 23;1582(1-3):112-20. doi: 10.1016/s1388-1981(02)00145-2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12069818 Review.
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate, a platelet-derived lysophospholipid mediator, negatively regulates cellular Rac activity and cell migration in vascular smooth muscle cells.Circ Res. 2002 Feb 22;90(3):325-32. doi: 10.1161/hh0302.104455. Circ Res. 2002. PMID: 11861422
-
Subtype-specific, differential activities of the EDG family receptors for sphingosine-1-phosphate, a novel lysophospholipid mediator.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001 May 25;177(1-2):3-11. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(01)00441-5. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001. PMID: 11377814 Review.
Cited by
-
S1P metabolism in cancer and other pathological conditions.Biochimie. 2010 Jun;92(6):716-23. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2010.02.014. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Biochimie. 2010. PMID: 20167244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FTY720, a sphingosine-1 phosphate receptor modulator, improves liver fibrosis in a mouse model by impairing the motility of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Inflammation. 2014 Aug;37(4):1326-36. doi: 10.1007/s10753-014-9877-2. Inflammation. 2014. PMID: 24682874
-
HDL-associated lysosphingolipids inhibit NAD(P)H oxidase-dependent monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 production.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008 Aug;28(8):1542-8. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.161042. Epub 2008 May 15. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008. PMID: 18483405 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of vascular physiology and pathology by the S1P2 receptor subtype.Cardiovasc Res. 2009 May 1;82(2):221-8. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvp088. Epub 2009 Mar 15. Cardiovasc Res. 2009. PMID: 19287048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor-2 Antagonists: Therapeutic Potential and Potential Risks.Front Pharmacol. 2016 Jun 21;7:167. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00167. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27445808 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adam L, Vadlamudi R, Kondapaka S B, Chernoff J, Mendelsohn J, Kumar R. Heregulin regulates cytoskeletal reorganization and cell migration through the p21-activated kinase-1 via phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:28238–28246. - PubMed
-
- Akasaki T, Koga H, Sunimoto H. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent and -independent activation of the small GTPase Rac2 in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:18055–18059. - PubMed
-
- An S, Zheng Y, Bleu T. Sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced cell proliferation, survival, and related signaling events mediated by G protein-coupled receptors Edg3 and Edg5. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:288–296. - PubMed
-
- An S. Molecular identification and characterization of G protein-coupled receptors for lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine 1-phosphate. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;905:25–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
