WormBase: network access to the genome and biology of Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 11125056
- PMCID: PMC29781
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/29.1.82
WormBase: network access to the genome and biology of Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
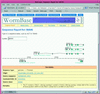
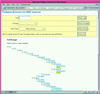
WormBase (http://www.wormbase.org) is a web-based resource for the Caenorhabditis elegans genome and its biology. It builds upon the existing ACeDB database of the C.elegans genome by providing data curation services, a significantly expanded range of subject areas and a user-friendly front end.
Figures
Similar articles
-
WormBase: methods for data mining and comparative genomics.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;351:31-50. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-151-7:31. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16988424 Review.
-
WormBase 2007.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36(Database issue):D612-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm975. Epub 2007 Nov 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 17991679 Free PMC article.
-
Methods and strategies for gene structure curation in WormBase.Database (Oxford). 2011 May 3;2011:baq039. doi: 10.1093/database/baq039. Print 2011. Database (Oxford). 2011. PMID: 21543339 Free PMC article.
-
WormBase: new content and better access.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jan;35(Database issue):D506-10. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl818. Epub 2006 Nov 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17099234 Free PMC article.
-
The draft genome sequence of the nematode Caenorhabditis briggsae, a companion to C. elegans.Genome Biol. 2003;4(12):238. doi: 10.1186/gb-2003-4-12-238. Epub 2003 Nov 18. Genome Biol. 2003. PMID: 14659008 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Description of International Caenorhabditis elegans Experiment first flight (ICE-FIRST).Adv Space Res. 2008 Sep 15;42(6):1072-1079. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2008.03.017. Adv Space Res. 2008. PMID: 22146801 Free PMC article.
-
The distributed annotation system.BMC Bioinformatics. 2001;2:7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-2-7. Epub 2001 Oct 10. BMC Bioinformatics. 2001. PMID: 11667947 Free PMC article.
-
GOtcha: a new method for prediction of protein function assessed by the annotation of seven genomes.BMC Bioinformatics. 2004 Nov 18;5:178. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-5-178. BMC Bioinformatics. 2004. PMID: 15550167 Free PMC article.
-
Extreme allelic heterogeneity at a Caenorhabditis elegans beta-tubulin locus explains natural resistance to benzimidazoles.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Oct 29;14(10):e1007226. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007226. eCollection 2018 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 30372484 Free PMC article.
-
Genome and proteome annotation: organization, interpretation and integration.J R Soc Interface. 2009 Feb 6;6(31):129-47. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2008.0341. J R Soc Interface. 2009. PMID: 19019817 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Riddle D.L., Blumenthal,T., Meyer,B.J. and Preiss,J.R. (1997) C. elegans II. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY. - PubMed
-
- Kimble J. and Hirsh,D. (1979) Post-embryonic cell lineages of the hermaphrodite and male gonads in Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Biol., 70, 396–417. - PubMed
-
- Sulston J.E., Schierenberg,E., White,J.G. and Thomson,J.N. (1983) The embryonic cell lineage of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Biol., 100, 64–119. - PubMed
-
- The C.elegans Sequencing Consortium (1998) Genome sequence of the Nematode C. elegans: platform for investigating biology. Science, 282, 2012–2018. - PubMed
-
- Fire A., Xu,S.Q., Montgomery,M.K., Kostas,S.A., Driver,S.E. and Mello,C.C. (1998) Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature, 391, 806–811. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

