Abnormal angiogenesis but intact hematopoietic potential in TGF-beta type I receptor-deficient mice
- PMID: 11285230
- PMCID: PMC145465
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.7.1663
Abnormal angiogenesis but intact hematopoietic potential in TGF-beta type I receptor-deficient mice
Abstract
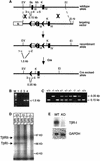
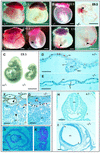
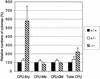
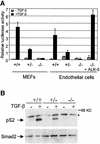
Deletion of the transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta1) gene in mice has previously suggested that it regulates both hematopoiesis and angiogenesis. To define the function of TGF-beta more precisely, we inactivated the TGF-beta type I receptor (TbetaRI) gene by gene _targeting. Mice lacking TbetaRI die at midgestation, exhibiting severe defects in vascular development of the yolk sac and placenta, and an absence of circulating red blood cells. However, despite obvious anemia in the TbetaRI(-/-) yolk sacs, clonogenic assays on yolk sac-derived hematopoietic precursors in vitro revealed that TbetaRI(-/-) mice exhibit normal hematopoietic potential compared with wild-type and heterozygous siblings. Endothelial cells derived from TbetaRI-deficient embryos show enhanced cell proliferation, improper migratory behavior and impaired fibronectin production in vitro, defects that are associated with the vascular defects seen in vivo. We thus demonstrate here that, while TbetaRI is crucial for the function of TGF-beta during vascular development and can not be compensated for by the activin receptor-like kinase-1 (ALK-1), functional hematopoiesis and development of hematopoietic progenitors is not dependent on TGF-beta signaling via TbetaRI.
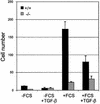
Figures

Similar articles
-
Overexpression of transforming growth factor beta type I receptor abolishes malignant phenotype of a rat bladder carcinoma cell line.Cell Growth Differ. 1997 Aug;8(8):921-6. Cell Growth Differ. 1997. PMID: 9269901
-
Differential responsiveness to autocrine and exogenous transforming growth factor (TGF) beta1 in cells with nonfunctional TGF-beta receptor type III.Cell Growth Differ. 1999 Jan;10(1):11-8. Cell Growth Differ. 1999. PMID: 9950213
-
Activin receptor-like kinase 1 modulates transforming growth factor-beta 1 signaling in the regulation of angiogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Mar 14;97(6):2626-31. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.6.2626. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10716993 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Smad signaling in vascular and hematopoietic development revealed by studies using genetic mouse models.Sci China Life Sci. 2010 Apr;53(4):485-9. doi: 10.1007/s11427-010-0087-3. Epub 2010 May 7. Sci China Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20596915 Review.
-
An emerging complexity of receptors for transforming growth factor-beta.Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1994;24:264-75. Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1994. PMID: 8983081 Review.
Cited by
-
TGFβ signaling and cardiovascular diseases.Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8(2):195-213. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.3805. Epub 2012 Jan 1. Int J Biol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22253564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TGF-β-activated kinase 1 (Tak1) mediates agonist-induced Smad activation and linker region phosphorylation in embryonic craniofacial neural crest-derived cells.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 10;288(19):13467-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.431775. Epub 2013 Apr 1. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23546880 Free PMC article.
-
Mononuclear cells and vascular repair in HHT.Front Genet. 2015 Mar 23;6:114. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00114. eCollection 2015. Front Genet. 2015. PMID: 25852751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 exerts anti-fibrotic effect after myocardial infarction by alleviation of fibroblasts proliferation and collagen deposition through TGFBR1 signaling pathways.J Ginseng Res. 2023 Nov;47(6):743-754. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2023.06.007. Epub 2023 Jul 3. J Ginseng Res. 2023. PMID: 38107395 Free PMC article.
-
Expression levels of endoglin distinctively identify hematopoietic and endothelial progeny at different stages of yolk sac hematopoiesis.Stem Cells. 2013 Sep;31(9):1893-901. doi: 10.1002/stem.1434. Stem Cells. 2013. PMID: 23712751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Attisano L., Carcamo,J., Ventura,F., Weis,F.M., Massagué,J. and Wrana,J.L. (1993) Identification of human activin and TGF-β type I receptors that form heteromeric kinase complexes with type II receptors. Cell, 75, 671–680. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin H.S. (1996) Early embryonic vascular development. Cardiovasc. Res., 31, E34–E45. - PubMed
-
- Chang H., Huylebroeck,D., Verschueren,K., Guo,Q., Matzuk,M.M. and Zwijsen,A. (1999) Smad5 knockout mice die at mid-gestation due to multiple embryonic and extraembryonic defects. Development, 126, 1631–1642. - PubMed
-
- Cross J.C., Werb,Z. and Fisher,S.J. (1994) Implantation and the placenta: key pieces of the development puzzle. Science, 266, 1508–1518. - PubMed
-
- Cumano A., Dieterlen-Lievre,F. and Godin,I. (1996) Lymphoid potential, probed before circulation in mouse, is restricted to caudal intraembryonic splanchnopleura. Cell, 86, 907–916. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

