A mammalian homolog of yeast MOB1 is both a member and a putative substrate of striatin family-protein phosphatase 2A complexes
- PMID: 11319234
- PMCID: PMC3503316
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M102398200
A mammalian homolog of yeast MOB1 is both a member and a putative substrate of striatin family-protein phosphatase 2A complexes
Abstract
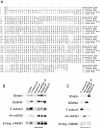
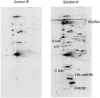
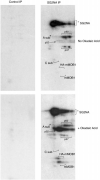
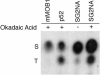
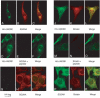
Striatin and S/G(2) nuclear autoantigen (SG2NA) are related proteins that contain membrane binding domains and associate with protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) and many additional proteins that may be PP2A regulatory _targets. Here we identify a major member of these complexes as class II mMOB1, a mammalian homolog of the yeast protein MOB1, and show that its phosphorylation appears to be regulated by PP2A. Yeast MOB1 is critical for cytoskeletal reorganization during cytokinesis and exit from mitosis. We show that mMOB1 associated with PP2A is not detectably phosphorylated in asynchronous murine fibroblasts. However, treatment with the PP2A inhibitor okadaic acid induces phosphorylation of PP2A-associated mMOB1 on serine. Moreover, specific inhibition of PP2A also results in hyperphosphorylation of striatin, SG2NA, and three unidentified proteins, suggesting that these proteins may also be regulated by PP2A. Indirect immunofluorescence produced highly similar staining patterns for striatin, SG2NA, and mMOB1, with the highest concentrations for each protein adjacent to the nuclear membrane. We also present evidence that these complexes may interact with each other. These data are consistent with a model in which PP2A may regulate mMOB1, striatin, and SG2NA to modulate changes in the cytoskeleton or interactions between the cytoskeleton and membrane structures.
Figures

Similar articles
-
WD40 repeat proteins striatin and S/G(2) nuclear autoantigen are members of a novel family of calmodulin-binding proteins that associate with protein phosphatase 2A.J Biol Chem. 2000 Feb 25;275(8):5257-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.8.5257. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10681496 Free PMC article.
-
Protein phosphatase 2a (PP2A) binds within the oligomerization domain of striatin and regulates the phosphorylation and activation of the mammalian Ste20-Like kinase Mst3.BMC Biochem. 2011 Oct 10;12:54. doi: 10.1186/1471-2091-12-54. BMC Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21985334 Free PMC article.
-
Methylation of the protein phosphatase 2A catalytic subunit is essential for association of Balpha regulatory subunit but not SG2NA, striatin, or polyomavirus middle tumor antigen.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Jan;12(1):185-99. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.1.185. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11160832 Free PMC article.
-
STRIPAK complexes: structure, biological function, and involvement in human diseases.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Feb;47:118-48. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.11.021. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24333164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein phosphatase 2A on track for nutrient-induced signalling in yeast.Mol Microbiol. 2002 Feb;43(4):835-42. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02786.x. Mol Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11929536 Review.
Cited by
-
Gastrodia elata Blume (tianma) mobilizes neuro-protective capacities.Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 2012;3(2):219-41. Epub 2012 Jun 3. Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22773961 Free PMC article.
-
STRN3 promotes tumour growth in hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting the hippo pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Mar;28(6):e18147. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18147. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38429901 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonistic roles of PP2A-Pab1 and Etd1 in the control of cytokinesis in fission yeast.Genetics. 2010 Dec;186(4):1261-70. doi: 10.1534/genetics.110.121368. Epub 2010 Sep 27. Genetics. 2010. PMID: 20876564 Free PMC article.
-
STRIPAK Limits Stem Cell Differentiation of a WNT Signaling Center to Control Planarian Axis Scaling.Curr Biol. 2020 Jan 20;30(2):254-263.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.11.068. Epub 2020 Jan 9. Curr Biol. 2020. PMID: 31928872 Free PMC article.
-
A novel non-canonical mechanism of regulation of MST3 (mammalian Sterile20-related kinase 3).Biochem J. 2012 Mar 15;442(3):595-610. doi: 10.1042/BJ20112000. Biochem J. 2012. PMID: 22229648 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

