The many faces of metalloproteases: cell growth, invasion, angiogenesis and metastasis
- PMID: 11684441
- PMCID: PMC2788992
- DOI: 10.1016/s0962-8924(01)02122-5
The many faces of metalloproteases: cell growth, invasion, angiogenesis and metastasis
Abstract
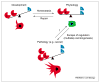
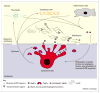
Metalloproteases are important in many aspects of biology, ranging from cell proliferation, differentiation and remodeling of the extracellular matrix (ECM) to vascularization and cell migration. These events occur several times during organogenesis in both normal development and during tumor progression. Mechanisms of metalloprotease action underlying these events include the proteolytic cleavage of growth factors so that they can become available to cells not in direct physical contact, degradation of the ECM so that founder cells can move across tissues into nearby stroma, and regulated receptor cleavage to terminate migratory signaling. Most of these processes require a delicate balance between the functions of matrix metalloproteases (MMPs) or metalloprotease-disintegrins (ADAMs) and natural tissue inhibitors of metalloproteases (TIMPs). In this review, we discuss recent progress in identifying an essential role for metalloproteases in axon outgrowth, as an example of a focal invasive event. We also discuss the evolving concept of how MMPs might regulate stem cell fate during tumor development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The role of metalloproteinases in modification of extracellular matrix in invasive tumor growth, metastasis and angiogenesis].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2012 Sep 10;66:609-28. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1009705. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2012. PMID: 23001203 Review. Polish.
-
The role of matrix metalloproteases and their inhibitors in tumour invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis.Eur Respir J. 1994 Nov;7(11):2062-72. Eur Respir J. 1994. PMID: 7533104 Review.
-
Ovarian tissue remodeling: role of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2002 May 31;191(1):45-56. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(02)00054-0. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2002. PMID: 12044918 Review.
-
Matrix metalloproteinases in tumor invasion.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2000 Jan 20;57(1):5-15. doi: 10.1007/s000180050495. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2000. PMID: 10949577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of matrix metalloproteinases in melanoma cell invasion.Biochimie. 2005 Mar-Apr;87(3-4):307-14. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2005.01.013. Biochimie. 2005. PMID: 15781317 Review.
Cited by
-
TNF-receptor-1 adaptor protein FAN mediates TNF-induced B16 melanoma motility and invasion.Br J Cancer. 2013 Jul 23;109(2):422-32. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.242. Epub 2013 May 14. Br J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23674089 Free PMC article.
-
Benzopyrene promotes lung cancer A549 cell migration and invasion through up-regulating cytokine IL8 and chemokines CCL2 and CCL3 expression.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016 Aug;241(14):1516-23. doi: 10.1177/1535370216644530. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016. PMID: 27075927 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive polymer scaffold for fabrication of vascularized engineering tissue.J Artif Organs. 2012 Sep;15(3):215-24. doi: 10.1007/s10047-012-0644-6. Epub 2012 Apr 21. J Artif Organs. 2012. PMID: 22527978 Review.
-
MMP-1 and -3 promoter variants are indicative of a common susceptibility for skin and lung aging: results from a cohort of elderly women (SALIA).J Invest Dermatol. 2015 May;135(5):1268-1274. doi: 10.1038/jid.2015.7. Epub 2015 Jan 19. J Invest Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25599395
-
Expression of metalloproteinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) in basal-cell carcinoma.Mol Biol Rep. 2016 Oct;43(10):1027-33. doi: 10.1007/s11033-016-4040-9. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Mol Biol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27406386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Werb Z. ECM and cell surface proteolysis: regulating cellular ecology. Cell. 1997;91:439–442. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Vu TH, Werb Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: effectors of development and normal physiology. Genes Dev. 2000;14:2123–2133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS039278/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA 72006/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS 39278/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES 07106/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR046238-07/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA072006-040003/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS039278-01/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AR 46238/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES007106/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES007106-17/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR046238/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA072006/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

