Beta-catenin--a linchpin in colorectal carcinogenesis?
- PMID: 11839557
- PMCID: PMC1850660
- DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)64856-0
Beta-catenin--a linchpin in colorectal carcinogenesis?
Abstract
An important role for beta-catenin pathways in colorectal carcinogenesis was first suggested by the protein's association with adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) protein, and by evidence of dysregulation of beta-catenin protein expression at all stages of the adenoma-carcinoma sequence. Recent studies have, however, shown that yet more components of colorectal carcinogenesis are linked to beta-catenin pathways. Pro-oncogenic factors that also release beta-catenin from the adherens complex and/or encourage translocation to the nucleus include ras, epidermal growth factor (EGF), c-erbB-2, PKC-betaII, MUC1, and PPAR-gamma, whereas anti-oncogenic factors that also inhibit nuclear beta-catenin signaling include transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta, retinoic acid, and vitamin D. Association of nuclear beta-catenin with the T cell factor (TCF)/lymphoid enhancer factor (LEF) family of transcription factors promotes the expression of several compounds that have important roles in the development and progression of colorectal carcinoma, namely: c-myc, cyclin D1, gastrin, cyclooxygenase (COX)-2, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-7, urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (aPAR), CD44 proteins, and P-glycoprotein. Finally, genetic aberrations of several components of the beta-catenin pathways, eg, Frizzled (Frz), AXIN, and TCF-4, may potentially contribute to colorectal carcinogenesis. In discussing the above interactions, this review demonstrates that beta-catenin represents a key molecule in the development of colorectal carcinoma.
Figures
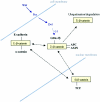

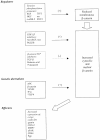
Similar articles
-
Selection of multipotent stem cells during morphogenesis of small intestinal crypts of Lieberkuhn is perturbed by stimulation of Lef-1/beta-catenin signaling.J Biol Chem. 2002 May 3;277(18):15843-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M200184200. Epub 2002 Feb 19. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11854293
-
Activation of the {beta}-catenin/T-cell-specific transcription factor/lymphoid enhancer factor-1 pathway by plasminogen activators in ECV304 carcinoma cells.Cancer Res. 2005 Jan 15;65(2):526-32. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15695395
-
Regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression by the Wnt and ras pathways.Cancer Res. 2003 Feb 1;63(3):728-34. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12566320
-
Wnt/beta-catenin/tcf signaling: a critical pathway in gastrointestinal tumorigenesis.Digestion. 2002;66(3):131-44. doi: 10.1159/000066755. Digestion. 2002. PMID: 12481159 Review.
-
[Genetics of colon carcinogenesis].Nihon Rinsho. 2003 Sep;61 Suppl 7:72-4. Nihon Rinsho. 2003. PMID: 14574858 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
IBSP, a potential recurrence biomarker, promotes the progression of colorectal cancer via Fyn/β-catenin signaling pathway.Cancer Med. 2021 Jun;10(12):4030-4045. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3959. Epub 2021 May 13. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 33987980 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-_target Approaches in Colon Cancer Chemoprevention Based on Systems Biology of Tumor Cell-Signaling.Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2008 May 2;2:163-176. doi: 10.4137/grsb.s486. Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2008. PMID: 19763245 Free PMC article.
-
The metastasis suppressor, NDRG1, inhibits "stemness" of colorectal cancer via down-regulation of nuclear β-catenin and CD44.Onco_target. 2015 Oct 20;6(32):33893-911. doi: 10.18632/onco_target.5294. Onco_target. 2015. PMID: 26418878 Free PMC article.
-
E-cadherin and beta-catenin expression in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma and their prognostic significance.World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Aug 7;13(29):3925-31. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i29.3925. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17663505 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of placental invasion and cancer metastasis are causally linked.Nat Ecol Evol. 2019 Dec;3(12):1743-1753. doi: 10.1038/s41559-019-1046-4. Epub 2019 Nov 25. Nat Ecol Evol. 2019. PMID: 31768023 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kemler R, Ozawa M: Uvomorulin-catenin complex: cytoplasmic anchorage of a Ca2+-dependent cell adhesion molecule. Bioessays 1989, 11:88-91 - PubMed
-
- Morin PJ: β-Catenin signaling and cancer. Bioessays 1999, 21:1021-1030 - PubMed
-
- Kikuchi A: Regulation of β-catenin signaling in the Wnt pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000, 268:243-248 - PubMed
-
- Potter JD: Colorectal cancer: molecules and populations. J Natl Cancer Inst 1999, 91:916-932 - PubMed
-
- Ilyas M, Tomlinson IPM: The interactions of APC, E-cadherin and β-catenin in tumour development and progression. J Pathol 1997, 182:128-137 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

