Severe iron deficiency anemia in transgenic mice expressing liver hepcidin
- PMID: 11930010
- PMCID: PMC123693
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.072632499
Severe iron deficiency anemia in transgenic mice expressing liver hepcidin
Abstract
We recently reported the hemochromatosis-like phenotype observed in our Usf2 knockout mice. In these mice, as in murine models of hemochromatosis and patients with hereditary hemochromatosis, iron accumulates in parenchymal cells (in particular, liver and pancreas), whereas the reticuloendothelial system is spared from this iron loading. We suggested that this phenotypic trait could be attributed to the absence, in the Usf2 knockout mice, of a secreted liver-specific peptide, hepcidin. We conjectured that the reverse situation, namely overexpression of hepcidin, might result in phenotypic traits of iron deficiency. This question was addressed by generating transgenic mice expressing hepcidin under the control of the liver-specific transthyretin promoter. We found that the majority of the transgenic mice were born with a pale skin and died within a few hours after birth. These transgenic animals had decreased body iron levels and presented severe microcytic hypochromic anemia. So far, three mosaic transgenic animals have survived. They were unequivocally identified by physical features, including reduced body size, pallor, hairless and crumpled skin. These pleiotropic effects were found to be associated with erythrocyte abnormalities, with marked anisocytosis, poikylocytosis and hypochromia, which are features characteristic of iron-deficiency anemia. These results strongly support the proposed role of hepcidin as a putative iron-regulatory hormone. The animal models devoid of hepcidin (the Usf2 knockout mice) or overexpressing the peptide (the transgenic mice presented in this paper) represent valuable tools for investigating iron homeostasis in vivo and for deciphering the molecular mechanisms of hepcidin action.
Figures
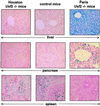
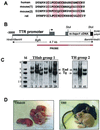
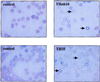


Similar articles
-
Hepatitis C virus-induced reactive oxygen species raise hepatic iron level in mice by reducing hepcidin transcription.Gastroenterology. 2008 Jan;134(1):226-38. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.10.011. Epub 2007 Oct 9. Gastroenterology. 2008. PMID: 18166355
-
Lack of hepcidin gene expression and severe tissue iron overload in upstream stimulatory factor 2 (USF2) knockout mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Jul 17;98(15):8780-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.151179498. Epub 2001 Jul 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11447267 Free PMC article.
-
Phlebotomies or erythropoietin injections allow mobilization of iron stores in a mouse model mimicking intensive care anemia.Crit Care Med. 2008 Aug;36(8):2388-94. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31818103b9. Crit Care Med. 2008. PMID: 18664788
-
[Properties and advance of hepcidin].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2006 May;22(3):361-5. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2006. PMID: 16755911 Review. Chinese.
-
New insights into the regulation of iron homeostasis.Eur J Clin Invest. 2006 May;36(5):301-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.2006.01633.x. Eur J Clin Invest. 2006. PMID: 16634833 Review.
Cited by
-
Ferroportin in monocytes of hemodialysis patients and its associations with hepcidin, inflammation, markers of iron status and resistance to erythropoietin.Int Urol Nephrol. 2014 Jan;46(1):161-7. doi: 10.1007/s11255-013-0497-9. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Int Urol Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 23860963
-
In Vivo Effects of Pichia Pastoris-Expressed Antimicrobial Peptide Hepcidin on the Community Composition and Metabolism Gut Microbiota of Rats.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 21;11(10):e0164771. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164771. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27768776 Free PMC article.
-
The N-terminus of hepcidin is essential for its interaction with ferroportin: structure-function study.Blood. 2006 Jan 1;107(1):328-33. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-05-2049. Epub 2005 Sep 1. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16141345 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of The Canidae Iron Regulatory Hormone Hepcidin.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 18;9(1):19400. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55009-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31852911 Free PMC article.
-
Iron homeostasis and the inflammatory response.Annu Rev Nutr. 2010 Aug 21;30:105-22. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.012809.104804. Annu Rev Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20420524 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

