Chromatin disruption and histone acetylation in regulation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat by thyroid hormone receptor
- PMID: 12024018
- PMCID: PMC133859
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.12.4043-4052.2002
Chromatin disruption and histone acetylation in regulation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat by thyroid hormone receptor
Abstract
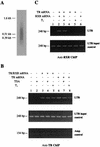
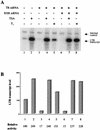
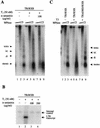
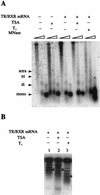
The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) long terminal repeat (LTR) controls the expression of HIV-1 viral genes and thus viral propagation and pathology. Numerous host factors participate in the regulation of the LTR promoter, including thyroid hormone (T(3)) receptor (TR). In vitro, TR can bind to the promoter region containing the NF-kappa B and Sp1 binding sites. Using the frog oocyte as a model system for chromatin assembly mimicking that in somatic cells, we demonstrated that TR alone and TR/RXR (9-cis retinoic acid receptor) can bind to the LTR in vivo independently of T(3). Consistent with their ability to bind the LTR, both TR and TR/RXR can regulate LTR activity in vivo. In addition, our analysis of the plasmid minichromosome shows that T(3)-bound TR disrupts the normal nucleosomal array structure. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays with anti-acetylated-histone antibodies revealed that unliganded TR and TR/RXR reduce the local histone acetylation levels at the HIV-1 LTR while T(3) treatment reverses this reduction. We further demonstrated that unliganded TR recruits corepressors and at least one histone deacetylase. These results suggest that chromatin remodeling, including histone acetylation and chromatin disruption, is important for T(3) regulation of the HIV-1 LTR in vivo.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Involvement of chromatin and histone acetylation in the regulation of HIV-LTR by thyroid hormone receptor.Cell Res. 2001 Mar;11(1):8-16. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7290061. Cell Res. 2001. PMID: 11305329
-
Distinct requirements for chromatin assembly in transcriptional repression by thyroid hormone receptor and histone deacetylase.EMBO J. 1998 Jan 15;17(2):520-34. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.2.520. EMBO J. 1998. PMID: 9430643 Free PMC article.
-
Role of chromatin disruption and histone acetylation in thyroid hormone receptor action: implications in the regulation of HIV-1 LTR.Histol Histopathol. 2003 Jan;18(1):323-31. doi: 10.14670/HH-18.323. Histol Histopathol. 2003. PMID: 12507309 Review.
-
Determinants of chromatin disruption and transcriptional regulation instigated by the thyroid hormone receptor: hormone-regulated chromatin disruption is not sufficient for transcriptional activation.EMBO J. 1997 Jun 2;16(11):3158-71. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.11.3158. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9214633 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleosomes and regulation of gene expression. Structure of the HIV-1 5'LTR.Acta Biochim Pol. 1998;45(1):209-19. Acta Biochim Pol. 1998. PMID: 9701513 Review.
Cited by
-
Liganded thyroid hormone receptor induces nucleosome removal and histone modifications to activate transcription during larval intestinal cell death and adult stem cell development.Endocrinology. 2012 Feb;153(2):961-72. doi: 10.1210/en.2011-1736. Epub 2011 Dec 6. Endocrinology. 2012. PMID: 22147009 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of epigenetic modifications in thyroid hormone-dependent formation of adult intestinal stem cells during amphibian metamorphosis.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2019 Jan 15;271:91-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2018.11.012. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 30472386 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce reactivation of herpes simplex virus type 1 in a latency-associated transcript-independent manner in neuronal cells.J Neurovirol. 2005 Jul;11(3):306-17. doi: 10.1080/13550280590952817. J Neurovirol. 2005. PMID: 16036811 Free PMC article.
-
Early growth response gene 1 (Egr-1) regulates HSV-1 ICP4 and ICP22 gene expression.Cell Res. 2007 Jun;17(6):546-55. doi: 10.1038/cr.2007.44. Cell Res. 2007. PMID: 17502875 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of human fetal hemoglobin: new players, new complexities.Blood. 2006 Jan 15;107(2):435-43. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-05-2113. Epub 2005 Aug 18. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16109777 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burke, L. J., and A. Baniahmad. 2000. Co-repressors 2000. FASEB J. 14:1876-1888. - PubMed
-
- Chen, H., R. J. Lin, R. L. Schiltz, D. Chakravarti, A. Nash, L. Nagy, M. L. Privalsky, Y. Nakatani, and R. M. Evans. 1997. Nuclear receptor coactivator ACTR is a novel histone acetyltransferase and forms a multimeric activation complex with P/CAF and CBP/p300. Cell 90:569-580. - PubMed
-
- Chen, J. D., and H. Li. 1998. Coactivation and corepression in transcriptional regulation by steroid/nuclear hormone receptors. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 8:169-190. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
