Functional and phenotypic studies of two variants of a human mast cell line with a distinct set of mutations in the c-kit proto-oncogene
- PMID: 12519307
- PMCID: PMC1782858
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2003.01559.x
Functional and phenotypic studies of two variants of a human mast cell line with a distinct set of mutations in the c-kit proto-oncogene
Abstract
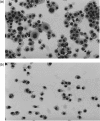
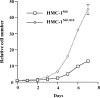
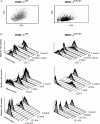
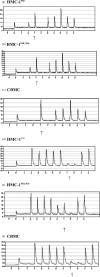
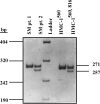
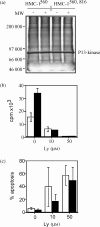
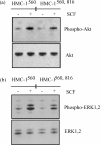
The human mast cell line (HMC)-1 cell line is growth-factor independent because of a constitutive activity of the receptor tyrosine kinase Kit. Such deregulated Kit activity has also been suggested causative in gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GISTs) and mastocytosis. HMC-1 is the only established continuously growing human mast cell line and has therefore been widely employed for in vitro studies of human mast cell biology. In this paper we describe two sublines of HMC-1, named HMC-1(560 ) and HMC-1(560,816 ), with different phenotypes and designated by the locations of specific mutations in the c-kit proto-oncogene. Activating mutations in the Kit receptor were characterized using the pyrosequencing trade mark method. Both sublines have a heterozygous T to G mutation at codon 560 in the juxtamembrane region of the c-kit gene causing an amino acid substitution of Gly-560 for Val. In contrast, only HMC-1(560,816) cells have the c-kitV816 mutation found in mast cell neoplasms causing an Asp-->Val substitution in the intracellular kinase domain. Kit was constitutively phosphorylated on tyrosine residues and associated with phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase (PI 3-kinase) in both variants of HMC-1, but this did not lead to a constitutive phosphorylation of Akt or extracellular regulated protein kinase (ERK), which are signalling molecules normally activated by the interaction of stem cell factor (SCF) with Kit. The documentation and characterization of two sublines of HMC-1 cells provides both information on the biological consequences of mutations in Kit and recognition of the availability of what in reality are two distinct cultured human mast cell lines.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of mutations in the coding sequence of the proto-oncogene c-kit in a human mast cell leukemia cell line causing ligand-independent activation of c-kit product.J Clin Invest. 1993 Oct;92(4):1736-44. doi: 10.1172/JCI116761. J Clin Invest. 1993. PMID: 7691885 Free PMC article.
-
Activating mutations of the c-kit proto-oncogene in a human mast cell leukemia cell line.Leukemia. 1994 Apr;8 Suppl 1:S18-22. Leukemia. 1994. PMID: 7512180
-
Substitution of an aspartic acid results in constitutive activation of c-kit receptor tyrosine kinase in a rat tumor mast cell line RBL-2H3.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1995 Apr;106(4):377-85. doi: 10.1159/000236870. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7536501
-
Negative regulation of mast cell proliferation by FcgammaRIIB.Mol Immunol. 2002 Sep;38(16-18):1295-9. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(02)00078-0. Mol Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12217398 Review.
-
c-Kit and c-kit mutations in mastocytosis and other hematological diseases.J Leukoc Biol. 2000 Feb;67(2):135-48. doi: 10.1002/jlb.67.2.135. J Leukoc Biol. 2000. PMID: 10670573 Review.
Cited by
-
Dendrobium nobile Lindley Administration Attenuates Atopic Dermatitis-like Lesions by Modulating Immune Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 18;23(8):4470. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084470. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457288 Free PMC article.
-
Mast cell survival and mediator secretion in response to hypoxia.PLoS One. 2010 Aug 23;5(8):e12360. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012360. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20808808 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical human models and emerging therapeutics for advanced systemic mastocytosis.Haematologica. 2018 Nov;103(11):1760-1771. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.195867. Epub 2018 Jul 5. Haematologica. 2018. PMID: 29976735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-engineering of HMC-1.2 cells renders a human mast cell line with a single D816V-KIT mutation: An improved preclinical model for research on mastocytosis.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 21;14:1078958. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1078958. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37025992 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic mastocytosis with KIT V560G mutation presenting as recurrent episodes of vascular collapse: response to disodium cromoglycate and disease outcome.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2017 Apr 24;13:21. doi: 10.1186/s13223-017-0193-x. eCollection 2017. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28439288 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Butterfield JH, Weiler D, Dewald G, Gleich GJ. Establishment of an immature mast cell line from a patient with mast cell leukemia. Leuk Res. 1988;12:345–55. - PubMed
-
- Nilsson G, Blom T, Kusche-Gullberg M, Kjellen L, Butterfield JH, Sundstrom C, Nilsson K, Hellman L. Phenotypic characterization of the human mast-cell line HMC-1. Scand J Immunol. 1994;39:489–98. - PubMed
-
- Valent P, Bettelheim P. Cell surface structures on human basophils and mast cells: biochemical and functional characterization. Adv Immunol. 1992;52:333–423. - PubMed
-
- Irani AM, Nilsson G, Miettinen U, Craig SS, Ashman LK, Ishizaka T, Zsebo KM, Schwartz LB. Recombinant human stem cell factor stimulates differentiation of mast cells from dispersed human fetal liver cells. Blood. 1992;80:3009–21. - PubMed
-
- Li L, Macpherson JJ, Adelstein S, Bunn CL, Atkinson K, Phadke K, Krilis SA. Conditioned media from a cell strain derived from a patient with mastocytosis induces preferential development of cells that possess high affinity IgE receptors and the granule protease phenotype of mature cutaneous mast cells. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:2258–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

