Tumor suppressor role of KiSS-1 in bladder cancer: loss of KiSS-1 expression is associated with bladder cancer progression and clinical outcome
- PMID: 12547718
- PMCID: PMC1851149
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63854-0
Tumor suppressor role of KiSS-1 in bladder cancer: loss of KiSS-1 expression is associated with bladder cancer progression and clinical outcome
Abstract
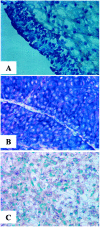
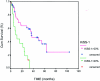
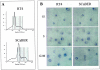
The expression profiles of nine bladder cancer cell lines were compared against a pool containing equal total RNA quantities of each of them. Lower expression of KiSS-1 was revealed in cells derived from the most advanced bladder tumors. When comparing 15 primary bladder tumors versus a pool of four bladder cancer cell lines, lower transcript levels of KiSS-1 were observed in the invasive bladder carcinomas as compared to superficial tumors. KiSS-1 expression ratios provided prognostic information. The expression pattern of KiSS-1 transcripts was analyzed using in situ hybridization in nine bladder cancer cells, paired normal urothelium and bladder tumor samples (n = 25), and tissue microarrays of bladder tumors (n = 173). We observed complete loss of KiSS-1 in all invasive tumors under study as compared to their respective normal urothelium. The expression of KiSS-1 was found to be significantly associated with histopathological stage. Patients with lower KiSS-1 expression showed a direct correlation with overall survival in a subset of bladder tumors whose follow-up was available (n = 69). We did not observe any significant differential KiSS-1 expression along cell cycle by sorting analysis. A potential tumor suppressor role in bladder cancer was revealed for KiSS-1. Moreover, it showed predictive value by identifying patients with poor outcome.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction analysis for KiSS-1 and orphan G-protein-coupled receptor (hOT7T175) gene expression in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2003 Sep;129(9):531-5. doi: 10.1007/s00432-003-0469-z. Epub 2003 Jul 25. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12898236
-
Gene discovery in bladder cancer progression using cDNA microarrays.Am J Pathol. 2003 Aug;163(2):505-16. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63679-6. Am J Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12875971 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of P27Kip1 expression correlates with tumor grade and with reduced disease-free survival in primary superficial bladder cancers.Cancer Res. 1999 Jul 1;59(13):3245-50. Cancer Res. 1999. PMID: 10397272
-
Molecular alterations associated with bladder cancer initiation and progression.Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl. 2008 Sep;(218):154-65. doi: 10.1080/03008880802291915. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl. 2008. PMID: 18815930 Review.
-
Mutation of cell cycle regulators and their impact on superficial bladder cancer.Urol Clin North Am. 2000 Feb;27(1):83-102, ix. doi: 10.1016/s0094-0143(05)70237-8. Urol Clin North Am. 2000. PMID: 10696248 Review.
Cited by
-
Metastin has potential as a suitable biomarker and novel effective therapy for cancer metastasis (Review).Oncol Lett. 2010 Sep;1(5):783-788. doi: 10.3892/ol_00000136. Epub 2010 Sep 1. Oncol Lett. 2010. PMID: 22966379 Free PMC article.
-
The KISS1 metastasis suppressor: mechanistic insights and clinical utility.Front Biosci. 2006 Jan 1;11:647-59. doi: 10.2741/1824. Front Biosci. 2006. PMID: 16146758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction analysis for KiSS-1 and orphan G-protein-coupled receptor (hOT7T175) gene expression in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2003 Sep;129(9):531-5. doi: 10.1007/s00432-003-0469-z. Epub 2003 Jul 25. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12898236
-
Reduced protein expression of metastasis-related genes (nm23, KISS1, KAI1 and p53) in lymph node and liver metastases of gastric cancer.Int J Exp Pathol. 2007 Jun;88(3):175-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2006.00510.x. Int J Exp Pathol. 2007. PMID: 17504447 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of Kisspeptin-10 on mesenchymal stem cells migration in vitro and in vivo.Adv Biomed Res. 2015 Jan 30;4:20. doi: 10.4103/2277-9175.149851. eCollection 2015. Adv Biomed Res. 2015. PMID: 25709985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- : Cancer Facts and Figures 2000.: American Cancer Society 2000,
-
- Fidler IJ: Critical factors in the biology of human cancer metastasis. Cancer Res 1990, 50:6130-6138 - PubMed
-
- Welch DR, Chen P, Miele ME, McGary CT, Bower JM, Weissman BE, Standbridge EJ: Microcell-mediated transfer of chromosome 6 into metastatic human C8161 melanoma cells suppresses metastasis but does not inhibit tumorigenicity. Oncogene 1994, 9:255-262 - PubMed
-
- Miele ME, Robertson G, Lee JH, Coleman A, McGarry CT, Fisher PB, Lugo TG, Welch DR: Metastasis suppressed, but tumorigenicity and local invasiveness unaffected in the human melanoma cell line MelJuSo after introduction of human chromosomes 1 or 6. Mol Carcinog 1996, 15:284-299 - PubMed
-
- Lee JH, Miele ME, Hicks DJ, Phillips KK, Trent JM, Weissman BE, Welch DR: KiSS-1, a novel human malignant melanoma metastasis-suppressor gene. J Natl Cancer Inst 1996, 88:1731-1737 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

