Similar behaviour of single-strand and double-strand siRNAs suggests they act through a common RNAi pathway
- PMID: 12711685
- PMCID: PMC154224
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg338
Similar behaviour of single-strand and double-strand siRNAs suggests they act through a common RNAi pathway
Abstract
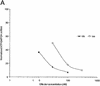
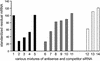
RNA interference (RNAi), mediated by either long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) or short interfering RNA (siRNA), has become a routine tool for transient knockdown of gene expression in a wide range of organisms. The antisense strand of the siRNA duplex (antisense siRNA) was recently shown to have substantial mRNA depleting activity of its own. Here, _targeting human Tissue Factor mRNA in HaCaT cells, we perform a systematic comparison of the activity of antisense siRNA and double-strand siRNA, and find almost identical _target position effects, appearance of mRNA cleavage fragments and tolerance for mutational and chemical backbone modifications. These observations, together with the demonstration that excess inactive double-strand siRNA blocks antisense siRNA activity, i.e. shows sequence-independent competition, indicate that the two types of effector molecules share the same RNAi pathway. Interest ingly, both FITC-tagged and 3'-deoxy antisense siRNA display severely limited activity, despite having practically wild-type activity in a siRNA duplex. Finally, we find that maximum depletion of _target mRNA expression occurs significantly faster with antisense siRNA than with double-strand siRNA, suggesting that the former enters the RNAi pathway at a later stage than double-strand siRNA, thereby requiring less time to exert its activity.
Figures


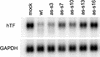
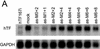
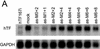
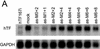
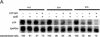
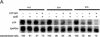
Similar articles
-
Tolerance for mutations and chemical modifications in a siRNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Jan 15;31(2):589-95. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg147. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12527766 Free PMC article.
-
Short interfering RNA strand selection is independent of dsRNA processing polarity during RNAi in Drosophila.Curr Biol. 2006 Mar 7;16(5):530-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.01.061. Curr Biol. 2006. PMID: 16527750
-
siRNA function in RNAi: a chemical modification analysis.RNA. 2003 Sep;9(9):1034-48. doi: 10.1261/rna.5103703. RNA. 2003. PMID: 12923253 Free PMC article.
-
RNAi: running interference for the cell.Org Biomol Chem. 2004 Jul 21;2(14):1957-61. doi: 10.1039/b404932m. Epub 2004 Jun 28. Org Biomol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15254617 Review.
-
Small RNA: can RNA interference be exploited for therapy?Lancet. 2003 Oct 25;362(9393):1401-3. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)14637-5. Lancet. 2003. PMID: 14585643 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances and Prospects of Nucleic Acid Therapeutics for Anti-Cancer Therapy.Molecules. 2024 Oct 7;29(19):4737. doi: 10.3390/molecules29194737. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39407665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide identification and validation of tomato-encoded sRNA as the cross-species antifungal factors _targeting the virulence genes of Botrytis cinerea.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Feb 2;14:1072181. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1072181. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36818832 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Modifications of siRNA Improve Its Performance In Vivo.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 4;24(2):956. doi: 10.3390/ijms24020956. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimization in Chemical Modification of Single-Stranded siRNA Encapsulated by Neutral Cytidinyl/Cationic Lipids.Front Chem. 2022 Mar 7;10:843181. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.843181. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 35345539 Free PMC article.
-
Foliar Delivery of siRNA Particles for Treating Viral Infections in Agricultural Grapevines.Adv Funct Mater. 2021 Jul 10;31(44):2101003. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202101003. eCollection 2021 Oct 26. Adv Funct Mater. 2021. PMID: 34744552 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guo S. and Kemphues,K. (1995) par-1, a gene required for establishing polarity in C. elegans embryos, encodes a putative Ser/Thr kinase that is asymmetrically distributed. Cell, 81, 611–620. - PubMed
-
- Fire A., Xu,S., Montgomery,M.K., Kostas,S.A., Driver,S.E. and Mello,C.C. (1998) Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature, 391, 806–811. - PubMed
-
- Zamore P.D. (2002) Ancient pathways programmed by small RNAs. Science, 296, 1265–1269. - PubMed
-
- Ahlquist A. (2002) RNA-dependent RNA polymerases, viruses, and RNA silencing. Science, 296, 1270–1273. - PubMed
-
- Plasterk R.H.A. (2002) RNA silencing: the genome’s immune system. Science, 296, 1263–1265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

