Identification of two-component regulatory systems in Bifidobacterium infantis by functional complementation and degenerate PCR approaches
- PMID: 12839803
- PMCID: PMC165215
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.69.7.4219-4226.2003
Identification of two-component regulatory systems in Bifidobacterium infantis by functional complementation and degenerate PCR approaches
Abstract
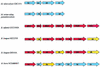
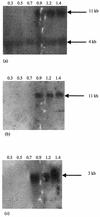
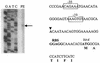
Two-component signal transduction systems (2CSs) are widely used by bacteria to sense and adapt to changing environmental conditions. With two separate approaches, three different 2CSs were identified on the chromosome of the probiotic bacterium Bifidobacterium infantis UCC 35624. One locus was identified by means of functional complementation of an Escherichia coli mutant. Another two were identified by PCR with degenerate primers corresponding to conserved regions of one protein component of the 2CS. The complete coding regions for each gene cluster were obtained, which showed that each 2CS-encoding locus specified a histidine protein kinase and an assumed cognate response regulator. Transcriptional analysis of the 2CSs by Northern blotting and primer extension identified a number of putative promoter sequences for this organism while revealing that the expression of each 2CS was growth phase dependent. Analysis of the genetic elements involved revealed significant homology with several distinct regulatory families from other high-G+C-content bacteria. The conservation of the genetic organization of these three 2CSs in other bacteria, including a number of recently published Bifidobacterium genomes, was investigated.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genetic and transcriptional organization of the clpC locus in Bifidobacterium breve UCC 2003.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Oct;71(10):6282-91. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.10.6282-6291.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16204550 Free PMC article.
-
Gene structure and transcriptional organization of the dnaK operon of Bifidobacterium breve UCC 2003 and application of the operon in bifidobacterial tracing.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Jan;71(1):487-500. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.1.487-500.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15640225 Free PMC article.
-
Use of tuf gene-based primers for the PCR detection of probiotic Bifidobacterium species and enumeration of bifidobacteria in fermented milk by cultural and quantitative real-time PCR methods.J Food Sci. 2010 Oct;75(8):M521-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2010.01816.x. J Food Sci. 2010. PMID: 21535508
-
Induction of sucrose utilization genes from Bifidobacterium lactis by sucrose and raffinose.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003 Jan;69(1):24-32. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.1.24-32.2003. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12513973 Free PMC article.
-
Genus- and species-specific PCR primers for the detection and identification of bifidobacteria.Curr Issues Intest Microbiol. 2003 Sep;4(2):61-9. Curr Issues Intest Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14503690 Review.
Cited by
-
Cloning and characterization of the bile salt hydrolase genes (bsh) from Bifidobacterium bifidum strains.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004 Sep;70(9):5603-12. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.9.5603-5612.2004. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15345449 Free PMC article.
-
A conserved two-component signal transduction system controls the response to phosphate starvation in Bifidobacterium breve UCC2003.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012 Aug;78(15):5258-69. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00804-12. Epub 2012 May 25. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22635988 Free PMC article.
-
A bile-inducible membrane protein mediates bifidobacterial bile resistance.Microb Biotechnol. 2012 Jul;5(4):523-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7915.2011.00329.x. Epub 2012 Feb 1. Microb Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22296641 Free PMC article.
-
Bifidobacterium lactis DSM 10140: identification of the atp (atpBEFHAGDC) operon and analysis of its genetic structure, characteristics, and phylogeny.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004 May;70(5):3110-21. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.5.3110-3121.2004. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15128574 Free PMC article.
-
Discovering novel bile protection systems in Bifidobacterium breve UCC2003 through functional genomics.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012 Feb;78(4):1123-31. doi: 10.1128/AEM.06060-11. Epub 2011 Dec 9. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22156415 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aiba, H., M. Nagaya, and T. Mizuno. 1993. Sensor and regulator proteins from the cyanobacterium Synechococcus species PCC7942 that belong to the bacterial signal-transduction protein families: implication in the adaptive response to phosphate limitation. Mol. Microbiol. 8:81-91. - PubMed
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tools. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
-
- Aravind, L., and C. P. Ponting. 1999. The cytoplasmic helical linker domain of receptor histidine kinase and methyl-accepting proteins is common to many prokaryotic signalling proteins. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 176:111-116. - PubMed
-
- Arthur, M., F. Depardieu, and P. Courvalin. 1999. Regulated interactions between partner and nonpartner sensors and response regulators that control glycopeptide resistance gene expression in enterococci. Microbiology 145:1849-1858. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

