Ligand-independent activation of estrogen receptor alpha by XBP-1
- PMID: 12954762
- PMCID: PMC203316
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg731
Ligand-independent activation of estrogen receptor alpha by XBP-1
Abstract
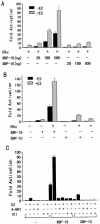
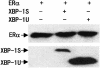
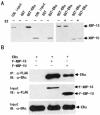
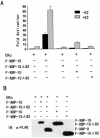
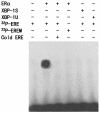
The estrogen receptor (ER) is a member of a large superfamily of nuclear receptors that regulates the transcription of estrogen-responsive genes. Several recent studies have demonstrated that XBP-1 mRNA expression is associated with ERalpha status in breast tumors. However, the role of XBP-1 in ERalpha signaling remains to be elucidated. More recently, two forms of XBP-1 were identified due to its unconventional splicing. We refer to the spliced and unspliced forms of XBP-1 as XBP-1S and XBP-1U, respectively. Here, we report that XBP-1S and XBP-1U enhanced ERalpha-dependent transcriptional activity in a ligand-independent manner. XBP-1S had stronger activity than XBP-1U. The maximal effects of XBP-1S and XBP-1U on ERalpha transactivation were observed when they were co-expressed with full-length ERalpha. SRC-1, the p160 steroid receptor coactivator family member, synergized with XBP-1S or XBP-1U to potentiate ERalpha activity. XBP-1S and XBP-1U bound to the ERalpha both in vitro and in vivo in a ligand-independent fashion. XBP-1S and XBP-1U interacted with the ERalpha region containing the DNA-binding domain. The ERalpha-interacting regions on XBP-1S and XBP-1U have been mapped to two regions, including the N-terminal basic region leucine zipper domain (bZIP) and the C-terminal activation domain. The bZIP-deleted mutants of XBP-1S and XBP-1U completely abolished ERalpha transactivation by XBP-1S and XBP-1U. These findings suggest that XBP-1S and XBP-1U may directly modulate ERalpha signaling in both the absence and presence of estrogen and, therefore, may play important roles in the proliferation of normal and malignant estrogen-regulated tissues.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[XBP-1 enhances the transcriptional activity of estrogen receptor alpha].Sheng Wu Hua Xue Yu Sheng Wu Wu Li Xue Bao (Shanghai). 2003 Sep;35(9):829-33. Sheng Wu Hua Xue Yu Sheng Wu Wu Li Xue Bao (Shanghai). 2003. PMID: 12958656 Chinese.
-
[XBP-1 interacts with estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha)].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2004 May;20(3):332-6. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2004. PMID: 15971600 Chinese.
-
[Expression of XBP-1 in breast cancer cell lines and its role in ERalpha signaling].Yi Chuan Xue Bao. 2004 Apr;31(4):380-4. Yi Chuan Xue Bao. 2004. PMID: 15487507 Chinese.
-
Molecular action of the estrogen receptor and hormone dependency in breast cancer.Breast Cancer. 2003;10(2):89-96. doi: 10.1007/BF02967632. Breast Cancer. 2003. PMID: 12736560 Review.
-
The physiological role of estrogen receptor functional domains.Essays Biochem. 2021 Dec 17;65(6):867-875. doi: 10.1042/EBC20200167. Essays Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34028522 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aberrant alternative splicing in breast cancer.J Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Oct 25;11(10):920-929. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjz033. J Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31065692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear expression of XBP1s is correlated with breast cancer survival: a retrospective analysis based on tissue microarray.Onco _targets Ther. 2017 Dec 13;10:5927-5934. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S147102. eCollection 2017. Onco _targets Ther. 2017. PMID: 29276395 Free PMC article.
-
X-box-binding protein 1 activates lytic Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in combination with protein kinase D.J Virol. 2007 Jul;81(14):7363-70. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00154-07. Epub 2007 May 9. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17494074 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional analysis of domains of the progesterone receptor.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012 Jan 30;348(2):418-29. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2011.07.017. Epub 2011 Jul 22. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 21803119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationships of ESR1 and XBP1 expression in human breast carcinoma and stromal cells isolated by laser capture microdissection compared to intact breast cancer tissue.Endocrine. 2011 Oct;40(2):212-21. doi: 10.1007/s12020-011-9522-x. Epub 2011 Aug 21. Endocrine. 2011. PMID: 21858728
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

