Addicting drugs utilize a synergistic molecular mechanism in common requiring adenosine and Gi-beta gamma dimers
- PMID: 14605213
- PMCID: PMC283600
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2336093100
Addicting drugs utilize a synergistic molecular mechanism in common requiring adenosine and Gi-beta gamma dimers
Abstract
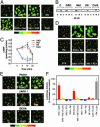
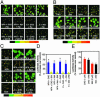
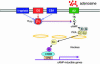
The mesolimbic dopamine system and cAMP-dependent/protein kinase A (PKA) pathways are strongly implicated in addictive behaviors. Here we determine the role of dopamine D2 receptors (D2) in PKA signaling responses to delta-opioid (DOR) and cannabinoid (CB1) receptors. We find in NG108-15/D2 cells and in cultured primary neurons that a brief exposure to saturating concentrations of DOR and CB1 agonists increases cAMP, promotes PKA C alpha translocation and increases cAMP-dependent gene expression. Activation of PKA signaling is mediated by Gi-beta gamma dimers. Importantly, subthreshold concentrations of DOR or CB1 agonists with D2 agonists, which are without effect when added separately, together activate cAMP/PKA signaling synergistically. There is also synergy between DOR or CB1 with ethanol, another addicting agent. In all instances, synergy requires adenosine activation of adenosine A2 receptors and is mediated by beta gamma dimers. Synergy by this molecular mechanism appears to confer hypersensitivity to opioids and cannabinoids while simultaneously increasing the sensitivity of D2 signaling when receptors are expressed on the same cells. This mechanism may account, in part, for drug-induced activation of medium spiny neurons in the nucleus accumbens.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adenosine A2a blockade prevents synergy between mu-opiate and cannabinoid CB1 receptors and eliminates heroin-seeking behavior in addicted rats.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 May 16;103(20):7877-82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0602661103. Epub 2006 May 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16684876 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the neurobiology of alcoholism: the role of adenosine.Pharmacol Ther. 2004 Jan;101(1):39-46. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2003.10.002. Pharmacol Ther. 2004. PMID: 14729391 Review.
-
betagamma Dimers mediate synergy of dopamine D2 and adenosine A2 receptor-stimulated PKA signaling and regulate ethanol consumption.Cell. 2002 Jun 14;109(6):733-43. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00763-8. Cell. 2002. PMID: 12086672
-
Nicotine and ethanol activate protein kinase A synergistically via G(i) betagamma subunits in nucleus accumbens/ventral tegmental cocultures: the role of dopamine D(1)/D(2) and adenosine A(2A) receptors.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Jul;322(1):23-9. doi: 10.1124/jpet.107.120675. Epub 2007 Apr 27. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007. PMID: 17468300
-
Regulation of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the central nervous system by chronic cannabinoids.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2003;15(2):91-119. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v15.i2.10. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2003. PMID: 14977366 Review.
Cited by
-
Atypical protein kinase C is a novel mediator of dopamine-enhanced firing in nucleus accumbens neurons.J Neurosci. 2005 Jan 26;25(4):985-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3099-04.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15673680 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological evidence for different populations of postsynaptic adenosine A2A receptors in the rat striatum.Neuropharmacology. 2011 Oct-Nov;61(5-6):967-74. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.06.025. Epub 2011 Jul 5. Neuropharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21752341 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transduction via cannabinoid receptors.CNS Neurol Disord Drug _targets. 2009 Dec;8(6):422-31. doi: 10.2174/187152709789824615. CNS Neurol Disord Drug _targets. 2009. PMID: 19839935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adenosine A(2A) receptors in psychopharmacology: modulators of behavior, mood and cognition.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2009 Sep;7(3):195-206. doi: 10.2174/157015909789152191. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2009. PMID: 20190961 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine A2a blockade prevents synergy between mu-opiate and cannabinoid CB1 receptors and eliminates heroin-seeking behavior in addicted rats.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 May 16;103(20):7877-82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0602661103. Epub 2006 May 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16684876 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Robbins, T. W. & Everitt, B. J. (1999) Nature 398, 567-570. - PubMed
-
- Nestler, E. J. (2001) Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 119-128. - PubMed
-
- Hyman, S. E. & Malenka, R. C. (2001) Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 695-703. - PubMed
-
- Albert, P. R. & Robillard, L. (2002) Cell. Signal. 14, 407-418. - PubMed
-
- Tang, W. J. & Gilman, A. G. (1991) Science 254, 1500-1503. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

