Anandamide initiates Ca(2+) signaling via CB2 receptor linked to phospholipase C in calf pulmonary endothelial cells
- PMID: 14645143
- PMCID: PMC1574152
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705529
Anandamide initiates Ca(2+) signaling via CB2 receptor linked to phospholipase C in calf pulmonary endothelial cells
Abstract
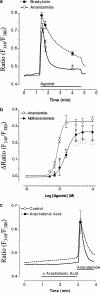
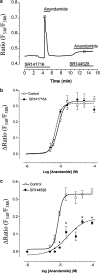
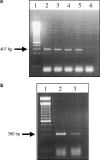
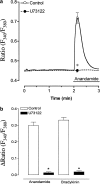
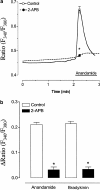
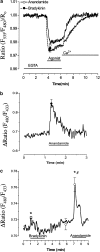
The endocannabinoid anandamide has been reported to affect neuronal cells, immune cells and smooth muscle cells via either CB1 or CB2 receptors. In endothelial cells, the receptors involved in activating signal transduction are still unclear, despite the fact that anandamide is produced in this cell type. The present study was designed to explore in detail the effect of this endocannabinoid on Ca2+ signaling in single cells of a calf pulmonary endothelial cell line. Anandamide initiated a transient Ca2+ elevation that was prevented by the CB2 receptor antagonist SR144528, but not by the CB1 antagonist SR141716A. These data were confirmed by molecular identification of the bovine CB2 receptor in these endothelial cells by partial sequencing. The phospholipase C inhibitor 1-[6-[[(17beta)-3-methoxyestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-yl]amino]hexyl]-1H-pyrrole-2,5dione and the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor antagonist 2-aminoethoxydiphenylborate prevented Ca2+ signaling in response to anandamide. Using an improved cameleon probe _targeted to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), fura-2 and ratiometric-pericam, which is _targeted to the mitochondria, anandamide was found to induce Ca2+ depletion of the ER accompanied by the activation of capacitative Ca2+ entry (CCE) and a transient elevation of mitochondrial Ca2+. These data demonstrate that anandamide stimulates the endothelial cells used in this study via CB2 receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase C, formation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, Ca2+ release from the ER and subsequent activation of CCE. Moreover, the cytosolic Ca2+ elevation was accompanied by a transient Ca2+ increase in the mitochondria. Thus, in addition to its actions on smooth muscle cells, anandamide also acts as a powerful stimulus for endothelial cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Anandamide-induced mobilization of cytosolic Ca2+ in endothelial cells.Br J Pharmacol. 1999 Apr;126(7):1593-600. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702483. Br J Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10323591 Free PMC article.
-
Human brain endothelium: coexpression and function of vanilloid and endocannabinoid receptors.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2004 Dec 6;132(1):87-92. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2004.08.025. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 15548432
-
Characterization of the vasorelaxant mechanisms of the endocannabinoid anandamide in rat aorta.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Nov;152(5):699-708. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707404. Epub 2007 Aug 20. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17704831 Free PMC article.
-
Anandamide as an intracellular messenger regulating ion channel activity.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2005 Sep;77(1-4):111-22. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2004.09.007. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2005. PMID: 16099396 Review.
-
The endocannabinoid-CB receptor system: Importance for development and in pediatric disease.Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2004 Feb-Apr;25(1-2):24-30. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2004. PMID: 15159678 Review.
Cited by
-
Research progress on the cannabinoid type-2 receptor and Parkinson's disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 Jan 8;15:1298166. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1298166. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38264546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of the CB2 Cannabinoid Receptor in Inflammatory Diseases: An Update.Molecules. 2024 Jul 18;29(14):3381. doi: 10.3390/molecules29143381. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39064959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cannabinoid-like anti-inflammatory compounds from flax fiber.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2012 Sep;17(3):479-99. doi: 10.2478/s11658-012-0023-6. Epub 2012 Jun 13. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22706678 Free PMC article.
-
How do phytocannabinoids affect cardiovascular health? An update on the most common cardiovascular diseases.Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2023 Jan 6;14:20406223221143239. doi: 10.1177/20406223221143239. eCollection 2023. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2023. PMID: 36636553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibacterial Effects of Phytocannabinoids.Life (Basel). 2022 Sep 7;12(9):1394. doi: 10.3390/life12091394. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36143430 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- ASCHNER J.L., LUM H., FLETCHER P.W., MALIK A.B. Bradykinin- and thrombin-induced increases in endothelial permeability occur independently of phospholipase C but require protein kinase C activation. J. Cell. Physiol. 1997;173:387–396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

