Reliability of gene expression ratios for cDNA microarrays in multiconditional experiments with a reference design
- PMID: 14966261
- PMCID: PMC373422
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gnh027
Reliability of gene expression ratios for cDNA microarrays in multiconditional experiments with a reference design
Abstract
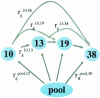
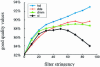
In a typical gene expression profiling experiment with multiple conditions, a common reference sample is used for co-hybridization with the samples to yield expression ratios. Differential expression for any other sample pair can then be calculated by assembling the ratios from their hybridizations with the reference. In this study we test the validity of this approach. Differential expression of a sample pair (i, j) was obtained in two ways: directly, by hybridizations of sample i versus j, and indirectly, by multiplying the expression ratios for hybridizations of sample i versus pool and pool versus sample j. We performed gene expression profiling using amphibian embryos (Xenopus laevis). Every sample combination of four different stages and a pool was profiled. Direct and indirect values were compared and used as the quality criterion for the data. Based on this criterion, 82% of all ratios were found to be sufficiently accurate. To increase the reliability of the signals, several widely used filtering techniques were tested. Filtering by differences of repeated hybridizations was found to be the optimal filter. Finally, we compared microarray-based gene expression profiles with the corresponding expression patterns obtained by whole-mount in situ hybridizations, resulting in a 90% correspondence.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Large scale real-time PCR validation on gene expression measurements from two commercial long-oligonucleotide microarrays.BMC Genomics. 2006 Mar 21;7:59. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-59. BMC Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16551369 Free PMC article.
-
Application of four dyes in gene expression analyses by microarrays.BMC Genomics. 2005 Jul 25;6:101. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-6-101. BMC Genomics. 2005. PMID: 16042794 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and handling of artifactual gene expression profiles emerging in microarray hybridization experiments.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Mar 3;32(4):e46. doi: 10.1093/nar/gnh043. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 14999086 Free PMC article.
-
Improving reliability and performance of DNA microarrays.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2006 May;6(3):481-92. doi: 10.1586/14737159.6.3.481. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2006. PMID: 16706748 Review.
-
Filter versus wrapper gene selection approaches in DNA microarray domains.Artif Intell Med. 2004 Jun;31(2):91-103. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2004.01.007. Artif Intell Med. 2004. PMID: 15219288 Review.
Cited by
-
XenDB: full length cDNA prediction and cross species mapping in Xenopus laevis.BMC Genomics. 2005 Sep 14;6:123. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-6-123. BMC Genomics. 2005. PMID: 16162280 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic interpretation of microarray data using experiment annotations.BMC Genomics. 2006 Dec 20;7:319. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-319. BMC Genomics. 2006. PMID: 17181856 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of rat lung--prominent genes by a parallel DNA microarray hybridization.BMC Genomics. 2006 Mar 13;7:47. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-47. BMC Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16533406 Free PMC article.
-
Ethylene-induced differential gene expression during abscission of citrus leaves.J Exp Bot. 2008;59(10):2717-33. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ern138. Epub 2008 May 29. J Exp Bot. 2008. PMID: 18515267 Free PMC article.
-
Gene ontology analysis of expanded porcine blastocysts from gilts fed organic or inorganic selenium combined with pyridoxine.BMC Genomics. 2018 Nov 21;19(1):836. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-5237-1. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30463510 Free PMC article.

