2'-O-methyl-modified phosphorothioate antisense oligonucleotides have reduced non-specific effects in vitro
- PMID: 15064360
- PMCID: PMC390367
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh516
2'-O-methyl-modified phosphorothioate antisense oligonucleotides have reduced non-specific effects in vitro
Abstract
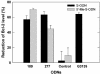
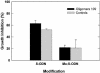
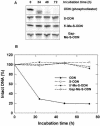
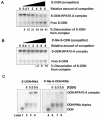
Antisense oligodeoxynucleotides (ODNs) have biological activity in treating various forms of cancer. The antisense effects of two types of 20mer ODNs, phosphorothioate-modified ODNs (S-ODNs) and S-ODNs with 12 2'-O-methyl groups (Me-S-ODNs), _targeted to sites 109 and 277 of bcl-2 mRNA, were compared. Both types were at least as effective as G3139 (Genta, Inc.) in reducing the level of Bcl-2 protein in T24 cells following a 4 h transfection at a dose of 0.1 micro M. Circular dichroism spectra showed that both types formed A-form duplexes with the complementary RNA, and the melting temperatures were in the order of Me-S-ODN.RNA > normal DNA.RNA > S-ODN.RNA. In comparison with the S-ODN, the Me-S-ODN had reduced toxic growth inhibitory effects, was less prone to bind the DNA-binding domain A of human replication protein A, and was as resistant to serum nucleases. Neither type of oligomer induced apoptosis, according to a PARP-cleavage assay. Hybrids formed with Me-S-ODN sequences were less sensitive to RNase H degradation than those formed with S-ODN sequences. Despite this latter disadvantage, the addition of 2'-O-methyl groups to a phosphorothioate-modified ODN is advantageous because of increased stability of binding and reduced non-specific effects.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antitumor effect of c-myc antisense phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides on human melanoma cells in vitro and and in mice.J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996 Apr 3;88(7):419-29. doi: 10.1093/jnci/88.7.419. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996. PMID: 8618233
-
The reduction of Raf-1 protein by phosphorothioate ODNs and siRNAs _targeted to the same two mRNA sequences.Oligonucleotides. 2003;13(5):313-24. doi: 10.1089/154545703322616998. Oligonucleotides. 2003. PMID: 15000822
-
Antitumor effect of bcl-2 antisense phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides on human renal-cell carcinoma cells in vitro and in mice.Mol Urol. 2001 Summer;5(2):71-8. doi: 10.1089/109153601300177583. Mol Urol. 2001. PMID: 11690551
-
[Antisense nucleic acid therapy of influenza virus].Nihon Rinsho. 1997 Oct;55(10):2765-71. Nihon Rinsho. 1997. PMID: 9360404 Review. Japanese.
-
[Specific regulation of gene expression in brain by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1997 Apr;109(4):187-91. doi: 10.1254/fpj.109.187. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1997. PMID: 9160348 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the multifaceted role of microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: Integrating literature review and bioinformatics analysis for therapeutic insights.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 18;10(20):e39489. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39489. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39498055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Versatile Roles of nc886, a Fascinating and Peculiar Regulatory Non-Coding RNA, in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 9;25(19):10825. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910825. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39409154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances and Prospects of Nucleic Acid Therapeutics for Anti-Cancer Therapy.Molecules. 2024 Oct 7;29(19):4737. doi: 10.3390/molecules29194737. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39407665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis, Biophysical and Biological Evaluation of Splice-Switching Oligonucleotides with Multiple LNA-Phosphothiotriester Backbones.J Am Chem Soc. 2024 Oct 30;146(43):29773-29781. doi: 10.1021/jacs.4c11402. Epub 2024 Oct 14. J Am Chem Soc. 2024. PMID: 39401255 Free PMC article.
-
A therapeutic approach for the hepatitis C virus: in silico design of an antisense oligonucleotide-based candidate capsid inhibitor.Virus Genes. 2024 Oct;60(5):446-454. doi: 10.1007/s11262-024-02088-1. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Virus Genes. 2024. PMID: 39083128
References
-
- Stein C.A. (1996) Phosphorothioate antisense oligodeoxynucleotides: questions of specificity. Trends Biotechnol., 14, 147–149. - PubMed
-
- Lebedeva I. and Stein,C.A. (2001) Antisense oligonucleotides: promise and reality. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 41, 403–419. - PubMed
-
- Braasch D.A. and Corey,D.R. (2002) Novel antisense and peptide nucleic acid strategies for controlling gene expression. Biochemistry, 41, 4503–4510. - PubMed
-
- Dove A. (2002) Antisense and sensibility. Nat. Biotechnol., 20, 121–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

