The complex life of simple sphingolipids
- PMID: 15289826
- PMCID: PMC1299119
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400208
The complex life of simple sphingolipids
Abstract
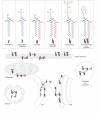
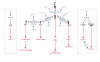
The extensive diversity of membrane lipids is rarely appreciated by cell and molecular biologists. Although most researchers are familiar with the three main classes of lipids in animal cell membranes, few realize the enormous combinatorial structural diversity that exists within each lipid class, a diversity that enables functional specialization of lipids. In this brief review, we focus on one class of membrane lipids, the sphingolipids, which until not long ago were thought by many to be little more than structural components of biological membranes. Recent studies have placed sphingolipids-including ceramide, sphingosine and sphingosine-1-phosphate-at the centre of a number of important biological processes, specifically in signal transduction pathways, in which their levels change in a highly regulated temporal and spatial manner. We outline exciting progress in the biochemistry and cell biology of sphingolipids and focus on their functional diversity. This should set the conceptual and experimental framework that will eventually lead to a fully integrated and comprehensive model of the functions of specific sphingolipids in regulating defined aspects of cell physiology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Biophysics of sphingolipids I. Membrane properties of sphingosine, ceramides and other simple sphingolipids.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Dec;1758(12):1902-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.09.011. Epub 2006 Sep 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 17070498 Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review: Sphingolipid Metabolism and Implications of Disruption in Sphingolipid Homeostasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 28;22(11):5793. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115793. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34071409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The chemistry and biology of 6-hydroxyceramide, the youngest member of the human sphingolipid family.Chembiochem. 2014 Jul 21;15(11):1555-62. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201402153. Epub 2014 Jul 2. Chembiochem. 2014. PMID: 24990520 Review.
-
The organizing potential of sphingolipids in intracellular membrane transport.Physiol Rev. 2001 Oct;81(4):1689-723. doi: 10.1152/physrev.2001.81.4.1689. Physiol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11581500 Review.
-
Sphingolipids--the enigmatic lipid class: biochemistry, physiology, and pathophysiology.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1997 Jan;142(1):208-25. doi: 10.1006/taap.1996.8029. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9007051 Review.
Cited by
-
Gaucher's disease and cancer: a sphingolipid perspective.Crit Rev Oncog. 2013;18(3):221-34. doi: 10.1615/critrevoncog.2013005814. Crit Rev Oncog. 2013. PMID: 23510065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl) Retinamide Suppresses SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein-Mediated Cell-Cell Fusion by a Dihydroceramide Δ4-Desaturase 1-Independent Mechanism.J Virol. 2021 Aug 10;95(17):e0080721. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00807-21. Epub 2021 Aug 10. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34106748 Free PMC article.
-
Ceramidases, roles in sphingolipid metabolism and in health and disease.Adv Biol Regul. 2017 Jan;63:122-131. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2016.10.002. Epub 2016 Oct 11. Adv Biol Regul. 2017. PMID: 27771292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long chain ceramides raise the main phase transition of monounsaturated phospholipids to physiological temperature.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 2;12(1):20803. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-25330-y. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36460753 Free PMC article.
-
Ceramide signaling in retinal degeneration.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;723:553-8. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-0631-0_70. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22183377 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P (2002) Molecular Biology of the Cell. Garland Science, New York, USA.
-
- Alvarez-Vasquez F, Sims KJ, Hannun YA, Voit EO (2004) Integration of kinetic information on yeast sphingolipid metabolism in dynamical pathway models. J Theor Biol 226: 265–291 - PubMed
-
- Brugger B, Graham C, Leibrecht I, Mombelli E, Jen A, Wieland F, Morris R (2004) The membrane domains occupied by glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored prion protein and Thy-1 differ in lipid composition. J Biol Chem 279: 7530–7536 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

