Cyclin D1 genetic heterozygosity regulates colonic epithelial cell differentiation and tumor number in ApcMin mice
- PMID: 15314168
- PMCID: PMC507010
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.17.7598-7611.2004
Cyclin D1 genetic heterozygosity regulates colonic epithelial cell differentiation and tumor number in ApcMin mice
Erratum in
- Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Jan;25(1):523
Abstract
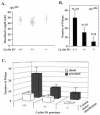
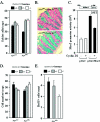
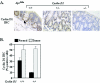
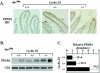
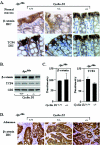
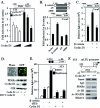
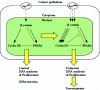
Constitutive beta-catenin/Tcf activity, the primary transforming events in colorectal carcinoma, occurs through induction of the Wnt pathway or APC gene mutations that cause familial adenomatous polyposis. Mice carrying Apc mutations in their germ line (ApcMin) develop intestinal adenomas. Here, the crossing of ApcMin with cyclin D1-/- mice reduced the intestinal tumor number in animals genetically heterozygous or nullizygous for cyclin D1. Decreased tumor number in the duodenum, intestines, and colons of ApcMin/cyclin D1+/- mice correlated with reduced cellular proliferation and increased differentiation. Cyclin D1 deficiency reduced DNA synthesis and induced differentiation of colonic epithelial cells harboring mutant APC but not wild-type APC cells in vivo. In previous studies, the complete loss of cyclin D1 through homozygous genetic deletion conveyed breast tumor resistance. The protection of mice, genetically predisposed to intestinal tumorigenesis, through cyclin D1 heterozygosity suggests that modalities that reduce cyclin D1 abundance could provide chemoprotection.
Copyright 2004 American Society for Microbiology
Figures
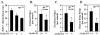
Similar articles
-
Colon epithelial cell differentiation is inhibited by constitutive c-myb expression or mutant APC plus activated RAS.DNA Cell Biol. 2005 Jan;24(1):21-9. doi: 10.1089/dna.2005.24.21. DNA Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15684716
-
Beta-catenin regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells.Nature. 1999 Apr 1;398(6726):422-6. doi: 10.1038/18884. Nature. 1999. PMID: 10201372
-
Down-regulation of beta-catenin TCF signaling is linked to colonic epithelial cell differentiation.Cancer Res. 2001 Apr 15;61(8):3465-71. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11309309
-
Beta-catenin--a linchpin in colorectal carcinogenesis?Am J Pathol. 2002 Feb;160(2):389-401. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)64856-0. Am J Pathol. 2002. PMID: 11839557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytoskeleton out of the cupboard: colon cancer and cytoskeletal changes induced by loss of APC.Nat Rev Cancer. 2006 Dec;6(12):967-74. doi: 10.1038/nrc2010. Epub 2006 Nov 9. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006. PMID: 17093505 Review.
Cited by
-
The requirement for cyclin D function in tumor maintenance.Cancer Cell. 2012 Oct 16;22(4):438-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.09.015. Cancer Cell. 2012. PMID: 23079655 Free PMC article.
-
New roles of cyclin D1.Am J Pathol. 2013 Jul;183(1):3-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.03.001. Am J Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23790801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The NF2 tumor suppressor gene product, merlin, inhibits cell proliferation and cell cycle progression by repressing cyclin D1 expression.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Mar;25(6):2384-94. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.6.2384-2394.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15743831 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of tumor growth and metastasis by non-small cell lung cancer cells transfected with cyclin D1-_targeted siRNA.Oligonucleotides. 2009 Jun;19(2):151-62. doi: 10.1089/oli.2008.0174. Oligonucleotides. 2009. PMID: 19355812 Free PMC article.
-
PKCalpha tumor suppression in the intestine is associated with transcriptional and translational inhibition of cyclin D1.Exp Cell Res. 2009 May 1;315(8):1415-28. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.02.002. Epub 2009 Feb 14. Exp Cell Res. 2009. PMID: 19232344 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albanese, C., M. D'Amico, A. T. Reutens, M. Fu, G. Watanabe, R. J. Lee, R. N. Kitsis, B. Henglein, M. Avantaggiati, K. Somasundaram, B. Thimmapaya, and R. G. Pestell. 1999. Activation of the cyclin D1 gene by the E1A-associated protein p300 through AP-1 inhibits cellular apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 274:34186-34195. - PubMed
-
- Albanese, C., A. Reutens, M. D'Amico, B. Boumediene, M. Fu, T. Link, R. Nicholson, R. A. Depinho, and R. G. Pestell. 2000. Sustained mammary gland directed ponasterone A-inducible expression in transgenic mice. FASEB J. 14:877-884. - PubMed
-
- Arber, N., Y. Doki, E. K.-H. Han, A. Sgambato, P. Zhou, N.-H. Kim, T. Delohery, M. G. Klein, P. R. Holt, and I. B. Weinstein. 1997. Antisense to cyclin D1 inhibits the growth and tumorigenicity of human colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 57:1569-1574. - PubMed
-
- Bartkova, J., J. Lukas, M. Strauss, and J. Bartek. 1994. The PRAD-1/cyclin D1 oncogene product accumulates in a subset of colorectal carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 58:568-573. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
