A gateway-compatible yeast one-hybrid system
- PMID: 15489331
- PMCID: PMC528925
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.2445504
A gateway-compatible yeast one-hybrid system
Abstract
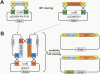
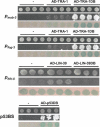
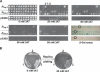
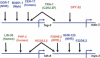
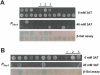
Since the advent of microarrays, vast amounts of gene expression data have been generated. However, these microarray data fail to reveal the transcription regulatory mechanisms that underlie differential gene expression, because the identity of the responsible transcription factors (TFs) often cannot be directly inferred from such data sets. Regulatory TFs activate or repress transcription of their _target genes by binding to cis-regulatory elements that are frequently located in a gene's promoter. To understand the mechanisms underlying differential gene expression, it is necessary to identify physical interactions between regulatory TFs and their _target genes. We developed a Gateway-compatible yeast one-hybrid (Y1H) system that enables the rapid, large-scale identification of protein-DNA interactions using both small (i.e., DNA elements of interest) and large (i.e., gene promoters) DNA fragments. We used four well-characterized Caenorhabditis elegans promoters as DNA baits to test the functionality of this Y1H system. We could detect approximately 40% of previously reported TF-promoter interactions. By performing screens using two complementary libraries, we found novel potentially interacting TFs for each promoter. We recapitulated several of the Y1H-based protein-DNA interactions using luciferase reporter assays in mammalian cells. Taken together, the Gateway-compatible Y1H system will allow the high-throughput identification of protein-DNA interactions and may be a valuable tool to decipher transcription regulatory networks.
Figures

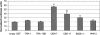
Similar articles
-
A gene-centered C. elegans protein-DNA interaction network.Cell. 2006 Jun 16;125(6):1193-205. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.04.038. Cell. 2006. PMID: 16777607
-
Gateway-compatible yeast one-hybrid screens.CSH Protoc. 2006 Oct 1;2006(5):pdb.prot4590. doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot4590. CSH Protoc. 2006. PMID: 22485967
-
A high-throughput screening system for Arabidopsis transcription factors and its application to Med25-dependent transcriptional regulation.Mol Plant. 2011 May;4(3):546-55. doi: 10.1093/mp/ssr002. Epub 2011 Feb 22. Mol Plant. 2011. PMID: 21343311
-
Unraveling transcription regulatory networks by protein-DNA and protein-protein interaction mapping.Genome Res. 2006 Dec;16(12):1445-54. doi: 10.1101/gr.5321506. Epub 2006 Oct 19. Genome Res. 2006. PMID: 17053092 Review.
-
Gene-centered regulatory network mapping.Methods Cell Biol. 2011;106:271-88. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-544172-8.00010-4. Methods Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 22118281 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exciting times: bountiful data to facilitate studies of cis-regulatory control.Nat Methods. 2011 Nov 29;8(12):1016-7. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1795. Nat Methods. 2011. PMID: 22127218 No abstract available.
-
Integrating physical and genetic maps: from genomes to interaction networks.Nat Rev Genet. 2007 Sep;8(9):699-710. doi: 10.1038/nrg2144. Nat Rev Genet. 2007. PMID: 17703239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription factors that directly regulate the expression of CSLA9 encoding mannan synthase in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Mol Biol. 2014 Mar;84(4-5):577-87. doi: 10.1007/s11103-013-0154-9. Epub 2013 Nov 17. Plant Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24243147
-
Systems approaches to identifying gene regulatory networks in plants.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2008;24:81-103. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.24.110707.175408. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18616425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Yeast one-hybrid assays for gene-centered human gene regulatory network mapping.Nat Methods. 2011 Oct 30;8(12):1050-2. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1764. Nat Methods. 2011. PMID: 22037702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams, M.D., Celniker, S.E., Holt, R.A., Evans, C.A., Gocayne, J.D., Amanatides, P.G., Scherer, S.E., Li, P.W., Hoskins, R.A., Galle, R.F., et al. 2000. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science 287: 2185-2195. - PubMed
-
- Boulton, S.J., Gartner, A., Reboul, J., Vaglio, P., Dyson, N., Hill, D.E., and Vidal, M. 2002. Combined functional genomic maps of the C. elegans DNA damage response. Science 295: 127-131. - PubMed
-
- The C. elegans Sequencing Consortium. 1998. Genome sequence of the nematode C. elegans: A platform for investigating biology. Science 282: 2012-2018. - PubMed
-
- Chen, P. and Ellis, R.E. 2000. TRA-1A regulates transcription of fog-3, which controls germ cell fate in C. elegans. Development 127: 3119-3129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
